In the intricate web of computer networks, the DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) play a role in shaping the connectivity and communication between devices. But what is a DHCP server, why use DHCP and how does DHCP work? This article of VinaHost will illuminate the essence of DHCP servers and delve into their inner workings. From the dynamic allocation of IP addresses to the orchestration of network configurations, start a journey to uncover the hidden mechanisms that empower DHCP servers to seamlessly integrate devices into the fabric of modern networks.
1. What is a DHCP Server?
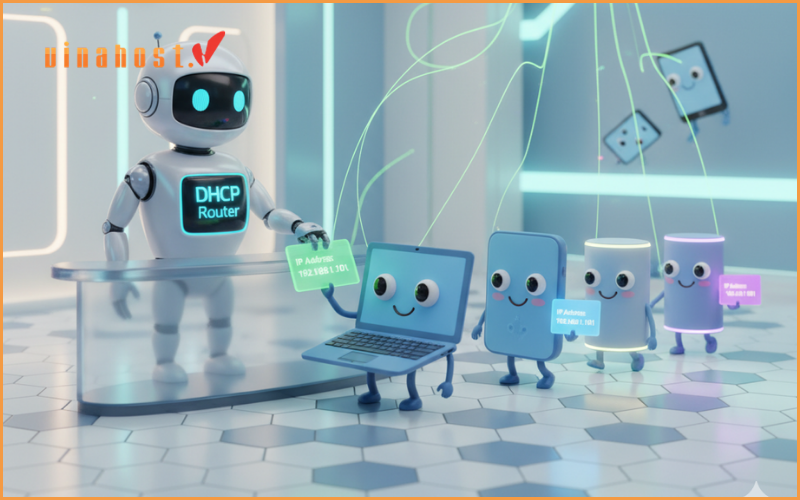
What is DHCP server and how it works? A DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server is a network server which assigns IP addresses and other network configuration settings automatically to devices on a local network.
When a device like a smartphone or computer, connects to a network, it sends a request to the DHCP server for an IP address.
The DHCP server then assigns a unique IP address from a pool of available addresses, along with additional configuration parameters such as subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server addresses.
dhcp server definition: A DHCP server acts like a landlord, automatically assigning IP addresses and other network settings to these devices whenever they connect to the network.
DHCP servers streamline the process of network configuration by dynamically assigning IP addresses to devices as they connect to the network, eliminating the need for manual configuration. This simplifies network administration and makes sure that efficient use of IP address space.
DHCP servers also support IP address lease management, allowing them to reclaim and reallocate IP addresses that are no longer in use, optimizing address allocation and preventing address conflicts. Overall, DHCP servers play a crucial role in simplifying network management and facilitating seamless connectivity in both home and enterprise environments.
Also read: [2024] What is a Cloud Server? | How does a Cloud Server work?
2. Why is DHCP Server important? Why use DHCP server?
- Automatic IP address assignment: DHCP servers automate the process of assigning IP addresses to devices on a network. This eliminates the need for manual configuration of IP addresses, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors, especially in large networks.
- Efficient address management: DHCP servers manage IP address allocation efficiently by dynamically assigning addresses from a pool of available addresses. This helps prevent address conflicts and ensures that IP addresses are utilized optimally.
- Simplified network administration: By automating IP address assignment and management, DHCP servers simplify network administration tasks. Network administrators don’t have to manually configure IP addresses for each device, reducing administrative overhead and allowing them to focus on other aspects of network management.
- Flexibility and scalability: DHCP servers support dynamic IP address allocation, which means that devices can obtain temporary IP addresses that are released when they are no longer needed. This flexibility allows networks to scale easily to accommodate new devices without requiring manual intervention.
- Centralized configuration: DHCP servers provide a centralized point for configuring network parameters such as subnet masks, default gateways, DNS server addresses, and other settings. This ensures consistency across the network and simplifies configuration management.
- Support for mobile devices: DHCP servers are essential for mobile devices such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets that frequently connect to different networks. These devices can obtain IP addresses dynamically from DHCP servers, enabling seamless connectivity without manual intervention.
- Security: Some DHCP servers offer advanced security features, such as allowing administrators to reserve specific IP addresses for authorized devices.
3. How Does a DHCP Server Work?
Now you know what is dhcp server, but how does it work? A DHCP server acts like an automated landlord in a network, dynamically assigning IP addresses and other network settings to devices that connect.
What is DHCP server how it works: By automating IP address assignment and network configuration, DHCP servers ensure a smooth and efficient network experience for all connected devices.
The process typically involves the following steps:
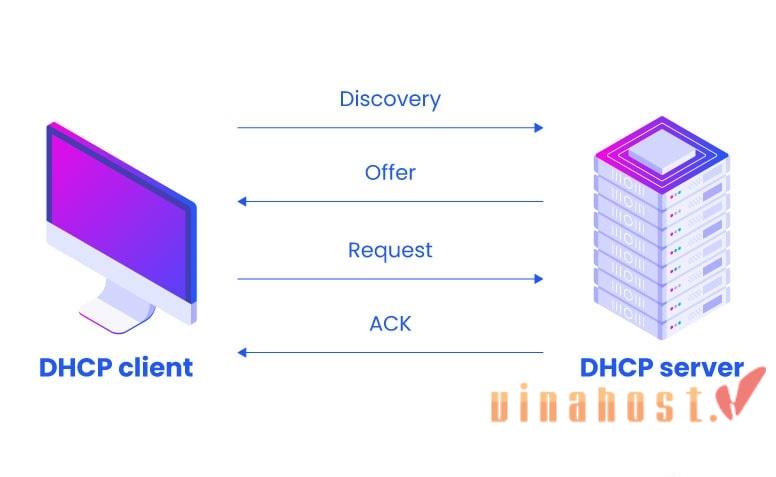
- Device discovers the network: When a new device (computer, phone, tablet, etc.) joins the network, it broadcasts a message called a DHCPDISCOVER packet. This packet acts like the device raising its hand, announcing its presence and requesting an IP address.
- DHCP server offers an address: The DHCP server hears the DHCPDISCOVER packet and checks its pool of available IP addresses. If an address is free, the server sends a DHCPOFFER packet back to the device. This packet includes a proposed IP address, subnet mask (defines the network segment), default gateway (the router’s IP address), and sometimes additional configuration details like DNS server addresses.
- Device selects and acknowledges: The device receives DHCPOFFER packets potentially from multiple DHCP servers on the network (if there are redundant servers for backup). It can choose the first offer or consider factors like lease time before selecting one. Once it selects an offer, the device sends a DHCPREQUEST packet back to the chosen server, basically saying “Yes, I want this IP address.”
- Server leases the IP address: Upon receiving the DHCPREQUEST packet, the server acknowledges the request by sending a DHCPACK (acknowledgement) packet to the device. This packet confirms the assigned IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and lease time (the duration for which the device can hold onto the IP address).
- Device configured and connected: With the DHCPACK packet, the device now has all the necessary network configuration information. It configures itself with the assigned IP address and other settings, allowing it to communicate and access resources on the network.
- Lease renewal (Optional): The DHCP lease is a temporary assignment. Before the lease expires, the device can send a DHCPREQUEST packet again to renew the lease for the same IP address. The server can choose to renew or offer a different address depending on its configuration and pool availability.
- Lease expiration and release: If the device doesn’t renew the lease on time or shuts down, the IP address is released back into the DHCP server’s pool and becomes available for other devices.
Also read: [2024] What is VPS? | Unveiling the Power Behind Virtual Private Servers
4. Advantages of DHCP Server?
4.1. Simplifies Network Management
Why use DHCP server? DHCP servers simplify network management by automating the process of IP address assignment and configuration. Instead of manually configuring IP addresses for each device on the network, administrators can rely on DHCP to handle this task automatically.
This reduces administrative overhead, minimizes the potential for human error, and streamlines network management processes.
4.2. Efficient IP Address Allocation
DHCP servers efficiently allocate IP addresses by dynamically assigning them from a pool of available addresses. This helps prevent IP address conflicts and ensures that addresses are utilized optimally.
Additionally, DHCP servers support IP address lease management, allowing them to reclaim and reallocate addresses that are no longer in use. This dynamic allocation of IP addresses improves address utilization efficiency and supports scalability as networks grow.
4.3. Centralized Configuration
DHCP servers provide a centralized point for configuring network parameters such as IP addresses, subnet masks, default gateways, DNS server addresses, and other settings.
Administrators can define these configuration parameters once on the DHCP server, and they will be automatically distributed to all devices that connect to the network. This ensures consistency across the network and simplifies configuration management tasks, especially in large or complex network environments.
5. Disadvantages of DHCP Server
If you take appropriate precautions and implementing best practices, you can leverage the advantages of DHCP servers while mitigating the associated drawbacks.
5.1. NAT
One potential disadvantage of DHCP is its reliance on NAT (Network Address Translation) in some network configurations. NAT is commonly used to map multiple private IP addresses to a single public IP address for outbound internet access.
While NAT can help conserve IPv4 address space and enhance network security by hiding internal IP addresses from external networks, it can also introduce complexity and limitations, particularly in large or complex network environments.
5.2. Security Issues
DHCP servers can introduce security vulnerabilities if not properly configured or secured. For example, rogue DHCP servers can be set up maliciously to distribute incorrect or unauthorized network configuration settings, potentially leading to network disruptions or security breaches.
Additionally, DHCP-based attacks such as DHCP spoofing or DHCP starvation can be used to overwhelm DHCP servers, exhaust available IP addresses, or intercept network traffic. Proper security measures, such as DHCP snooping, DHCP authentication, and access control lists (ACLs), are necessary to mitigate these risks.
5.3. Failure
Like any network service, DHCP servers are susceptible to failure, which can result in disruptions to network connectivity and service availability.
If a DHCP server becomes unavailable due to hardware failure, software issues, or network problems, devices may be unable to obtain or renew IP addresses, leading to communication failures and connectivity issues.
To mitigate the impact of DHCP server failure, redundant DHCP servers can be deployed in a failover configuration to provide backup services and ensure continuous operation.
Also read: [2024] What is a Top-Level domain? | Everything You Need to Know TLDs
6. DHCP Server Components
6.1. DHCP Client
- Software on devices: Every device that needs to connect to a network using DHCP has a DHCP client software component built-in. This software is responsible for automatically requesting, obtaining, configuring, renewing, and releasing IP addresses from the DHCP server.
- Initiates communication: When a device joins the network, the DHCP client software broadcasts a DHCPDISCOVER packet to locate a DHCP server. This packet announces the device’s presence and requests an IP address.
- Maintains lease: The DHCP client manages the leased IP address throughout its assigned lifespan. It can automatically send a DHCPREQUEST packet to renew the lease before it expires or release the address back to the server pool when no longer needed.
6.2. DHCP Server
- Centralized service: The DHCP server acts as the main authority for IP address assignment and network configuration within a specific scope or network segment. It manages a pool of IP addresses and provides them to DHCP clients upon request.
- Responds to requests: The DHCP server listens for DHCPDISCOVER packets from DHCP clients. It verifies the availability of IP addresses in its pool and sends DHCPOFFER packets back to clients with proposed IP addresses, subnet mask, default gateway, and potentially other settings.
- Lease management: The server keeps track of leased IP addresses and their corresponding devices. It acknowledges lease requests with DHCPACK packets, confirming the assigned configuration and lease time. The server can also reclaim addresses upon lease expiration or release.
- Configuration options: Administrators can configure various aspects of the DHCP server, such as the IP address pool, lease times, security settings, and reservation of specific IP addresses for critical devices.
6.3. DHCP Relay Agent
- Network bridge: In large networks with segmented subnets that may not be reachable by a single DHCP server, DHCP relay agents are deployed. These agents forward DHCPDISCOVER packets from clients in one subnet to the DHCP server in another subnet. They essentially act as bridges, enabling communication between clients and the server across network boundaries.
- Packet forwarding: The relay agent receives DHCPDISCOVER packets from clients and modifies them slightly before forwarding them to the DHCP server. It might add information about the subnet where the request originated to assist the server in assigning appropriate IP addresses.
- Transparent operation: Ideally, the presence of a DHCP relay agent is transparent to DHCP clients. They send their requests as usual, and the relay agent handles the communication with the server in the background.
7. The Future of DHCP

The future of DHCP is likely to be characterized by advancements in IPv6 adoption, enhanced security features, integration with SDN architectures, support for IoT devices, and the emergence of cloud-based DHCP services.
These developments will help ensure the continued relevance and effectiveness of DHCP in dynamically configuring and managing IP addresses and network resources in evolving networking environments.
- AI-Driven optimization: Artificial intelligence (AI) could potentially play a role in optimizing DHCP server performance. AI could analyze network usage patterns and dynamically adjust lease times or address allocation to improve efficiency.
- IPv6 adoption: As the depletion of IPv4 addresses accelerates, the adoption of IPv6 is expected to increase. DHCPv6, the DHCP protocol for IPv6 networks, will play a crucial role in dynamically assigning IPv6 addresses and configuration parameters to devices. The future of DHCP may involve greater emphasis on DHCPv6 implementation and support to facilitate the transition to IPv6 and ensure efficient address allocation in IPv6-enabled networks.
- Enhanced security features: DHCP servers and clients may incorporate additional security features to mitigate the risk of DHCP-based attacks, such as DHCP spoofing, DHCP starvation, and rogue DHCP servers. Future DHCP implementations may include mechanisms for DHCP authentication, DHCP snooping, and DHCPv6 Secure Neighbor Discovery (SEND) to enhance security and prevent unauthorized access and network disruptions.
- Integration with software-defined networking (SDN): DHCP may become more closely integrated with Software-Defined Networking (SDN) architectures to support dynamic network provisioning, automated configuration management, and policy-based network control. SDN controllers may leverage DHCP information to dynamically configure network devices, enforce network policies, and optimize network performance based on real-time traffic and user requirements.
- IoT (Internet of Things) support: With the proliferation of IoT devices, DHCP will continue to play a crucial role in dynamically assigning IP addresses and configuration parameters to IoT devices connecting to the network. Future DHCP implementations may include optimizations for handling large numbers of IoT devices, support for IoT-specific protocols and standards, and integration with IoT management platforms to streamline device provisioning and management.
- Cloud-Based DHCP services: Cloud-based DHCP services may gain popularity as organizations seek to simplify network management, improve scalability, and reduce infrastructure costs. Future DHCP solutions may leverage cloud-based architectures to provide centralized management, dynamic scaling, and high availability, enabling organizations to deploy and manage DHCP services more efficiently across distributed and hybrid cloud environments.
Also read: [2024] The Value of Domain Names: Choosing the Right Domain for Your Website
8. FAQs
8.1. What happens if the DHCP server goes down?

- IP address exhaustion: DHCP clients may continue to use their current IP addresses until the alease duration expires or they disconnect from the network. However, if new devices join the network or existing devices request IP address renewals while the DHCP server is down, they will be unable to obtain new IP addresses. This can lead to IP address exhaustion if the available addresses are all in use, preventing new devices from connecting to the network.
- Inability to renew leases: DHCP clients may be unable to renew their IP address leases when they expire, leading to network connectivity issues. Without a functioning DHCP server to respond to lease renewal requests, clients may lose their IP addresses and be unable to communicate on the network until the DHCP server is restored.
- Manual IP configuration: In the absence of DHCP services, network administrators may need to configure IP addresses manually on devices to restore network connectivity. This can be a time-consuming and error-prone process, especially in large or complex networks with many devices.
- Service disruption: DHCP-related services such as DNS (Domain Name System) and NTP (Network Time Protocol) may also be affected if the DHCP server is down. For example, DNS resolution may fail if DNS server addresses are not dynamically assigned by the DHCP server, and network time synchronization may be disrupted if NTP server addresses are not provided through DHCP.
- Loss of centralized configuration: DHCP servers typically provide centralized configuration management for network parameters such as subnet masks, default gateways, and DNS server addresses. In the absence of DHCP services, devices may revert to default or previously configured settings, leading to inconsistencies and potential security vulnerabilities.
8.2. Is DHCP limited to assigning IP addresses only?
No, DHCP is not limited to assigning IP addresses only. Alongside IP address allocation, DHCP servers can provide additional network configuration parameters to DHCP clients, such as subnet masks, default gateways, DNS server addresses, domain names, hostnames, time server addresses, domain search lists, and WINS server addresses.
These parameters streamline network configuration and management, ensuring efficient and reliable network connectivity across devices.
8.3. Can I assign a static IP address to a device while using a DHCP server?
Yes, you can assign a static IP address to a device even if you are using a DHCP server. This is known as a static IP reservation or DHCP reservation. With a static IP reservation, you configure the DHCP server to always assign the same IP address to a specific device based on its MAC address (Media Access Control address). This ensures that the device receives a consistent IP address every time it connects to the network, similar to a manually configured static IP address.
Static IP reservations offer the convenience of centrally managing IP address assignments through the DHCP server while providing the stability and predictability of static IP addressing for certain devices, such as servers, printers, or network devices. This approach allows you to maintain a mix of dynamically and statically assigned IP addresses on your network, providing flexibility and ease of management.
8.4. Can DHCP be used in both IPv4 and IPv6 networks?

In IPv4 networks, DHCP is commonly used to dynamically assign IP addresses, subnet masks, default gateways, DNS server addresses, and other configuration parameters to DHCP clients. It simplifies network management by automating the process of IP address allocation and centralizing configuration management.
In IPv6 networks, DHCPv6 fulfills a similar role by dynamically assigning IPv6 addresses and configuration parameters to DHCPv6 clients. DHCPv6 can provide IPv6 addresses, prefix delegation information, DNS server addresses, domain search lists, and other network configuration options to clients. It enables efficient and centralized management of IPv6 addressing and configuration, ensuring seamless connectivity and interoperability in IPv6-enabled networks.
8.5. Do all network devices support DHCP?
No, not all network devices support DHCP.
While DHCP is widely supported by most modern network devices, not all devices may support DHCP, particularly in specialized or embedded systems where network configuration options are limited.
Devices that typically use DHCP:
- Computers (desktops, laptops): Most personal computers and laptops rely on DHCP to automatically obtain IP addresses and network configurations. This simplifies user experience and network management.
- Smartphones and tablets: Mobile devices often utilize DHCP to connect to Wi-Fi networks at home or public hotspots. This allows them to seamlessly access the internet without manual configuration.
- Gaming consoles: Modern gaming consoles frequently use DHCP to connect to the internet for online gaming and updates.
- Smart home devices: Many smart home devices like speakers, thermostats, and lights rely on DHCP to obtain IP addresses for communication and internet connectivity.
- Printers (network printers): Network printers can leverage DHCP to receive an IP address, allowing them to be shared and accessed by multiple devices on the network.
Devices that often use static IP addresses:
- Routers: Routers typically have a static IP address assigned within the network they manage. This ensures consistent addressing for other devices to connect and communicate with the router.
- Servers: Network servers like web servers, file servers, and email servers usually have static IP addresses for reliable identification and accessibility on the network.
- Network switches: Switches often have pre-configured static IP addresses for management purposes, allowing network administrators to access and configure them remotely.
- Access points: Wireless access points often have static IP addresses to provide a consistent connection point for devices within their wireless range.
- Printers (print servers): Print servers that manage multiple printers on a network might require static IP addresses for proper operation.
Also read: [2024] What is a Game Server? | How Game Servers Work?
9. Conclusion
I think this post has help youanswer the question What is a DHCP Server, why use DHCP server an how does DHCP work. By understanding the essence of DHCP servers, both novice users and seasoned network administrators can gain insights into the vital role they play in enabling seamless connectivity and efficient network.
Read more:


 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt English
English 简体中文
简体中文