What is KVM VPS? KVM VPS (Kernel-based Virtual Private Server) is a powerful solution in the field of web hosting and virtualization technology. With superior kernel-level capabilities, KVM VPS provides a flexible, secure, and scalable hosting environment for both businesses and individuals. This article will delve into the fundamentals of KVM VPS, highlight its advantages over traditional hosting options, and explain how it puts the power in the hands of users to optimize performance and control.
1. What is KVM VPS?
Using VPS is easy to understand because you share a physical server with many other people, but it feels like you are using a separate server.
Unlike shared hosting, VPS allows you to host and manage large projects without slowing down the system. Choosing a self-managed plan means you can choose your favorite operating system and have full control over your server.
Everything can work thanks to virtualization.
Virtualization allows multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run on one physical server. These virtual machines share system resources but operate independently. You can install software and configure each virtual machine separately if needed. The best thing is that each user has their own resources, so no one affects anyone else.
So what types of virtualization are there?
KVM VPS, or Kernel-based Virtual Machine, is a way to create virtual machines on a computer or server. It is integrated into the Linux kernel, turning it into a hypervisor for creating and managing virtual machines.
With KVM VPS, you can switch between Linux and Windows on the same physical server. Virtualization uses the server’s hardware to allow you to run separate operating systems. This means that even if the main server uses Linux, you can still run Windows or any other operating system you like.
Even though KVM VPS is built on a Linux platform, you can still use it to run other operating systems like Windows. KVM connects the operating system kernel to the hardware, allowing you to run the server on any operating system you want.

Also Read: What is VPS? | Unveiling the Power Behind Virtual Private Servers
2. How does KVM VPS work?
VPS KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) uses virtualization technology in the Linux kernel to create and manage virtual machines (VMs) on a physical server. Here’s how it works:
- Host: A physical server, usually running a Linux operating system, that acts as the main server and has a KVM module in the kernel.
- Hypervisor: KVM turns the Linux kernel into a hypervisor, software that creates and manages virtual machines. It allocates hardware resources such as CPU, memory, and storage to each VM.
- Virtual Machine: Each VM operates as an independent computer with its own operating system, applications, and configuration. Virtual machines share the physical resources of the server but operate as if they were on separate machines.
- Isolation: KVM ensures each VM is isolated from other VMs, so the performance and security of one VM does not impact other VMs. Each VM has its own virtual hardware such as virtual CPU, memory, network interface, and storage.
- Resource Allocation: Hypervisor allocates specific CPU, RAM, and disk space to each VM according to the configuration set by the user or service provider. These resources are dedicated to the VM to ensure stable performance.
- OS independence: With KVM, you can run any operating system in the VM, regardless of the host’s operating system. For example, you can run a Windows VM on a Linux server or vice versa.
- Management and control: Users have full control over their virtual machines, including root access, allowing software installation and configuration, security management, and performance optimization.
- Live migration: KVM supports live migration, meaning you can move running virtual machines from one host to another without disruption. This is useful for maintenance, load balancing, and ensuring high availability.
Thanks to KVM, VPS service providers can provide flexible, scalable, and secure virtual environments for a variety of applications and workloads.
Also Read: What is Windows VPS? | Who Should Use a Windows VPS?
3. The Benefits of KVM VPS Hosting
3.1. Enhanced Security and Isolation
KVM enhances security by isolating virtual machines (VMs). Each VM has its own operating system in a separate environment, so it cannot affect other VMs. KVM also uses Linux security features, such as SELinux and access controls, for better protection.
3.2. Superior Performance and Scalability
KVM improves performance by integrating deeply into the Linux kernel and effectively leveraging hardware virtualization. This integration enables direct access to the server’s hardware resources, minimizing latency and maximizing throughput for virtual machines. KVM performance is comparable to applications running directly on the server.
KVM is known as a reliable virtualization solution, deeply integrated into the Linux kernel with a robust code base and long development history. It is an important part of the Linux ecosystem, regularly updated with security patches and supporting a variety of hardware. Thanks to its reliability and widespread adoption, KVM is a popular choice for many organizations and businesses.
3.3. Full Control and Customization
KVM VPS hosting gives users complete control to manage their virtual servers. This includes the ability to customize their configuration, install the operating system they prefer, and manage applications according to their specific needs.
3.4. Flexibility for Diverse Applications
KVM’s virtualization technology allows running many different operating systems and applications simultaneously on the same physical hardware. This is useful for hosting a variety of applications, from web servers to complex databases, ensuring optimal performance and scalability.
Also Read: What is Linux VPS? | Choosing the Right Linux VPS Provider
4. Drawbacks of KVM VPS Hosting
4.1. Higher Cost Compared to Shared Hosting
One downside to VPS KVM hosting is its higher cost compared to shared hosting. This is mainly because KVM VPS provides dedicated resources and allows running multiple operating systems on the same server. This requires more robust infrastructure and maintenance, and the cost reflects the level of assurance for these features. Therefore, KVM VPS is less suitable for narrow budgets or users with simple storage needs.
However, investing in KVM VPS often pays off, improving scalability and security. This is very useful for businesses and individuals who need more management and flexibility in their hosting environment.
4.2. Requires Technical Knowledge for Management
Because KVM operates at the kernel level, it often requires a deeper understanding of system fundamentals and Linux administration than other user-level virtualization solutions. To configure and manage KVM, it is often necessary to use command line tools and interact directly with the Linux kernel. This can be more complicated for users who do not have much experience in this area.
5. Who Needs KVM VPS?
5.1. Developers and Programmers
VPS KVM is ideal for developers and programmers who need a flexible environment to test and deploy applications on different operating systems. It provides the resources and control needed to optimize the development process.
5.2. Businesses with Growing Online Presence
Businesses with a growing online presence will benefit from a KVM VPS thanks to its scalability and dedicated resources. It supports handling high traffic volumes, managing databases, and running complex applications securely.
5.3. Anyone Seeking More Control
Individuals and organizations who want greater control over their hosting environment will find KVM VPS an attractive choice. It allows customizing server configurations, installing specific software, and managing security settings to effectively meet unique requirements.

Also Read: What is SSD VPS Hosting? | Everything You Need to Know
6. Choosing the Right KVM VPS Provider
To choose the right VPS KVM provider, you need to consider some of the following factors:
6.1. Factors to Consider (CPU, RAM, Storage)
Evaluate vendor products based on CPU performance, RAM allocation, and storage capacity. Make sure these resources are enough for your application to operate efficiently and meet your storage needs.
6.2. Scalability and Upgrade Options
Look for a provider that offers flexible service plans, allowing you to easily upgrade or reduce resources as needed. This gives you the flexibility to accommodate scaling requirements or adjust resource allocation over time.
6.3. Customer Support and Reputation
Research the provider’s reputation for customer support quality. Read reviews and feedback from other users to gauge your responsiveness, technical expertise, and problem-solving reliability. Vendors should provide reliable and professional support channels.
By carefully considering these factors, you will be able to make an informed decision on choosing the VPS KVM provider that best fits your technical needs and business goals.
VinaHost is one of the leading VPS virtual server providers in Vietnam. We provide a variety of VPS packages in Vietnam and foreign VPS, helping customers have many choices to suit the needs of each individual and organization.
VinaHost is committed to using the best VPS server equipment, ensuring high speed and stability for VPS. Our support team is always ready to assist 24/7 during the process of using the service.
When registering for VPS hosting at VinaHost, customers will receive the following benefits:
- Powerful hardware: SSD hard drive combined with NVMe standard hard drive (RAID 10) provides superior speed compared to conventional VPS, improving performance and data security.
- Optimal Virtualizor management interface: Customers have full control over the server with a simple, full-featured administration page that allows users to change passwords, grant IPs, add hard drives, and change information on VPS is more convenient.
- Quick deployment: After completing payment, you will not have to wait long to activate the VPS server. Creating virtual servers takes place quickly with just a few mouse clicks.
- KVM virtualization technology: Full KVM virtualization (can run Linux/Windows OS), supports running Docker on VPS.
- Free Directadmin: VinaHost provides free DirectAdmin to all customers using Pro VPS SSD service at VinaHost. VinaHost commits not to use cracked/nulled versions.
- Data backup: Free weekly backup and store 3 backup copies in the last 3 weeks, ensuring data safety.
- IPv6 support: ProVPS SSD supports IPv6, you can refer to the upgrade price list if you need to order more.
- 99.9% uptime commitment: Server reaches Tier 3 Data center, unlimited data transmission traffic, 99.9% uptime commitment, ensuring VPS always operates stably.
- 24/7 technical support: 24/7/365 technical support via email, livechat, hotline with maximum response time within 15 minutes.
- Unlimited Data Transfer: Helps maximize the performance of the VPS virtual machine system and the system always operates smoothly.
- Operating system installation support: VinaHost ensures support for a variety of operating systems according to each customer’s choice and needs to save administration and operation time.
- Refund commitment: VinaHost commits to 100% refund if you are not satisfied with the quick procedure.
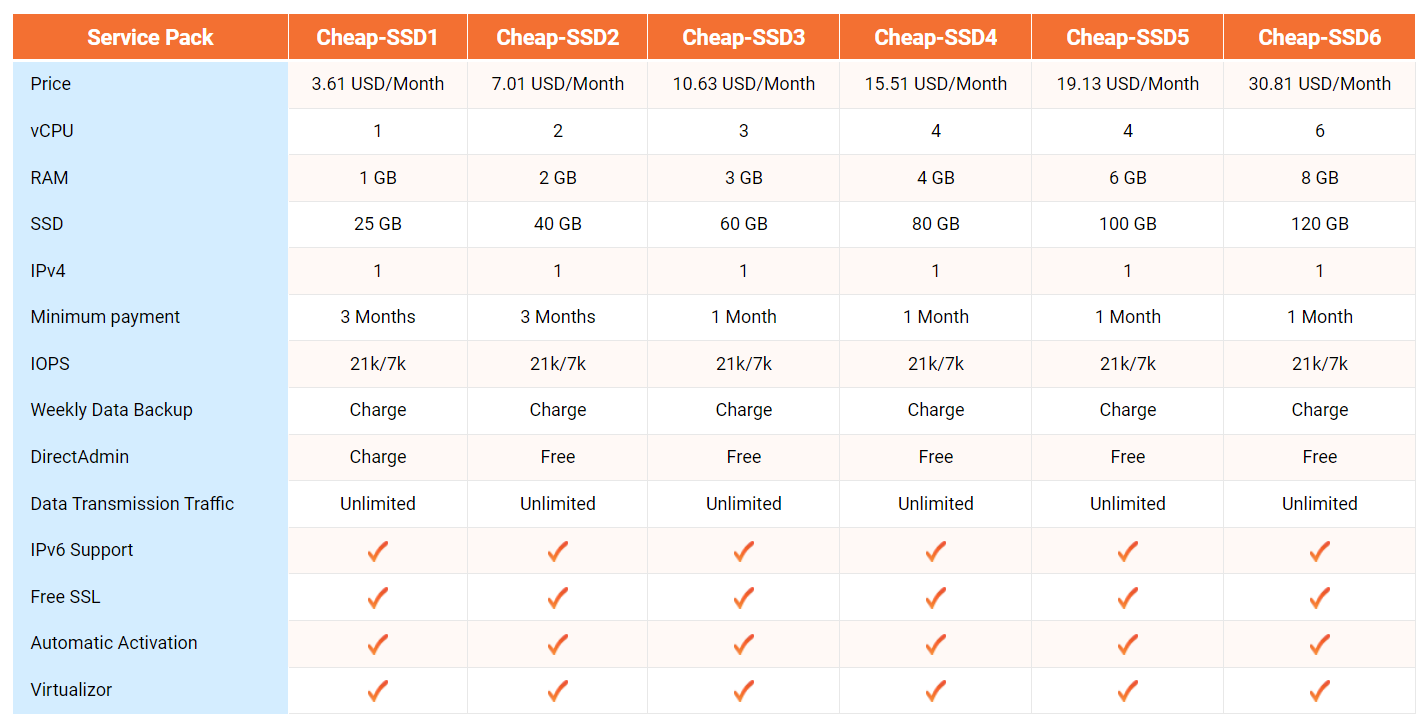
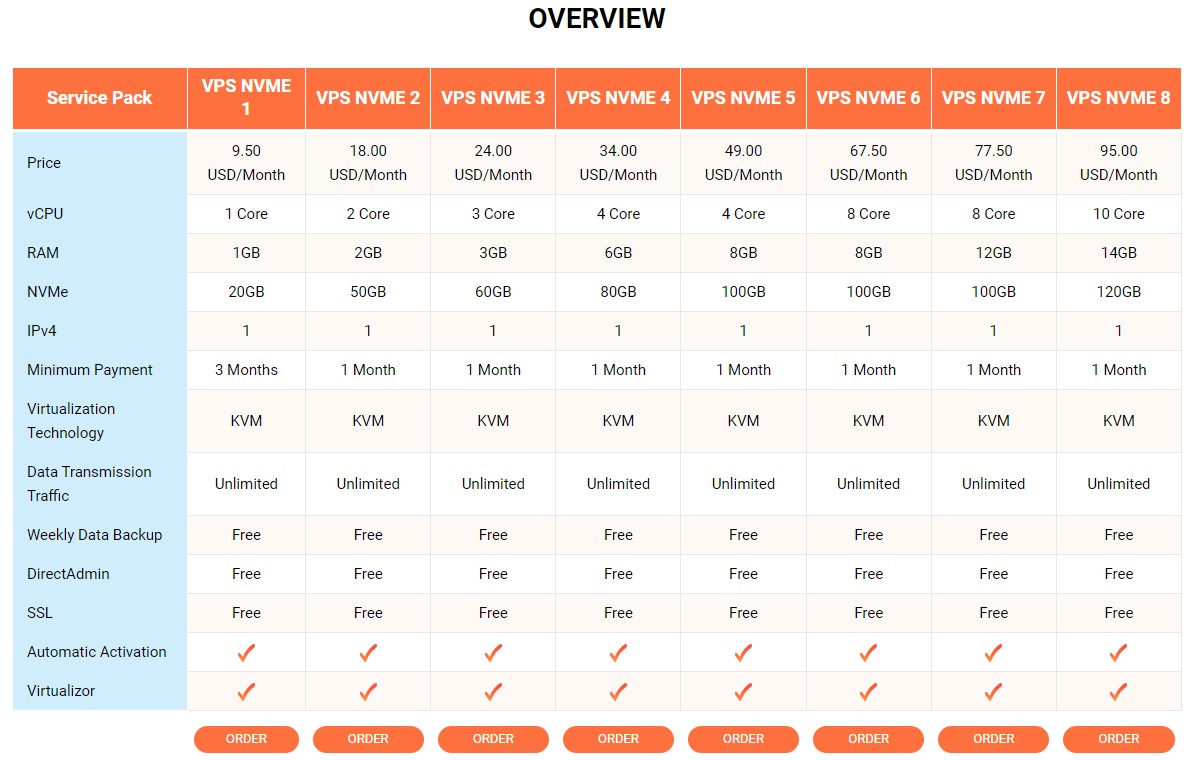
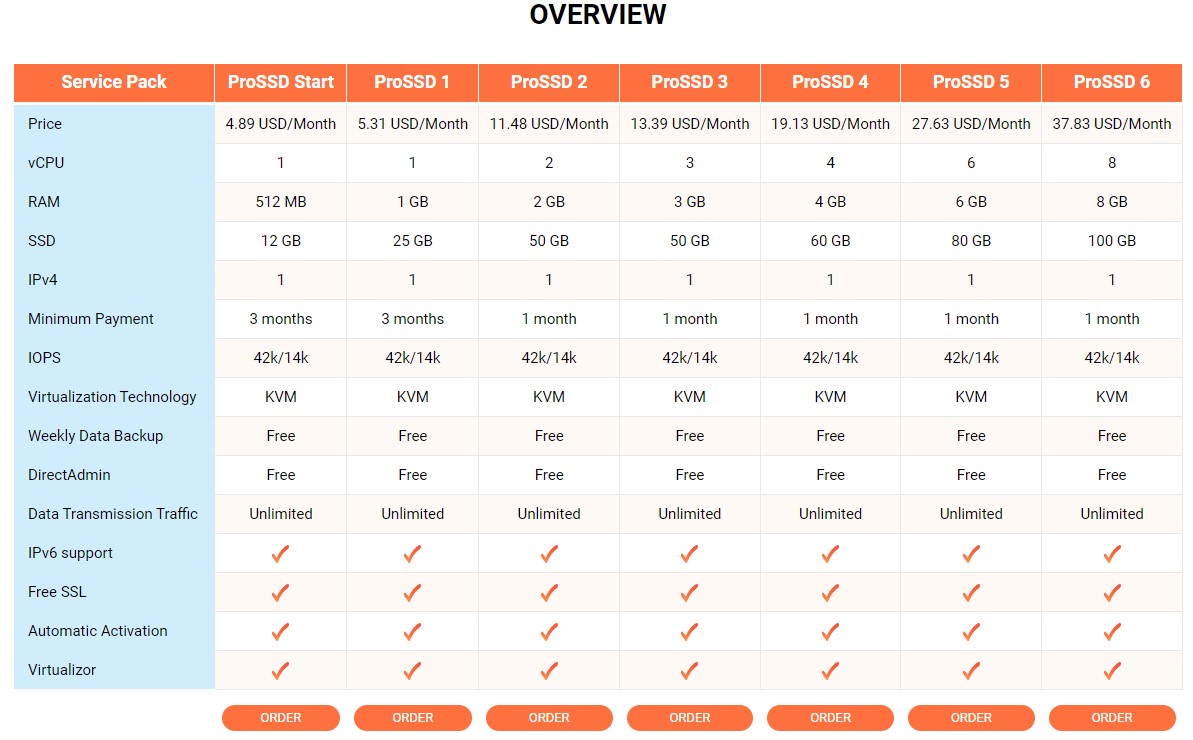
Additionally, we also provide:
7. KVM VPS vs. Other Hosting Solutions
Here’s a comparison table of KVM VPS vs Shared Hosting, Cloud Hosting, and Dedicated Servers
| Feature | KVM VPS | Shared Hosting | Cloud Hosting | Dedicated Server |
| Virtualization Technology | KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) | None or limited | Hypervisor-based | None (dedicated hardware) |
| Resource Allocation | Dedicated resources per virtual server | Shared resources among multiple websites | Distributed across multiple servers | Entire server dedicated to one user |
| Performance | Better than shared hosting, scalable | Limited due to resource sharing | Scalable, generally better than shared hosting | Highest performance, dedicated resources |
| Cost | More affordable than dedicated servers | Least expensive | Variable based on usage and scalability | Most expensive |
| Scalability | Scalable, resources can be adjusted | Limited scalability | Highly scalable, resources on demand | Limited scalability without hardware upgrade |
| Control | Full control over server configurations | Limited control | More control than shared hosting | Complete control |
Summary
- Shared Hosting: Suitable for small websites with low cost, but lacks performance and management.
- Cloud Hosting: Scalable and flexible, providing better performance than Shared Hosting.
- Dedicated server: Ensures top performance and complete control, suitable for high-demand applications.
- KVM VPS: Balances performance, management and cost, ideal for users who need dedicated resources and flexibility without investing in a dedicated server.
8. The Future of KVM VPS
The future of KVM VPS (Kernel-based Virtual Private Server) has great potential for growth, thanks to the following key trends and advancements:
- Increased performance: Continuous improvements in hardware and virtualization technology can deliver superior performance for KVM VPS. This includes advances in CPU architecture, memory management and storage technology, which increase processing speed and reduce latency.
- Integration with Cloud Services: Expect stronger integration between KVM VPS and cloud services. This allows for easy migration, common deployment, and scaling across various cloud platforms.
- Security Improvements: With growing concerns about cybersecurity, KVM VPS providers can focus on improving security. This can include improvements in virtual machine isolation, encryption technology, and integration of new security tools and protocols.
- Automation and orchestration: Automation tools and orchestration systems will play an important role in the future of KVM VPS. This includes automated provisioning, scaling, and management of VPS instances, making it easy for users to deploy and manage their virtual environments.
- Containerization and Microservices: The development of container technologies such as Docker and Kubernetes may affect KVM VPS in the future. Vendors can integrate solutions that combine the benefits of virtual machines with the flexibility of containers, catering to modern development applications.
- AI and Machine Learning: The increase in the use of AI and machine learning applications will increase the need for high-performance computing environments, which KVM VPS can effectively support. Vendors can offer special configurations optimized for AI workloads.
- Edge Computing: As edge computing grows, KVM VPS can play an important role in delivering computing resources closer to end users and IoT devices. This can improve latency-sensitive applications and support real-time data processing requirements.
In summary, the future of KVM VPS is promising with continuous development, towards more powerful, flexible and secure virtualization solutions to meet the increasing needs of information technology applications.
9. FAQs
9.1. What is the difference between KVM and OpenVZ?
OpenVZ is an open source virtualization technology designed for the Linux operating system. It allows you to create and manage multiple independent Linux containers on the same physical server. Using a modified Linux kernel, OpenVZ divides the server into zones called “containers”, each of which acts as a separate virtual server with shared resources.
Each container includes features such as root account, memory limits, CPU limits, process management, and network configuration. Each container is identified by a unique container ID, called CTID, for easy management and identification. OpenVZ is available for free and requires no special license or usage fees.
KVM and OpenVZ differ greatly in their virtualization methods. KVM provides complete virtualization, allowing each user to have separate resources like a real server. This is an excellent choice for applications that require a high degree of isolation and control.
In contrast, OpenVZ provides operating system-level virtualization, meaning multiple containers share fixed resources on the same server node. This limits OpenVZ to only supporting Linux operating systems, not allowing other operating systems to run.
With KVM, you can choose from a variety of operating systems, providing extensive flexibility to users.
When comparing OpenVZ and KVM, the main difference lies in how resources are allocated. In OpenVZ, resources are shared between users and are fixed and cannot be adjusted even if more resources are needed. Meanwhile, KVM provides dedicated RAM, CPU, and storage for each user.
In terms of usability, OpenVZ is more user-friendly and suitable for people with limited technical skills. However, users cannot change the Linux kernel or adjust network parameters using OpenVZ. In contrast, KVM offers greater flexibility with the ability to modify the Linux kernel and adjust network parameters. Furthermore, KVM is not limited in terms of deployment of operating systems, while OpenVZ has limitations on this.
9.2. Is KVM VPS difficult to manage?
Managing a KVM VPS (Kernel-based Virtual Private Server) can vary in complexity depending on your technical level and the specific needs of each job. Here are some key points:
- Initial setup: VPS KVM setup includes operating system installation, network configuration, and resource allocation. This can be as simple as basic Linux administration knowledge or using the vendor’s control panel.
- Configuration and Maintenance: KVM VPS management requires familiarity with the command line interface (CLI) for installing software, setting up firewalls, configuring services, and monitoring performance. This level is more complex than shared hosting but offers greater control.
- Security: KVM VPS protection includes regular updates, security settings, firewall deployment, and vulnerability monitoring. Although requiring attention, it is manageable with knowledge or support from the supplier.
- Expand and upgrade: KVM VPS allows expansion by upgrading resources when needed. Managing this includes adjusting configurations and migrating data, often through the vendor’s management tool.
- Support options: Vendors often offer support ranging from troubleshooting to proactive monitoring or management. Managed services simplify management, making KVM VPS more accessible to less experienced users.
Overall, although KVM VPS management can be complex with a certain level of technical proficiency, it offers greater flexibility, performance, and customization than shared hosting. With the right knowledge and support, you can effectively manage KVM VPS to meet diverse hosting needs.

9.3. What operating systems can I install on a KVM VPS?
You can install a variety of operating systems on a KVM VPS (Kernel-based Virtual Private Server). KVM supports both Linux and non-Linux operating systems, giving you the flexibility to choose to suit your unique needs and preferences. These are some operating systems commonly installed on KVM VPS:
Linux Distributions:
- Ubuntu
- CentOS
- Debian
- Fedora
- Arch Linux
- OpenSUSE
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL)
- Linux Mint
- and many more…
Windows Server Versions:
- Windows Server 2019
- Windows Server 2016
- Windows Server 2012 R2
- Windows Server 2008 R2
Other Operating Systems
- FreeBSD
- OpenBSD
- NetBSD
- Solaris
- CentOS Stream
- CoreOS
- and others…
This capability is one of the main advantages of KVM virtualization, helping users choose the most suitable operating system for purposes such as web hosting, development environments, databases or other applications.
9.4. How much does a KVM VPS cost?
The cost of KVM VPS (Kernel-based Virtual Private Server) can vary due to some of the following factors:
- Service providers and plans: Different hosting providers will have different pricing structures, depending on the resources provided such as CPU cores, RAM, storage, Additional features like bandwidth and backup options, as well as managed or unmanaged services.
- Resource Allocation: Price will depend on the specific amount of resources such as CPU, RAM and memory allocated to each package. Plans with higher resources will typically cost more than plans that offer less resources.
- Geographic location: Costs will also vary based on the location of the data center. Data centers in prime areas often have higher costs than other locations.
- Managed and self-managed services: Provider-managed plans will cost more than self-managed plans, as the provider will be responsible for the tasks management like updates and security.
- Billing Cycle: Costs may vary depending on the billing cycle you choose, including monthly, quarterly, annually or longer. Usually, discounts will apply to long-term packages.
It’s important to compare plans from different vendors to choose the plan that best fits your needs in terms of performance, scalability, support, and budget.
Also Read: What is NVMe VPS? | The Difference between NVMe VPS vs SSD VPS
9.5. Do I need a dedicated IP address with a KVM VPS?
Of course, often you need a dedicated IP address for a KVM VPS. Here are a few main reasons:
- Direct Access: Dedicated IP address allows your KVM VPS to be accessible directly from the internet. This is important when you host websites, applications or services that need to be accessed from anywhere in the world.
- SSL Certificate: If you are using websites or applications that require SSL/TLS (HTTPS) certificates, a dedicated IP address is necessary. SSL is associated with a specific IP address, and using a dedicated IP helps ensure compatibility and easy certificate management.
- Special Server Applications: Some server applications or services may require a dedicated IP address to function properly or to configure domain-based access control.
- Email delivery: If you want to set up an email service on a KVM VPS, using a dedicated IP address can improve email deliverability and minimize the risk of being blacklisted, a problem. Common problems with shared IP addresses.
- Control and Security: Dedicated IP addresses give you more control over traffic and server operations, helping to increase security and manage access control effectively.
While some hosting providers may provide a shared IP address initially, choosing a dedicated IP address is often recommended because of these benefits, especially when you are operating services or important applications on your VPS KVM.
10. Conclusion
So what is KVM VPS? KVM VPS (Kernel-based Virtual Private Server) is a flexible and powerful solution for those who need high control, performance, and security in their hosting environment. With kernel-level virtualization, KVM VPS provides dedicated resources, allowing you to choose flexible operating systems and handle resource-intensive applications efficiently. Find out more articles at our Blog and don’t hesitate to contact us for support:
- Email: support@vinahost.vn
- Hotline: 1900 6046
- Livechat: https://livechat.vinahost.vn/chat.php
What is VPS Security? | 13 Best Practices for VPS Security
What is gaming VPS? | Choosing the Right gaming VPS Provider


 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt English
English 简体中文
简体中文