Linux VPS is an advanced server technology, attracting many customers due to its high security, flexibility, and stable performance. So what is Linux VPS? How to use it and how to choose a reputable Linux VPS service provider? The following article by VinaHost will address your questions.
1. What is Linux VPS?
VPS stands for Virtual Private Server. It is a virtual server created by partitioning a physical server into multiple different VPS.
Each virtual server functions similarly to a dedicated server, running as a shared resource from the original physical server. Each VPS is a completely separate system, from CPU, RAM, HDD storage, IP address to operating system. Users have full root access and can restart the system anytime.
Compared to other types of servers, VPS offers the following advantages:
- Low cost: VPS is cheaper than dedicated servers, as you only pay for the resources you use.
- Flexibility: You can customize resources to suit your usage needs.
- Easy management: You can access and manage VPS through a web interface or SSH.
VPS is a good choice for businesses or individuals needing a highly flexible, efficient, and cost-effective server solution.

Linux VPS is a virtual server installed with the Linux operating system.
Specifically, Linux is an open-source, free operating system with many powerful features, such as:
- High security: Linux is designed with high security features to protect your data from network attacks.
- Stable operation: Linux has high stability and can run continuously for many years without issues.
- Good performance: Linux offers high performance, capable of running heavy applications and websites without lagging.
Here are some popular Linux operating systems used on VPS:
- CentOS
- Ubuntu
- Debian
- Fedora
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux
Each Linux operating system has its own advantages and disadvantages. You should choose the Linux operating system that suits your usage needs.
Also Read: What is VPS? | Unveiling the Power Behind Virtual Private Servers
2. How Does a Linux VPS Work?
2.1. Virtualization technology
Linux VPS operates through virtualization technology, which allows a physical server to be divided into multiple virtual servers. This is typically achieved using hypervisor software, such as KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) or Xen. Each virtual server, or VPS, acts as an independent instance with its own set of resources and operating system.
2.2. Resource allocation on a VPS
Resources on a Linux VPS, including CPU, RAM, disk space, and bandwidth, are allocated based on the requirements of each virtual server. The physical server’s resources are partitioned and distributed among the VPS instances. This allocation is typically customizable, allowing users to adjust resource levels according to their needs.
2.3. Operating system isolation
Each Linux VPS runs its own isolated operating system instance. This means that even though multiple VPS may be running on the same physical server, they operate independently of each other. They have their own file systems, processes, users, and configurations. This isolation ensures that activities on one VPS do not affect the others, providing security and stability to each virtual server.
Also Read: What is a Server? Understanding the Backbone of Modern Technology
3. Types of Linux VPS
3.1. Unmanaged VPS
In an unmanaged VPS, you’re essentially given a blank slate. The hosting provider provides the server for you, installs the operating system (in this case, Linux), and gives you root access. From there, you’re responsible for everything: installing software, configuring security settings, monitoring, updates, backups, and troubleshooting. This option is typically chosen by users who have the technical expertise to manage a server independently.
Utilizing unmanaged VPS hosting offers several advantages:
- Economical: Unmanaged VPS hosting tends to be more budget-friendly compared to managed VPS hosting, as users handle server management themselves.
- Empowerment: Users wield total control over the server, enabling customization tailored to their specifications without constraints from the hosting provider.
- Adaptability: Unmanaged VPS hosting boasts high adaptability, allowing users to tailor it precisely to their website’s or application’s requirements.
Nevertheless, there are drawbacks associated with unmanaged VPS hosting:
- Technical proficiency required: Advanced technical expertise, including server administration and Linux operating systems knowledge, is necessary for effective management.
- Time-intensive: Server management can consume significant time, particularly for users lacking experience in administrative tasks.
- Support deficiency: Unmanaged VPS hosting lacks server management services or technical support, placing the burden of issue resolution squarely on users.
3.2. Managed VPS
With a managed VPS, the hosting provider takes care of the server management tasks for you. This includes initial setup, software installation, security patches, monitoring, backups, and troubleshooting. Managed VPS plans often come with a control panel interface for easier management, and technical support is provided to assist with any issues that may arise. Managed VPS is a good option for users who prefer to focus on their website or application rather than server administration.
Managed VPS hosting offers several advantages:
- Technical assistance: Hosting providers offer 24/7 technical support, resolving issues promptly for users.
- Time efficiency: Managed hosting spares users from server management responsibilities, enabling them to allocate time and resources elsewhere.
- Enhanced security: Managed hosts deliver robust security measures and regular updates to safeguard the server.
- Convenience: Managed hosts handle all server management tasks, enabling users to focus on their business or website.
However, there are drawbacks associated with managed VPS hosting:
- Expense: Managed VPS hosting typically incurs higher costs compared to unmanaged VPS hosting.
- Control limitations: Hosting providers may impose restrictions on server customization, limiting options for users who require extensive modifications.
- Dependency: Users rely on hosting providers for technical support and maintenance, posing a challenge if the provider experiences downtime or other issues.
Read More: The difference between Managed VPS and Unmanaged VPS
3.3. Cloud VPS
Cloud VPS is a virtual private server that runs on a cloud infrastructure. Unlike traditional VPS, which typically operates on a single physical server, cloud VPS utilizes resources from a network of interconnected physical servers.

This setup offers scalability, allowing users to easily adjust their resources (such as CPU, RAM, and storage) based on their needs. Cloud VPS often comes with features like high availability, redundancy, and automatic failover, making it suitable for applications requiring high reliability and performance.
Cloud VPS hosting offers several key benefits:
- Scalability: Cloud VPS hosting allows for easy adjustment of server resources, making it suitable for businesses experiencing fluctuations in traffic or demand.
- Cost efficiency: With cloud VPS hosting, users pay only for the resources they use, making it an economical choice, especially for small businesses and startups with budget constraints.
- High availability: Cloud VPS hosting ensures high uptime by utilizing multiple servers, minimizing the risk of downtime.
- Manageability: Cloud VPS hosting is user-friendly, enabling users to manage their servers remotely and modify configurations as needed.
However, there are some drawbacks to consider:
- Security concerns: Cloud VPS hosting may not offer the same level of security as dedicated hosting, as multiple users share the same server environment.
- Limited control: Users have restricted control over the server in cloud VPS hosting, as the hosting provider manages the hardware and software infrastructure.
- Potential performance issues: Shared resources in cloud VPS hosting can lead to performance degradation if other users consume excessive resources on the same server.
Each type of VPS has its own advantages and considerations, so the choice depends on factors such as technical expertise, resource requirements, scalability needs, and budget.
Also Read: What is a Cloud Server? | How does a Cloud Server work?
4. Advantages of Using a Linux VPS
4.1. Cost-effective solution
Linux is open-source, meaning you don’t have to pay for the operating system itself. This can significantly reduce your hosting costs compared to proprietary operating systems like Windows.
A Linux VPS provides many of the features found in dedicated server hosting, but at a significantly lower cost. This makes it a perfect choice for businesses seeking greater power and resources than what shared hosting provides, without the expense of a dedicated server.
Furthermore, the setup process for a VPS is straightforward and swift compared to dedicated hosting, enabling you to launch your website promptly.
4.2. Scalability and flexibility
Linux VPS hosting provides excellent flexibility when scaling your website or application. You can easily increase resources with minimal effort and expense, and likewise, scale down resources as required, optimizing usage and cost-effectiveness.
4.3. Security and control
Linux is inherently more secure than some other operating systems due to its architecture and the open-source community’s constant vigilance in identifying and patching vulnerabilities. Additionally, Linux distributions often come with robust security features and tools built-in.
Linux VPS hosting provides users with significantly greater control and flexibility compared to shared hosting. With VPS, you enjoy root access to the server, empowering you to install any necessary applications or software for your website and configure server settings to your precise requirements.
Furthermore, Linux VPS hosting allocates dedicated resources to your website, eliminating the need to share CPU and RAM as with shared hosting. This enhances the reliability of your website and applications by reducing competition for resources.

4.4. Customization options
Linux provides extensive customization options, allowing you to tailor your VPS environment to your specific needs. You can choose from a wide range of distributions (such as Ubuntu, CentOS, Debian) and customize everything from the kernel to the software stack.
4.5. Open-source software support
Linux VPS provides robust support for open-source software, allowing users to leverage a wide range of freely available tools and applications to enhance their server functionality and meet diverse needs.
Linux has a large and active community of users and developers who contribute to its ongoing development and provide support through forums, mailing lists, and online resources. This means you can easily find help and solutions to any issues you encounter with your Linux VPS.
Overall, using a Linux VPS can offer cost savings, customization options, stability, security, performance, flexibility, and robust community support, making it an excellent choice for hosting a wide range of applications and services.
Also Read: What is a Dedicated Server? | How Does a Dedicated Server Work?
5. Disadvantages of Using a Linux VPS
5.1. Requires technical knowledge
Linux VPS typically requires a certain level of technical expertise to set up, configure, and maintain. Users need to have familiarity with the Linux operating system, command line interface, and various server technologies.
5.2. Management responsibility
Unlike managed hosting solutions where the provider takes care of server maintenance, updates, and troubleshooting, with a Linux VPS, users are responsible for managing the server themselves. This includes tasks such as installing software, configuring security settings, monitoring performance, and handling backups.
5.3. Security vulnerabilities (if not managed properly)
Linux VPS can be vulnerable to security breaches if not properly managed and secured. Users need to stay vigilant about applying security patches, configuring firewalls, implementing access controls, and regularly auditing the system for potential vulnerabilities.
Linux VPS is a flexible and cost-effective solution with many advantages, including low cost, high security, stable operation, high performance, and easy management. However, Linux VPS also has some disadvantages such as requiring knowledge and may be difficult to maintain.
6. Who Should Use a Linux VPS?
All three groups you mentioned can benefit from using a Linux VPS:
6.1. Growing businesses with increasing website traffic
As businesses grow and their website traffic increases, they often need more control, flexibility, and resources than shared hosting can provide. A Linux VPS allows them to scale their hosting environment according to their needs, ensuring reliable performance and uptime for their website.
6.2. Developers and programmers
Developers and programmers often require a customizable environment to develop, test, and deploy their applications. Linux VPS offers them full root access and the ability to install and configure any software they need, making it an ideal choice for development and testing purposes.
6.3. Users who need specific software or configurations
Some users may require specific software or configurations that are not available in shared hosting environments. With a Linux VPS, they have the freedom to install and customize their software stack according to their requirements, whether it’s for hosting a specific application, running a custom database setup, or implementing advanced security measures.
Overall, a Linux VPS provides the flexibility, control, and scalability that these groups need to meet their hosting requirements effectively.
7. Popular Linux Distributions for VPS
Linux’s modular design allows it to be tailored for specific purposes, spawning numerous distributions. Presently, more than six hundred Linux distributions are recognized. Naturally, each enjoys varying degrees of popularity among users. Over time, certain distributions have become favored for web and physical server applications. Prominent examples include CentOS, Debian, Ubuntu, and OpenSUSE.
7.1. Ubuntu
Although Ubuntu is widely recognized as a desktop Linux distribution, it also performs admirably in virtual server environments. Its widespread popularity ensures readily available support and familiarity among users.
Advantages:
- Simple to maintain with frequent updates
- Abundant availability of packages
- Strong community support
Disadvantages:
- Challenges in compatibility with Windows products
- Potential steep learning curve for certain users
7.2. CentOS/AlmaLinux
Renowned for its remarkable stability and extensive compatibility with installation packages, this Linux distribution stands out as a preferred choice for web servers. Its infrequent version updates contribute to decreased server maintenance needs.
Advantages:
- Extensive compatibility with diverse packages
- Exceptional stability
- Minimal maintenance demands
- Robust community support
Disadvantage:
- Slower adoption of new applications
7.3. Debian
Within the spectrum of Linux distributions, Debian is often regarded as a viable alternative to CentOS. CentOS is renowned for its stability and boasts a user-friendly installation and configuration process, making it an ideal choice for Virtual Private Server (VPS) deployment.
Advantages:
- Manageable remotely
- Seamless system integration
- Preconfigured packages for convenience
Disadvantages:
- Lagging behind in the latest Linux updates
- Limited enterprise-level support
7.4. Fedora
Fedora is a popular Linux distribution sponsored by Red Hat, known for its community-driven development model and its focus on innovation. It serves as a free and open-source platform for users who seek cutting-edge technologies and software.
Fedora is often used for desktop computing, but it’s also suitable for server environments. It provides a balance between stability and the latest software updates, making it a favorite among developers, enthusiasts, and users who want to explore new features in the Linux ecosystem.
Advantages:
- Cutting-edge technology
Disadvantages:
- Shorter support cycle

8. Choosing the Right Linux VPS Provider
Choosing the right Linux VPS provider requires careful consideration of several factors. Here’s a breakdown of key considerations:
8.1. Performance and Reliability
- Look for providers that offer solid-state drives (SSDs) for storage, as they provide better performance compared to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs).
- Check for uptime guarantees and read reviews to assess the provider’s reliability track record.
8.2. Pricing
- Compare pricing plans across different providers, considering factors such as CPU cores, RAM, storage, and bandwidth allocation.
- Be wary of providers offering excessively low prices, as they may compromise on performance or support.
8.3. Customer Support
- Evaluate the responsiveness and expertise of customer support by reading reviews or engaging with their support channels before making a decision.
- Look for providers offering 24/7 support through various channels like live chat, email, and phone.
8.4. Security and Privacy
- Ensure the provider offers robust security measures, such as firewalls, DDoS protection, and regular security updates.
- Look for providers with a strong commitment to privacy, including data encryption and compliance with relevant regulations (e.g., GDPR).
8.5. Server Location and Network Connectivity
- Choose a provider with data centers located close to your target audience to minimize latency and improve performance.
- Assess the provider’s network infrastructure and connectivity to ensure fast and reliable access to your VPS.
8.6. User Interface and Control Panel
- Consider the ease of use of the provider’s user interface and control panel, as it will affect your ability to manage and configure your VPS.
- Look for providers offering intuitive control panels, such as cPanel or Plesk, or robust management interfaces like SSH or a web-based dashboard.
Choosing a Linux VPS provider is crucial as it directly impacts the performance of the website. Currently, VinaHost is one of the leading VPS server providers with top quality in Vietnam. VinaHost meets all the criteria for reliability, service quality, and pricing.
With nearly 15 years of experience in the field, VinaHost has provided services to millions of users both domestically and internationally, meeting the needs of websites requiring fast data access speeds, high stability, and large resource usage. When renting a VPS at VinaHost, customers will receive complimentary utilities and 24/7 technical support services.
- Outstanding speed with NVMe SSD standard (RAID 10)
- Ensuring 99.9% Uptime with tier 3 Data Center
- Supporting Docker execution on VPS, full KVM virtualization
- Using a user-friendly and intuitive Virtualizor management interface
- Activating VPS immediately after customer payment
- Free weekly scheduled backups
- Free DirectAdmin.
- Supporting IPv6.
Additionally, we also provide:
- Server Vietnam
- Colocation in Vietnam
- Server Cambodia
- Cloud VPS Cambodia
- Linux VPS Thailand
- VPS Linux Indonesia
- Linux VPS Germany
9. Linux VPS Vs Windows VPS – Know The Difference
Deciding between a Linux VPS and a Windows VPS is straightforward. Begin by assessing your project needs. Once you determine the architecture for your website, it’s a matter of identifying the optimal operating system for hosting. Since Windows products are predominantly proprietary, they function best within a Windows-based server environment. Conversely, if your website relies on open-source CMS or other Linux-related software, the choice becomes clear.
However, if you haven’t finalized your choice of applications yet?
Linux VPS offers are esteemed by web developers and individuals seeking complete control over their environment. Given the prevalence of open-source solutions, hosting expenses tend to be notably more budget-friendly.
Conversely, enterprises often opt for Windows server plans. The streamlined services, frequent updates, and the reputable corporate backing provide business owners with peace of mind and ample opportunities for growth.
10. FAQs
10.1. What is the difference between a Linux VPS and a shared hosting plan?
A Linux VPS (Virtual Private Server) and a shared hosting plan are two different types of web hosting services, each with its own advantages and use cases:
Linux VPS (Virtual Private Server)
- A VPS is a virtualized server environment created by partitioning a physical server into multiple virtual servers.
- Each VPS operates independently with its own operating system, resources (CPU, RAM, disk space), and software.
- Users have more control and flexibility over their server environment. They can install and configure software, customize server settings, and have root access.
- Resources are dedicated to each VPS, meaning performance is more stable and predictable.
- Typically, VPS hosting is more scalable, allowing users to easily upgrade or downgrade resources based on their needs.
- Suitable for websites or applications with moderate to high traffic, e-commerce sites, development environments, and custom configurations.
Shared Hosting
- Shared hosting involves multiple websites sharing resources on a single server.
- Resources such as CPU, RAM, and disk space are shared among multiple users, which can lead to performance issues if one website experiences high traffic or resource usage.
- Users have limited control over the server environment and are typically restricted in terms of software installations and configurations.
- Shared hosting plans are usually more affordable compared to VPS hosting.
- Suitable for small websites, blogs, personal sites, or businesses with low to moderate traffic and resource requirements.
The main differences between a Linux VPS and a shared hosting plan lie in the level of control, resource allocation, performance, and scalability. VPS hosting offers more control, dedicated resources, and scalability but may require more technical expertise, while shared hosting is more user-friendly and cost-effective but offers less control and resource allocation.
Also Read: Unveiling the Web’s Hidden Foundation: What is Web Hosting?
10.2. Do I need any technical knowledge to use a Linux VPS?
Using a Linux VPS typically requires some level of technical knowledge, especially compared to shared hosting, where most of the server management tasks are handled by the hosting provider. However, the degree of technical expertise required depends on the complexity of your needs and the level of control you want over your server environment. Here are some key aspects of using a Linux VPS and the technical knowledge required:
- Server Setup: Setting up a Linux VPS usually involves tasks such as choosing a Linux distribution, configuring network settings, and securing the server. While some VPS providers offer managed services that handle the initial setup for you, having basic knowledge of Linux server administration can be beneficial.
- Command Line Interface (CLI): Unlike shared hosting control panels, which often provide graphical user interfaces (GUIs) for server management, VPS management is typically done through the command line interface (CLI). Familiarity with basic Linux commands is important for tasks such as navigating the file system, managing users and permissions, installing software, and troubleshooting.
- Security: Securing your VPS involves implementing best practices such as configuring firewalls, keeping software up to date, and managing user permissions. Understanding Linux security concepts and tools is essential for protecting your server from unauthorized access and vulnerabilities.
- Software Installation and Configuration: With a Linux VPS, you have full control over the software stack, including web servers (e.g., Apache, Nginx), databases (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL), and programming languages (e.g., PHP, Python). Installing and configuring these components requires some knowledge of server administration and the specific technologies you’re using.
- Maintenance and Monitoring: Regular maintenance tasks such as software updates, backups, and performance monitoring are essential for keeping your VPS running smoothly. Understanding how to automate these tasks and interpret server logs can help ensure the reliability and security of your server.
While technical knowledge is beneficial for using a Linux VPS effectively, many resources are available to help you learn, including online tutorials, documentation, and community forums. Additionally, managed VPS services are available from some providers, which handle many of the server management tasks for you, allowing you to focus on your website or application without needing extensive technical expertise.

10.3. How secure is a Linux VPS?
The security of a Linux VPS depends on several factors, including the configuration of the server, the applications running on it, the adherence to security best practices, and the diligence of the server administrator in keeping the system up to date and monitoring for security threats. Here are some aspects that contribute to the security of a Linux VPS:
- Operating System Security: The security of your VPS starts with the underlying operating system. Linux is known for its robust security features, including strong user permissions, file system security, and built-in firewall capabilities. Keeping the operating system up to date with security patches and updates is crucial for addressing known vulnerabilities.
- User Authentication and Access Control: Proper user authentication and access control measures should be implemented to prevent unauthorized access to the server. This includes using strong passwords, disabling root login via SSH, and limiting SSH access to specific users or IP addresses. Additionally, implementing two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security for user logins.
- Firewall Configuration: Configuring a firewall is essential for controlling network traffic to and from your VPS. Firewall rules can be used to allow or deny access to specific ports and services, helping to protect against unauthorized access and network-based attacks. Regularly reviewing and updating firewall rules is important for maintaining security.
- Software Security: The security of the software running on your VPS, including web servers, databases, and other applications, is critical for overall server security. Keeping software up to date with the latest security patches and following secure configuration practices help mitigate vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
- Monitoring and Logging: Monitoring server logs and system metrics can help identify potential security issues or suspicious activity. Tools such as intrusion detection systems (IDS), log analysis tools, and security information and event management (SIEM) solutions can aid in detecting and responding to security incidents in real time.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery: Implementing regular backups of your VPS data is essential for mitigating the impact of security incidents such as data loss or server compromise. Having a robust backup and disaster recovery plan in place ensures that you can restore your server to a known good state in the event of a security breach or other unexpected event.
While a Linux VPS can be secured effectively with proper configuration and maintenance, it’s important to recognize that no system is completely immune to security threats. Regularly assessing and updating your security measures, staying informed about emerging threats, and adopting a proactive approach to security are key components of maintaining a secure Linux VPS environment.
10.4. What are some popular control panels for managing a Linux VPS?
Several popular control panels are available for managing a Linux VPS, each offering a range of features for server administration, website management, and application deployment. Here are some of the most widely used control panels:
cPanel
- cPanel is one of the most popular and widely used control panels for Linux-based web hosting environments.
- It offers a user-friendly graphical interface for managing various aspects of the server, including website management, email accounts, databases, file management, and security settings.
- cPanel also provides tools for installing and managing applications (such as WordPress), monitoring server performance, and generating backups.
DirectAdmin
- DirectAdmin is another popular control panel alternative to cPanel, offering similar features for server and website management.
- It provides a simplified interface for managing domains, email accounts, databases, FTP users, and DNS settings.
- DirectAdmin is known for its lightweight and resource-efficient design, making it a suitable choice for smaller VPS environments.
Plesk
- Plesk is a comprehensive control panel that supports both Linux and Windows servers.
- It offers a wide range of features for server management, website hosting, and application deployment, including support for Docker containers and Git integration.
- Plesk provides a user-friendly interface for managing domains, email accounts, databases, security settings, and server resources.
Webmin
- Webmin is an open-source control panel that offers a web-based interface for managing Linux servers.
- It provides modules for configuring various server services and settings, including Apache, MySQL, PHP, DNS, and firewall configurations.
- Webmin is highly customizable and extensible, allowing users to add additional modules and features as needed.
ISPConfig
- ISPConfig is an open-source control panel designed for managing Linux servers in web hosting environments.
- It offers features for managing websites, email accounts, FTP users, databases, and DNS settings.
- ISPConfig also includes support for multi-server setups, allowing users to manage multiple servers from a single interface.
These are just a few examples of popular control panels for managing a Linux VPS. The choice of control panel often depends on factors such as user preference, specific feature requirements, ease of use, and budget constraints. Additionally, some VPS providers offer their own custom control panels or management interfaces as part of their hosting services.

10.5. How much does Linux VPS hosting cost?
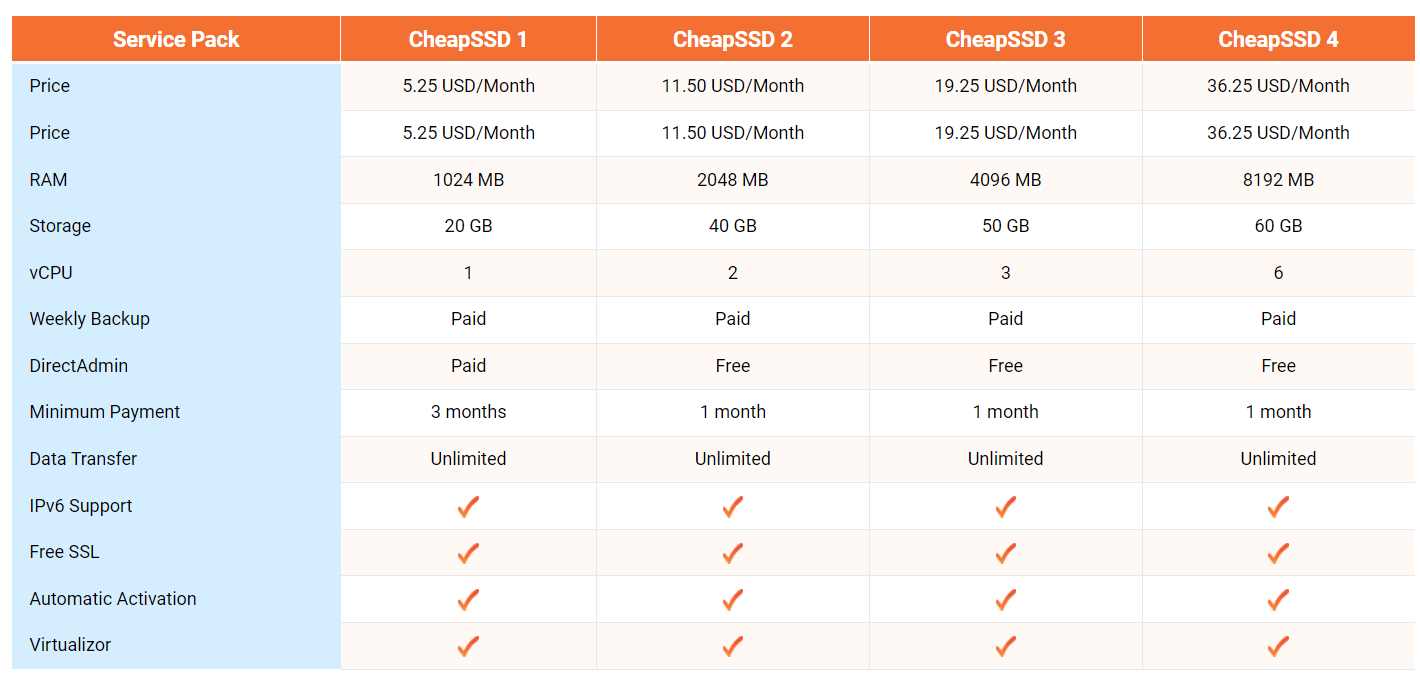
The cost of Linux VPS hosting can vary widely depending on factors such as the VPS provider, the specifications of the server (e.g., CPU, RAM, storage), the level of management (managed or unmanaged), additional features included in the hosting plan, and the billing cycle (monthly, annually, etc.). Here are some general guidelines regarding the pricing of Linux VPS hosting of VinaHost:
CheapSSD 1
- Basic Linux VPS hosting plans with modest resources (e.g, 1 vCPU, 1024MB RAM, 20GB SSD storage) typically start at around $5 per month.
- These plans are suitable for small websites, blogs, personal projects, or development environments with low to moderate traffic.
CheapSSD 2
Mid-range Linux VPS hosting plans with higher resource allocations (e.g, 2 vCPU, 2048MB RAM, 40GB SSD storage) generally range from $10 per month.
These plans are suitable for websites or applications with moderate traffic, e-commerce sites, or businesses with growing resource requirements.
CheapSSD 3
High-end Linux VPS hosting plans with robust specifications (e.g, 3 vCPU, 4096MB RAM, 50GB SSD storage) can cost upwards of $50 to $100 or more per month.
These plans are suitable for high-traffic websites, resource-intensive applications, or businesses requiring dedicated resources and performance guarantees.
CheapSSD 4
These plans with 6 vCPU, 8192MB RAM, 60 GB SSD storage, may start at around $30 per month.
It’s important to carefully review the features, specifications, and pricing of different Linux VPS hosting plans to ensure they meet your requirements and budget. Some VPS providers offer customizable plans, allowing you to adjust the resources and features based on your needs, while others may offer bundled packages with predefined configurations. Additionally, keep in mind that promotional discounts, introductory offers, and long-term contracts may affect the overall cost of VPS hosting.
11. Conclusion
The above article has comprehensively summarized information about “What is Linux VPS?”. Hopefully, you have gained a better understanding of this technology, grasped the basics of how to use it, and been able to choose a reputable provider. If you have any questions that need clarification, please don’t hesitate to contact us.
- Email: support@vinahost.vn
- Hotline: 1900 604
- Livechat: https://livechat.vinahost.vn/chat.php
You can also check out other interesting articles HERE to stay updated with new knowledge every day.
What is a Game Server? | How Game Servers Work?
Maximizing Efficiency and Performance: What is Blade Server?


 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt English
English 简体中文
简体中文