What is Domain Hijacking? Domain hijacking is a serious threat to both businesses and individuals on the internet. This practice involves unauthorized access and control of a domain name, often resulting in financial loss, reputational loss, and operational disruption. Understanding the mechanisms and risks associated with domain hijacking is critically important to protecting digital assets. Let’s join VinaHost to learn information about domain hijacking through the following article.
1. What is Domain Hijacking?
Domain name hijacking often involves unauthorized intrusion into the domain name registration and management system.
An attacker will seek to improperly gain control of a company’s domain name registration account, thereby making illegal changes and transfers for personal use.
Cyber security breaches are becoming an increasingly serious threat to both individuals and businesses. In recent years, domain name hacking has increased, carrying higher risks than before. The consequences of these attacks are severe, ranging from reputational damage to data breaches and financial loss.

Also Read: What is Domain & How It Impacts Your Online Presence
2. How does Domain hijacking works?
When you purchase a domain name, its registration information is provided by your registrar or hosting provider, giving you full control over its settings. You can change every detail of the domain name, like owner information and links to the website. Access to this control panel is limited to domain owners only, ensuring they maintain exclusive control to adjust settings.
Cybercriminals use a variety of techniques to take over valuable domains, with social engineering being one of the most common and most effective strategies.
For example, an attacker could impersonate a company or domain registrar through a phone call to obtain the domain registrar’s login information. They can also fool domain managers in companies into providing login information to phishing websites. With this information, criminals can transfer domain name registrations to overseas service providers, often in remote locations.
Furthermore, attackers may try to install malware on your computer through social engineering techniques. By deploying software such as trojans or keyloggers, they aim to obtain credentials to access the domain management control panel.
Another method involves guessing weak passwords used to break into domain control panels. Once successful in guessing the password, the attacker will be able to access the domain admin panel.
Additionally, intruders can take advantage of domain expiration, based on human negligence in renewing the domain on time, even though registrars often send periodic renewal reminders. However, these reminders can sometimes be ignored if mistakenly viewed as spam by email systems.
Although not common, exploiting vulnerabilities in domain name registration systems is another option for hijackers. If these vulnerabilities exist, they can be leveraged to transfer the domain name to another registrar.
Also Read: What is Domain Squatting? | Everything you need to know
3. Types of Domain Hijacking
Domain hijacking is different from domain spoofing. When spoofing, hackers slightly edit the spelling of the domain name and copy the original website onto the fake domain name. In contrast, domain hijacking involves taking complete control of a website’s original domain name. Forms of domain name appropriation include:
3.1. Registrar Security Breaches
This happens when administrative accounts on the registrar’s support system are compromised, leading to unauthorized access and the risk of domain name takeover.
3.2. Social Engineering
These phishing techniques target website administrators or owners, causing them to reveal login information for their domain registrar’s account, or download a spyware (keylogger).
3.3. Web Vulnerabilities
By finding and exploiting vulnerabilities in websites, digital asset management systems, and web servers, intruders can gain unauthorized access and control of domains.
3.4. Expired Domain Registration
This involves third parties legally acquiring expired domain names, from which they can control and redirect visitors to the IP address associated with the malware.

Also Read: What are expired Domains? | How to check domain expiration?
4. The Impact of Domain Hijacking
Domain hijacking can have serious consequences for individuals and businesses. Here are the main impacts:
4.1. Financial Losses
- Attackers can access financial accounts associated with the domain, causing direct monetary loss.
- The attacker can demand a ransom to return the domain name.
- Legal fees and technical costs associated with domain name recovery and system security can be substantial.
- Business interruption can result in significant revenue loss.
4.2. Reputational Damage
- Customers may lose trust in businesses that fail to protect their domains, reducing long-term loyalty.
- Negative publicity about the robbery could damage the company’s reputation and brand image.
- Hijacked domains can be used for malicious activities, leading to being blacklisted by search engines, affecting visibility online marketing of businesses.
4.3. Loss of Business
- Access to the website and email system may be interrupted, disrupting business operations.
- Customers may go elsewhere if they cannot access the company’s services or are concerned about security.
- Sensitive customer and business data can be lost or stolen in a hijacking.
4.4. Email Takeover
- An attacker can send phishing emails from a compromised domain, targeting customers, employees, and partners.
- Accessing business email accounts can lead to exposure of sensitive information and other security breaches.
- Loss of email access can seriously disrupt internal communications and operations within the business.
To minimize these risks, businesses should implement strong security measures such as two-factor authentication, regular domain monitoring, and working with reputable domain registrars.
5. Is Domain Hijacking Illegal?
The legal status of domain name squatting remains ambiguous, although some federal courts in many countries have begun to recognize claims to reclaim stolen domains to their rightful owners.
There are several forms of domain name hijacking. One of them is domain name squatting, where an individual purchases a domain name just to prevent someone else from buying it. The squatter often aims to resell the domain name at a higher price to someone who has an urgent need. This practice prevents the rightful owner of a trademark or brand from obtaining a domain name and using it to enhance their online presence. Legally, domain name hijacking is often considered holding a domain name for ransom and is a violation of trademark rights.
Another form of domain hijacking is to quickly purchase an expired domain name from the previous owner. While purchasing an expired domain name is not illegal, it can still raise ethical and business concerns.
Also Read: What is a Domain Extension? | How to Choose a Domain Extension
6. How to Prevent Domain Hijacking?
In addition to the precautions we will take, there have been a number of security standards established between domain name providers and the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN).
To reduce the risk of domain name hijacking, ICANN requires a 60-day waiting period after any changes to registration information before a domain name can be transferred to a new registrar. This waiting period is intended to make transferring a hijacked domain name more difficult, allowing the original owner more time to detect and report unauthorized changes during that period.
The most effective way to prevent domain hijacking is to take proactive measures. Here are some steps you can take:
6.1. Choose a Reputable Registrar
Work with accredited domain registrars instead of shady registrars that offer free or low-cost services. Reputable registrars provide secure DNS management panels and 24/7 technical support. Choosing a trustworthy domain name provider will provide additional security for your domain name.
It is important to have access to technical support at any time. You should be able to contact them via email, phone, and ticketing system. In the event of a domain name takeover, immediate assistance is critical to restoring the domain name.
VinaHost is a domain registrar based in Vietnam, offering domain registration services along with web hosting solutions. We provide options for registering domain names, managing DNS settings, and hosting websites and emails. When purchasing a domain from VinaHost, you can expect several advantages:
- Local Expertise: As a Vietnamese registrar, VinaHost offers localized support and understanding of local market needs and regulations.
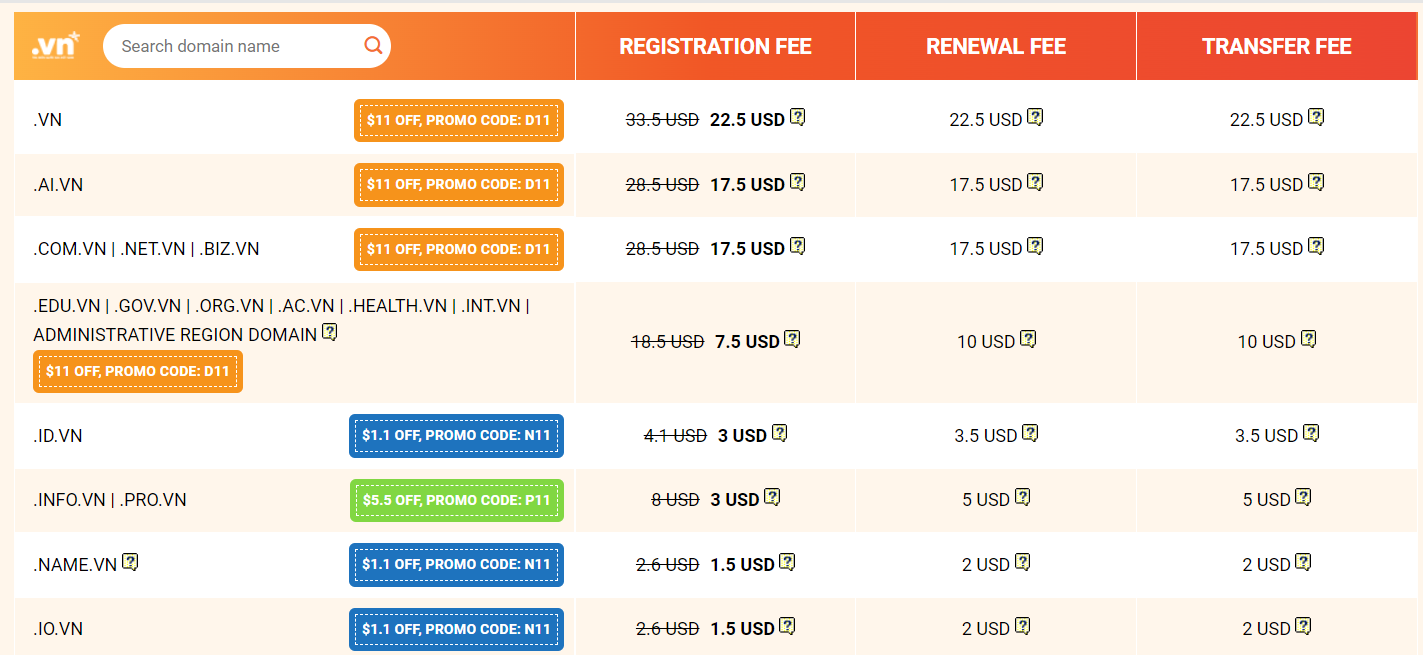
- Competitive Pricing: We often provide competitive pricing for domain registration, renewal, and transfer fees.
- Additional Services: VinaHost typically offers additional services such as web hosting, email hosting, SSL certificates, and DNS management, making it a convenient one-stop solution for your online presence needs.
- Customer Support: We usually provide responsive customer support in Vietnamese and sometimes in English, ensuring assistance when needed.
- Security Features: VinaHost may offer security features such as domain locking, WHOIS privacy protection, and two-factor authentication to enhance the security of your domain.
- Reliability: With established operations in Vietnam, VinaHost can offer reliable domain registration and management services tailored to local businesses and individuals.
6.2. Strong Passwords & Two-Factor Authentication
Using weak passwords for your domain and email accounts can easily lead to loss of control. Always choose a strong password that includes a combination of lowercase letters, uppercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Strong passwords help protect against brute force attacks and unauthorized access.
Also, make sure that the passwords for your domain name and email account are unique and not used for any other online accounts. Security experts typically recommend changing your password every 72 to 90 days for added security.
It’s important to enable two-factor authentication (2FA) on all accounts to prevent domain hijacking. This is an extra layer of security that can prevent unauthorized access even if someone might know your password. 2FA is considered one of the most effective protection measures to protect your account. By requiring a unique verification code sent to your smartphone after entering your password, 2FA ensures that only you can access your account.
Also Read: What is a root domain? | Why does a root domain matter?
6.3. Beware of Phishing Scams
Phishing is a common type of online attack, often carried out via email. Attackers send phishing emails to thousands of people, asking them to provide sensitive information such as passwords, bank account details, make money transfers, or download malicious files. These emails often contain malware or links to fake websites, intended to scam individuals into revealing personal information.
Phishing attacks are common, often using domains that resemble your legitimate registrar or impersonating a trusted sender trust. Always verify the legitimacy of such emails by contacting your domain registrar directly via their official website and forwarding suspicious emails to them for confirmation.
6.4. Keep Your Contact Information Updated
Some successful domain hijackings occur when a domain’s contact information, such as an email address, is outdated or expired and can be re-registered by an attacker. It’s important to keep your contact information up to date to prevent potential risks to your domain.
6.5. Domain Locking
To prevent unauthorized transfers of your domain name to another registrar, make sure your registrar offers a domain locking feature for added security. While many registrars have implemented this feature, you should contact them to confirm and enable this domain locking feature yourself as an additional precaution.
6.6. Regular Monitoring
Keep a close eye on your domain name’s expiration date and enable auto-renewal to avoid accidentally losing it. Regularly check domain registration details to quickly detect invalid changes.
Also Read: What is a Top Level domain? | Everything You Need to Know TLDs
7. FAQs
7.1. How can I tell if my domain has been hijacked?
You can detect if your domain is being taken over by looking for the following signs:
- Changes to the website: Check if the content or appearance of the website has been changed suddenly without your permission.
- DNS Change: Confirm if your domain’s DNS settings have changed in an unusual way, such as changing nameservers or other DNS records.
- WHOIS Information: Look up your domain’s WHOIS information to see if there have been any recent updates you weren’t aware of, like changes to contact details or the domain’s status.
- Email issues: Monitor for any unusual activity related to email accounts in your domain, such as not being able to send or receive emails, or reports of phishing emails sent from your domain.
- Site accessibility: Check to see if the website is suddenly inaccessible, or visitors report being redirected to unknown or suspicious websites.
- Registrar notifications: Pay attention to notifications from your domain registrar about any changes to your domain that you did not approve.
- Search engine warning: If your domain is flagged by search engines as potentially compromised or associated with malicious activities, this could be a sign of control being usurped.
If you suspect your domain has been taken over, act quickly by contacting your registrar’s support team to report the incident and begin the recovery process. They’ll guide you on how to protect your domain and restore control.
7.2. I think my domain has been hijacked. What should I do first?
If you suspect your domain has been taken over, take immediate action with these steps:
- Contact the domain registrar: Call the domain registrar’s customer support department immediately to report the incident and ask them to lock your domain.
- Proof of ownership: Prepare proof of domain ownership, including account information, payment history, and any other documents that prove you are the legal owner of the domain.
- Lock the domain name: Ask the registrar to lock the domain name to prevent any illegal changes or further transfers.
- Check for recent activity: Monitor and check for recent activity on your domain, such as DNS records and WHOIS information, to promptly detect and handle any unauthorized changes.
- Restore from backup: If applicable, restore your website and email service from the most recent backup to ensure they are not affected.
- Change passwords: Change passwords associated with accounts such as domain registrars, website hosting services, and email to prevent further unauthorized access.
- Close monitoring: Monitor your domain regularly going forward to promptly detect and resolve any suspicious activity.
- Report to the appropriate authorities: If you suspect your domain name hijacking is part of a larger cybercrime incident, report it to the appropriate authorities such as the police or security organizations network so they can assist and investigate further.
By taking these steps promptly, you can increase your chances of recovering your domain name and minimize the impact of a hijacking on your business and website.
Also Read: What is Domain Privacy? | Do you need Domain Privacy?
7.3. How long does it take to recover a hijacked domain?
The time it takes to restore a hijacked domain can vary depending on the following factors:
- Registrar’s Policy: Each domain registrar may have different processes and processing times for the recovery of hijacked domains. There are registrars that may have a faster and priority process, while others may require more detailed verification steps.
- Documentation proving ownership: The speed of domain recovery often depends on the ability to quickly provide the necessary documents to prove you are the rightful owner of the domain. These can be identity documents, payment records and other evidence.
- Case complexity: If the domain hijacking involves complex legal disputes or multiple parties involved in ownership, recovery may take longer to solve.
- Legal and Administrative Processes: In some cases, you may need to follow legal or administrative processes, which may lengthen the time needed to restore the domain.
In general, simple cases can be resolved in a few days to a few weeks if you provide adequate information and documents in a timely manner. However, complex cases can take longer, lasting from several weeks to several months, especially when legal issues or disputes are involved. It is important to maintain regular contact with the registrar to ensure a quick and efficient resolution process.
7.4. What other security measures can I take to protect my domain?
To increase the security of your domain and protect against various threats, take the following security measures:
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA): Enable 2FA for your domain registrar account and associated email accounts. This provides an extra layer of protection by requiring a second verification in addition to the password.
- Use strong passwords: Make sure every domain-related account (like registration, hosting, and email accounts) has a strong and unique password, including upper and lower case letters, numbers and special characters.
- Update and patch software regularly: Always update your website software, CMS, plugins and server operating system with the latest security patches to prevent attacks through known software vulnerabilities.
- Monitor domain activity: Regularly check DNS records, WHOIS information and website traffic to detect unusual activities or unauthorized changes early.
- Domain lock: Enable the domain lock function on your registrar’s control panel to prevent unauthorized domain transfers.
- Restrict access: Limit access to domain management and registrar accounts to essential personnel only, using role-based access control (RBAC) where applicable can.
- Regular backups: Perform regular backups of your website and important domain-related data and store them securely elsewhere than on your website system.
- User Education: Train employees on strategies to prevent and respond to phishing attacks and other intrusions into domain security.
- Protect email accounts: Since email is often used for domain management and password resetting, make sure your email account is also protected with a strong password and 2FA.
- WHOIS Privacy: Consider protecting your domain’s privacy by hiding personal contact information in the public WHOIS database to reduce the risk of identity theft.
By taking these measures, you can reduce the risk of domain hijacking and better protect your online presence and business.
Also Read: What is Registry Lock? | Protect Domain with Registry Lock
8. Conclusion
So what is domain hijacking? Domain name hijacking remains a major cybersecurity threat that can have serious consequences. This highlights the importance of adopting security measures such as using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and regularly monitoring domain activity. By staying alert and following domain name management best practices, individuals and businesses can minimize the risk of domain name hijacking and protect their digital identities. Find out more articles at our Blog and don’t hesitate to contact us for support:
- Email: support@vinahost.vn
- Hotline: 1900 6046
- Livechat: https://livechat.vinahost.vn/chat.php
What is Domain Backorder? | Everything you need to know
What is VNNIC? | Everything you need to know VNNIC VN
What is a Domain Registrar? | Function of a Domain Registrar
The Value of Domain Names: Choosing the Right Domain for Your Website


 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt English
English 简体中文
简体中文