What is a ccTLD? ccTLDs (country code top-level domains) are two-letter domain extensions that represent a specific country or territory. For example, “.uk” is for the United Kingdom, and “.jp” is for Japan. ccTLDs help identify the geographic location of a website and can increase the trust and relevance of that website in that country. VinaHost will explain what a ccTLD is, the benefits of ccTLDs, and the difference between ccTLDs and gTLDs.
1. What is a ccTLD? CCTLD examples?
ccTLD stands for “Country Code Top-Level Domain“. It is a two-letter domain extension assigned to each country, territory, or sovereign territory.
These domains help identify websites that belong to a particular country or region. Each ccTLD is managed by an organization within that country, often called a national registry.

Also Read: What is a Top Level domain? | Everything You Need to Know TLDs
2. History of ccTLDs
The history of ccTLDs (country-code top-level domains) dates back to the early days of the Internet when the Domain Name System (DNS) was created. DNS was introduced by Paul Mockapetris in 1983 and included top-level domains (TLDs). By 1984, the ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 standard provided two-letter country codes, which formed the basis for ccTLDs. The first ccTLDs, such as .us (United States), .uk (United Kingdom), and .de (Germany), were authorized in 1985.
Throughout the late 1980s and 1990s, the use of ccTLDs expanded as more countries connected to the Internet. Each country had a national registry to manage its ccTLDs. Initially, the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) oversaw the assignment of ccTLDs. In 1998, the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) was established to oversee the global DNS.
The 2000s saw continued growth of ccTLDs, and into the 2010s. Today, ccTLDs are important for national identity, branding, and localized content on the internet.
3. Why Do ccTLDs Matter?
ccTLDs (Country Code Top-Level Domains) are important for a number of reasons, including increasing trust and authority, boosting local SEO, and protecting your brand.
3.1. Increased Trust and Authority
Using a ccTLD makes your website more trustworthy to local users. When people see a domain extension that is familiar to their country, such as .uk for the United Kingdom or .de for Germany, they are more likely to trust the content and services on your website. This is especially important for businesses and organizations that want to build a strong local presence and build trust in the region.
3.2. Local SEO Boost
ccTLDs can improve your website’s SEO for local searches. Search engines like Google use ccTLDs as a signal that a website is intended for users in a particular country. This can help a website rank higher in relevant search results in that region. By using a ccTLD, businesses can target the right audience and increase their visibility in local search results, attracting more organic traffic from users in that country.
3.3. Brand Protection
Registering a ccTLD helps protect a brand by preventing others from using the same domain name in different countries. This is important for businesses that operate in multiple regions, ensuring brand consistency and preventing misuse or confusion. By protecting a brand name across multiple ccTLDs, companies can maintain their reputation and avoid issues related to domain squatting or domain name conflicts.
Also Read: The Value of Domain Names: Choosing the Right Domain for Your Website
4. What is the difference between a ccTLD and a gTLD?
Here is a comparison table between ccTLDs and gTLDs to clarify the differences between them:
| ccTLD (Country Code Top Level Domain) | gTLD (Generic Top Level Domain) | |
| Definition | Two-letter domain extensions for specific countries or territories. | Three-letter or more domain extensions, not associated with any specific country. |
| Purpose | Indicates a specific geographic location or country. | Intended for general use on the internet, representing a wide variety of websites and industries. |
| Examples | .us (United States), .vn (Viet Nam), .de (Germany), .jp (Japan), .in (India) | .com (commercial), .org (organization), .net (network), .edu (education), .gov (government), .info (information) |
| Administration | Administered by a designated authority in the respective country (national registry). | Administered by various organizations, often overseen by ICANN. |
| Usage | For businesses, organizations, and individuals who want a local presence. | For entities that want a global presence, suitable for many different types of websites. |
This table outlines the key differences between ccTLDs and gTLDs, making it easy to compare them in terms of definition, purpose, examples, management and usage.

5. Country code top-level domain list
Here’s a list of some common country code top-level domains (ccTLDs) along with their corresponding countries or territories:
| ccTLD | Country/Territory |
| .us | United States |
| .uk | United Kingdom |
| .ca | Canada |
| .de | Germany |
| .fr | France |
| .jp | Japan |
| .cn | China |
| .in | India |
| .au | Australia |
| .br | Brazil |
| .ru | Russia |
| .za | South Africa |
| .it | Italy |
| .es | Spain |
| .nl | Netherlands |
| .se | Sweden |
| .no | Norway |
| .dk | Denmark |
| .fi | Finland |
| .pl | Poland |
| .ch | Switzerland |
| .be | Belgium |
| .at | Austria |
| .sg | Singapore |
| .hk | Hong Kong |
| .kr | South Korea |
| .tw | Taiwan |
| .my | Malaysia |
| .ph | Philippines |
| .ae | United Arab Emirates |
| .sa | Saudi Arabia |
| .eg | Egypt |
| .tr | Turkey |
| .il | Israel |
| .gr | Greece |
| .cz | Czech Republic |
| .hu | Hungary |
| .ro | Romania |
| .bg | Bulgaria |
| .sk | Slovakia |
| .lt | Lithuania |
| .lv | Latvia |
| .ee | Estonia |
| .si | Slovenia |
| .mt | Malta |
| .cy | Cyprus |
| .pt | Portugal |
| .mk | North Macedonia |
| .ba | Bosnia and Herzegovina |
| .rs | Serbia |
| .me | Montenegro |
| .ws | Western Samoa |
| .tv | Tuvalu |
This list includes a range of ccTLDs from around the world, each representing a specific country or territory.
Also Read: What is a root domain? | Why does a root domain matter?
6. How to Choose the Right ccTLD
When choosing the right ccTLD (country-code top-level domain), you should consider the following:
6.1. Target Market
The most important thing when choosing a ccTLD is to understand your target market. If your website focuses on a specific country or region, choosing a corresponding ccTLD will help increase relevance and appeal to a local audience. For example, if you target customers in Canada, using a .ca domain will help build trust and brand identity locally.
6.2. Brand Image
Your ccTLD should reflect your brand image and strategy. A suitable ccTLD can highlight your presence and commitment in a specific region, helping to build brand credibility in that region. Make sure the ccTLD supports your brand identity and doesn’t confuse or detract from your message.
6.3. Availability
Before you decide, check to see if the domain name you want is available. Popular domain names may already be registered, so you may need to look for variations or other names. Make sure to choose a memorable and relevant domain name to build a strong online presence.
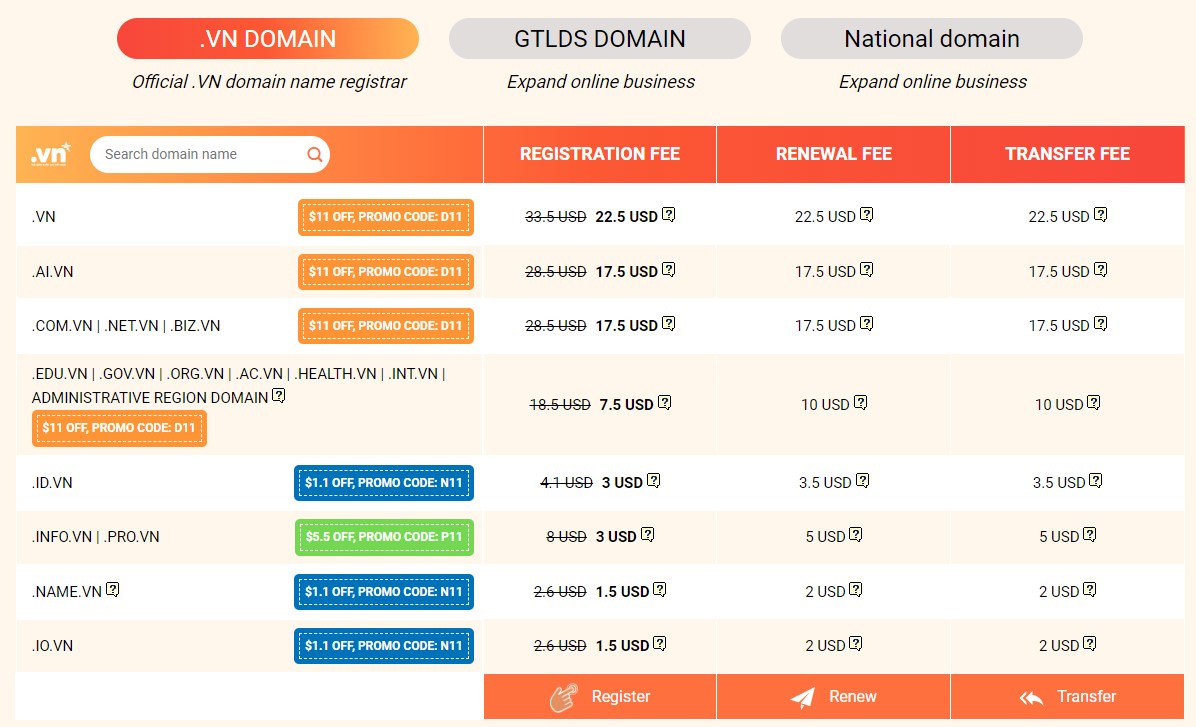
6.4. Cost
ccTLDs can cost differently depending on registration fees, renewal fees, and additional services from domain registrars. Consider your budget and calculate the total cost of ownership, including management and privacy fees. Choose a ccTLD that fits your budget and meets your local presence and branding needs.
Carefully considering these factors will help you choose the right ccTLD for your website or business.

Also Read: What is Domain Privacy? | Do you need Domain Privacy?
7. How to Register a CCTLD
Registering a ccTLD (country code top-level domain) involves a few basic steps. Here is a simple guide to walk you through the process:
7.1. Choose a Domain Name
Choose a domain name that truly reflects your business, brand, or personal identity. Make sure it is memorable, easy to spell, and relevant to your target audience. You can also incorporate keywords related to your industry to increase relevance.
7.2. Check Availability
Use a domain name search tool to check if the domain name you want is still available with the ccTLD you choose. If the domain name is already registered, you may want to try other names or variations. Many registrars provide search tools on their websites to make it easy for you to check.
7.3. Select a Registrar
Find a reputable domain name registrar that services your country’s ccTLD. Make sure the registrar has good customer support, security features, and additional services like privacy protection. Check to see if they have the authority to register domain names for the ccTLD you want.
Also Read: What is a Domain Registrar? | Function of a Domain Registrar
7.4. Complete Registration
Provide the necessary information to the registrar, including your chosen domain name, contact information, and any required documents. Pay the registration fee to complete the process. Depending on the ccTLD, you may need to provide additional documents or meet specific requirements.
7.5. Domain Management
Once you register, you will have access to a domain management dashboard through your registrar. Use this dashboard to configure DNS settings, renew your domain name, update contact information, and perform other domain-related tasks. Check your renewal date regularly to avoid losing ownership of your domain name.
Selecting a domain name, checking availability, selecting a registrar, completing registration, and managing your domain name will help you successfully register and maintain a ccTLD for your website or business.
8. FAQs
8.1. Can I use multiple ccTLDs?
Yes, you can absolutely use multiple ccTLDs (country-code top-level domains) for your website or business. Here’s why and how to manage multiple ccTLDs:
- Geo-Targeting: If your business operates in multiple countries, using a separate ccTLD for each region (like .uk for the UK, .de for Germany) helps you reach and serve local customers more effectively. This can also improve local SEO.
- Brand Protection: Registering multiple ccTLDs helps protect your brand from domain hijacking or unauthorized use. By owning relevant domain names in multiple countries, you protect your online reputation.
- Local Presence: Using the right ccTLD for each region helps your business appear locally based, which builds trust with customers in those areas.
- Domain Strategy: Multiple ccTLDs can be part of your overall strategy, such as redirecting users to regional websites or using different ccTLDs for different products or services.
How to Manage Multiple ccTLDs
- Centralized Management: Use a domain management service or registrar that allows you to manage multiple ccTLDs from a single dashboard. This simplifies domain name management, renewals, and configurations.
- Brand Consistency: Make sure your branding and messaging are consistent across all ccTLDs. Your website content should be relevant to each region, while still maintaining a consistent brand identity.
- SEO Considerations: Optimize each ccTLD for its respective region by using local content, relevant keywords, and addressing the unique needs of each audience.
- Renewals and Security: Track the renewal dates of each domain and ensure they are always up to date. Use security measures like privacy protection and domain monitoring to avoid loss of ownership or unauthorized access.
Using multiple ccTLDs can help you expand your global reach, improve local targeting, and protect your brand, creating huge benefits for businesses and individuals.
8.2. Do I need a ccTLD for every country I want to target?
You don’t have to use a ccTLD (country-code top-level domain) for every country you want to target, but using a ccTLD can provide benefits depending on your strategy. Here’s when you should consider using a ccTLD and alternative strategies:
When to Use a ccTLD
- Build a Local Presence: If you want to build a strong presence in specific countries, using a country-specific ccTLD (like .fr for France and .de for Germany) can help boost trust and connect with local users.
- Improve Local SEO: ccTLDs help with search engine optimization (SEO) by clearly indicating that your content is geared toward a specific region. This can help you rank higher in local search results.
- Brand Protection: Registering multiple ccTLDs helps protect your brand from misuse or hijacking. This prevents others from registering similar domain names in different regions.
Alternative Strategies
- Subdomains: Instead of using multiple ccTLDs, you can use subdomains (like uk.example.com) or subdirectories (like example.com/uk) to target different countries. This allows you to manage content from a single domain while still serving different regions.
- Geo-Targeted gTLDs: You can also use generic top-level domains (gTLDs) like .com or .net, combined with a geo-SEO strategy and localized content to serve different regions. For example, a .com domain with geo-targeted content and content can be as effective as ccTLDs.
- Country-Specific Content: On a single domain, you can create country-specific content and use SEO techniques to reach different regions. This approach is often easier to manage and more cost-effective than maintaining multiple ccTLDs.
Factors to Consider
- Budget: Managing multiple ccTLDs can be more expensive due to registration and renewal costs. Consider your budget to decide if this approach is right for you.
- Complexity: Managing multiple domains can be more complex in terms of administration, SEO, and content. Make sure you have the resources to handle this complexity.
- Strategic Goals: Consider your strategic goals and the importance of a local presence. If building local authority and SEO is important, a ccTLD may be a good choice.
Using a ccTLD can be a big benefit for local targeting and brand protection, but alternative strategies like subdomains, subdirectories, or gTLDs can be just as effective. Choose the approach that fits your business goals, budget, and management capabilities.
Also Read: What is Domain Backorder? | Everything you need to know
8.3. What if my desired ccTLD is already taken?
If the ccTLD you want is already registered, you still have other options to consider:
Explore Domain Name Variations
If the domain name you want is already registered, think about variations of the domain name. You can add keywords, use abbreviations, or combine numbers to find an available domain name. For example, if example.co.uk is already registered, you can try example-online.co.uk or example1.co.uk.
Consider Alternative ccTLDs
Consider other ccTLDs that might serve your target market. If .us is already taken, you can consider other ccTLDs such as .net or .co, if they fit your brand.
Use gTLDs
Instead of a ccTLD, you can choose a gTLD like .com, .net, or .info, which are popular and can help build a global brand. You can also explore newer gTLDs that are relevant to your industry, such as .tech, .shop, or .design.
Negotiate with the Current Owner
If the domain name you want is already registered, you can try contacting the current owner to negotiate buying or leasing the domain name. Tools like WHOIS can help you find their contact information.
Use Other Domain Strategies
If you can’t get the ccTLD you want, consider using a subdomain to target specific regions from a main domain.
Track Availability
If you don’t need it right away, you can track the status of the ccTLD you want. Some services can notify you when the domain becomes available again.
If the ccTLD you want is already taken, you can try domain name variations, consider other ccTLDs or gTLDs, contact the current owner, or use other domain strategies like subdomains and subdirectories. Choose the option that best fits your branding needs and budget.

8.4. Are CCTLDs suitable for global businesses?
Using a ccTLD (country-code top-level domain) can provide benefits for global businesses, including:
- Local presence: Helps build trust in specific countries.
- Local SEO: Improves search rankings in target regions.
- Brand protection: Prevents misuse and keeps brands from being infringed upon.
- Customer trust: Builds trust with consumers in local areas.
However, there are some factors to consider
- Management complexity: Managing multiple ccTLDs can be difficult and expensive.
- Cost: Registering and renewing ccTLDs for multiple countries can increase costs.
- Duplicate content: Care must be taken with content management and SEO to avoid duplicate issues.
- Alternative strategy: Using a global gTLD along with a subdomain or subdirectory can be a simpler and more cost-effective option.
8.5. Can I transfer my website from a gTLD to a CCTLD?
You can move your website from a gTLD (generic top-level domain) to a ccTLD (country-code top-level domain) by following these steps:
- Choose and register a ccTLD: Choose a ccTLD that matches your target country (like .uk, .de). Register the ccTLD through a reputable domain registrar.
- Backup your website: Make sure to back up all your website files, databases, and important data before making any changes.
- Update DNS settings: Set up the DNS settings for the new ccTLD to point to your hosting server. You will need to configure records like A, CNAME, etc.
- Content Migration: Move all content from the gTLD to the new ccTLD. This includes copying files and databases to the new domain’s hosting environment.
- Set up redirects: Set up 301 redirects from the old gTLD to the new ccTLD to ensure visitors and search engines are automatically redirected to the new domain. This helps maintain SEO rankings and user experience.
- Update internal links: Check and update all internal links on your site so they point to the new ccTLD.
- Notify search engines: Update your sitemap and notify search engines of the domain change using tools like Google Search Console.
- Monitor and Test: Monitor the new site to detect and fix any issues. Make sure that redirects are working properly and that the site is stable.
By following these steps, you can efficiently convert your site from gTLD to ccTLD, minimizing downtime and maintaining SEO performance.
Also Read: What is Transfer Domain? & How to Transfer a Domain?
8.6. Do I need to use a local hosting provider for a CCTLD website?
You are not required to use a local hosting provider for a website with a ccTLD, but there are some benefits to doing so. Here are the advantages and when local hosting may not be necessary:
Advantages of using a local hosting provider
- Faster load times: Hosting your website with a local provider can reduce latency, making your site load faster for users in that country.
- Good for local SEO: Search engines may favor sites hosted in the same country as the ccTLD, helping to improve your local search rankings.
- Compliance with local regulations: Local providers are often familiar with regional regulations and can better assist you with local requirements.
- Local Customer Support: Using a local hosting provider can make it easier for you to contact and get support from customer service in the same region.
When Local Hosting May Not Be Necessary
- Global Audience: If your site serves a global audience and speed is not affected much, local hosting may not be necessary.
- Quality Global Hosting Providers: Many global providers have data centers in multiple locations and offer fast service, which can reduce the need for local hosting.
- Cost and Convenience: Depending on your budget and needs, global providers may offer better prices or better features than local hosting.
While local hosting can improve your performance and SEO, it is not always necessary. Consider your audience, performance needs, and budget to decide whether to use local storage, or whether you can use a global provider.
8.7. Will a CCTLD automatically improve my website’s ranking?
Using a ccTLD (country code top-level domain) can help improve your site’s local search rankings, but it’s not the only factor that determines it. Here’s how ccTLDs can affect SEO and what else to look out for:
- Local SEO: A ccTLD indicates that your site is targeting a specific country, which can help it appear in searches in that country. For example, a .uk domain name can help your site rank higher in searches in the United Kingdom.
- Trust and engagement: Users in your target country may trust and engage more with a site with the appropriate ccTLD. This can lead to increased traffic and improved rankings indirectly.
- Geo-Targeting: ccTLDs help search engines better understand the geographic target of your site, which helps you appear in searches related to that country.
Other Factors to Improve Rankings
- Quality Content: Content must be quality, relevant, and localized to the needs of local users. Good content is the most important factor in improving rankings.
- Backlinks: Links from reputable and relevant sites in the region can increase the trust and rankings of your site. Build a strong link profile.
- Technical SEO: Technical factors such as page speed, mobile usability, and meta tags are also important to improve rankings.
- User Experience: Make sure your website is easy to use, easy to navigate, and provides a positive user experience.
- Competitor Analysis: Understand and analyze your competitors in your target country. A ccTLD alone is not enough to guarantee high rankings if your competitors have better SEO strategies.
ccTLDs can help improve local search rankings and user trust, but they are not the only factor. For optimal results, combine the use of ccTLDs with a comprehensive SEO strategy that includes quality content, backlinks, technical SEO, and good user experience.
Also Read: What is Whois? | Everything You Need To Know Whois
9. Conclusion
In summary, what is a ccTLD? ccTLDs (country-code top-level domains) are an important tool for building an online presence in a specific country. They help increase trust and improve visibility on search engines in that region.
Using ccTLDs allows businesses and individuals to easily indicate their geographic focus, build trust with local users, and optimize SEO for their target markets. While ccTLDs have many benefits, you should also consider your overall domain strategy, including the cost and complexity of management. Using ccTLDs effectively can be a significant contributor to online success and engagement with local markets. Find out more articles at our Blog and don’t hesitate to contact us for support:
- Email: support@vinahost.vn
- Hotline: 1900 6046
- Livechat: https://livechat.vinahost.vn/chat.php
What is Registry Lock? | Protect Domain with Registry Lock
What is domain .com.vn? | Overview of domain names .com.vn


 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt English
English 简体中文
简体中文