Every Node.js developer knows the thrill of seeing their application run perfectly on localhost:3000. But the journey from your local machine to a live, stable, and secure production environment is a giant leap. How do you ensure your app stays running 24/7? How do you handle crashes gracefully? And how do you serve it to the world on a standard, professional domain name?
Simply running node app.js on a server and hoping for the best is not a strategy—it’s a recipe for disaster. Production environments demand robustness, security, and automation.
This is the definitive guide for developers looking to solve that exact problem. We will walk you through the professional, industry-standard method to deploy a Node.js application on a VPS. You will learn how to:
Set up your server with a solid security foundation.
Install Node.js using a flexible version manager.
Use PM2, a powerful process manager, to keep your app alive forever.
Configure Nginx as a reverse proxy to securely serve your app to the world.
Add free SSL with Let’s Encrypt to secure your application with HTTPS.
Choosing Your Battlefield: The Importance of Server Location
Before we dive in, let’s talk about a crucial strategic decision: server location. The physical distance between your server and your users directly impacts your application’s speed and responsiveness (latency). For a global audience, you might use a CDN, but for a regional user base, placing your server at the heart of that region is paramount.
This guide uses a server Laos as its foundation. This is an ideal choice for applications targeting users across the Mekong sub-region, including Laos, Thailand, Vietnam, and Cambodia, ensuring the lowest possible latency and a superior user experience. The principles you learn here, however, are universal and can be applied to any VPS, anywhere in the world.
By the end of this guide, you will have transformed a blank VinaHost Laos VPS into a production-grade hosting platform for your JavaScript applications.
1. The Production Stack: Why PM2 and Nginx?
Let’s briefly understand the role of our two key players:
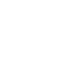
PM2: When your Node.js app crashes, the process stops. PM2 is a guardian that constantly watches your app. If it crashes, PM2 instantly restarts it. It also allows you to run your app in a “cluster,” leveraging all CPU cores of your VPS, and provides tools for monitoring and logging.
Nginx: Your Node.js app typically runs on a high-numbered port like 3000 or 8080. Nginx is a high-performance web server that sits in front of your app. It listens on the standard web ports (80 for HTTP, 443 for HTTPS) and acts as a “reverse proxy.” It takes incoming traffic from users and intelligently forwards it to your Node.js app. This is more secure, more efficient, and allows you to host multiple websites on the same server.
2. Prerequisites
A VinaHost VPS: We’ll be using a server running Ubuntu 24.xx.
A Domain Name: You should have a domain name pointed to your VPS’s IP address.
An SSH Client: PuTTY for Windows or Terminal for macOS/Linux.
Your Node.js Application: Ready to be deployed, likely in a Git repository.
Step 1: Initial Server Setup & Security
Before deploying any code, we must secure our server. We’ll perform the essential “first hour” security tasks. For a deep dive, check out our guide to securing a new VPS.
Connect as root:
Bash
ssh root@your_server_ipCreate a new sudo user (replace devuser with your choice):
Bash
adduser devuser usermod -aG sudo devuserSet up a basic firewall (UFW):
Bash
ufw allow OpenSSH ufw allow 'Nginx Full' ufw enableLog out and log back in as your new user:
Bash
exit ssh devuser@your_server_ip
From now on, we will execute all commands as this new devuser.
Step 2: Installing Node.js with NVM
Hard-coding a single version of Node.js on a server is inflexible. We’ll use NVM (Node Version Manager), which allows you to easily install and switch between multiple Node.js versions.
Install NVM:
Bash
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.39.1/install.sh | bashSource your profile to activate NVM:
Bash
source ~/.bashrcInstall the latest LTS (Long-Term Support) version of Node.js:
Bash
nvm install --ltsVerify the installation:
Bash
node -v npm -vYou should see the versions of Node and npm printed to the console.
Step 3: Get Your Application on the Server
The most common way to bring your application code to the server is by using Git.
Install Git:
Bash
sudo apt update sudo apt install git -yClone your repository:
Bash
git clone https://github.com/yourusername/your-node-app.gitNavigate into your project directory and install dependencies:
Bash
cd your-node-app npm installNote: If your application requires environment variables (like API keys or database credentials), now is the time to create a .env file.
Test your app to make sure it runs correctly:
Bash
node app.js # Or whatever your entry file isIf it starts without errors, you’re ready for the next step. Press Ctrl+C to stop it.
Step 4: Keep Your App Alive with PM2
Now, we’ll install PM2 and use it to manage our application process.
Install PM2 globally using npm:
Bash
sudo npm install pm2@latest -gStart your application with PM2:
Bash
pm2 start app.js --name my-apppm2 start app.js: This is the main command.
–name my-app: This gives the process a memorable name, which is useful when you have multiple apps.
Check the status:
Bash
pm2 statusYou will see a table with your app, its status (online), CPU usage, and memory usage.
Crucial Step: Make PM2 start on boot. This command generates a startup script that will automatically resurrect all your PM2 processes after a server reboot.
Bash
pm2 startupPM2 will give you a command to run. Copy and paste it into the terminal and execute it. It will look something like sudo env PATH=$PATH:/home/user/.nvm/versions/node/v18.12.1/bin /home/user/.nvm/versions/node/v18.12.1/lib/node_modules/pm2/bin/pm2 startup systemd -u devuser –hp /home/devuser.
Save the current process list:
Bash
pm2 save
Your app is now running and managed by PM2. It will restart automatically if it crashes or if the server reboots.
Step 5: Configure Nginx as a Reverse Proxy
Our app is running (probably on port 3000), but we need Nginx to route public traffic to it.
Install Nginx:
Bash
sudo apt install nginx -yCreate a server block configuration file. This file tells Nginx how to handle traffic for your specific domain. Replace your_domain with your actual domain name.
Bash
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/your_domainPaste the following configuration into the file. Read the comments to understand what each part does.
Nginx
server { # Listen on port 80 for incoming connections listen 80; listen [::]:80; # The domain name this server block will respond to server_name your_domain www.your_domain; # The location of your website's files (optional, but good practice) root /home/devuser/your-node-app; # Main configuration for proxying requests location / { # Forward the request to your Node.js app running on port 3000 proxy_pass http://localhost:3000; # Forward essential headers to your application proxy_http_version 1.1; proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade; proxy_set_header Connection 'upgrade'; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade; } }Make sure to replace your_domain and http://localhost:3000 with your actual domain and the port your app is running on.
Enable the configuration file by creating a symbolic link to the sites-enabled directory:
Bash
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/your_domain /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/Test your Nginx configuration for syntax errors:
Bash
sudo nginx -tIf it says syntax is ok and test is successful, you’re good to go.
Restart Nginx to apply the changes:
Bash
sudo systemctl restart nginx
Now, if you visit http://your_domain in your browser, you should see your Node.js application!
Step 6: Secure Your App with a Free SSL Certificate (HTTPS)
Running a site on HTTP is not secure. We’ll use Let’s Encrypt and Certbot to automatically install a free SSL certificate.
Install Certbot and its Nginx plugin:
Bash
sudo apt install certbot python3-certbot-nginx -yRun Certbot. It will automatically read your Nginx configuration, issue a certificate for your domains, and reconfigure Nginx to use it.
Bash
sudo certbot --nginx -d your_domain -d www.your_domainFollow the prompts. It will ask for your email address, agree to the terms of service, and ask if you want to redirect HTTP traffic to HTTPS (choose the redirect option, it’s more secure).
That’s it! Certbot will handle the renewal automatically. Your application is now live, stable, and securely served over HTTPS at https://your_domain.
3. Scaling Your Operations: Deploying in New Regions
Congratulations! You have successfully mastered the art of deploying a production-ready Node.js application. The setup on a VinaHost Laos VPS is a powerful foundation for serving users throughout the Indochina peninsula with minimal latency.
However, business growth often means audience growth in new regions. If your application starts gaining traction in markets like Malaysia, Singapore, or Indonesia, serving them from a server in Laos will introduce noticeable delays, negatively impacting user experience.
The professional solution is to replicate this exact high-performance stack on infrastructure physically closer to your new users. To deliver a lightning-fast experience for a Malaysian audience, the optimal strategy is to deploy your application on a server Malaysia. This move not only drastically reduces latency but can also improve your site’s SEO ranking within that specific region. By using the same PM2 and Nginx architecture, you can manage multiple regional deployments with a consistent and reliable workflow.
4. Conclusion: You Are Now a Deployment Pro
You’ve gone from a simple node app.js command to a fully-fledged, production-ready deployment. Your Node.js application is now:
Always-On: Managed by PM2, it will automatically restart on failure or reboot.
High-Performance: Served by the lightning-fast Nginx web server.
Secure: Protected by a firewall and served exclusively over HTTPS.
Professional: Accessible via your own domain name on standard web ports.

This robust setup gives you the confidence to build and scale your applications, knowing that the underlying infrastructure is solid.
Ready to launch your next big idea? Get the perfect VPS to power it.
>> Deploy Your Node.js App on a High-Performance VinaHost VPS Today! <<
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt English
English 简体中文
简体中文