Think you understand the internet? Now think again. Beneath the sleek interface and captivating content lies a hidden world, a realm of servers, code, and invisible forces shaping our online experience. We call it web hosting, and it is about time we demystified its power and impact. Are you ready to dive deeper with VinaHost for What is Web Hosting, peel back the layers, and uncover the true foundation of the it? Let’s get started!
1. The Basics of Hosting
1.1. What is web hosting?
Web hosting is known as a service which allows individual, company and organization to make their sites accessible on the internet. In essence, it involves renting or leasing space on a server, which is a powerful computer connected to the internet. This server stores the files and data necessary for a website to function and makes them available to users who visit the site.
Web hosting providers offer various hosting plans with different features, resources, and levels of support to accommodate the diverse needs of website owners. The hosting service includes elements such as server maintenance, security, bandwidth, and storage, enabling websites to be consistently available and accessible online.
Whether it’s a personal blog, business website, or e-commerce platform, web hosting is a fundamental component for establishing an online presence.

1.2. The role of hosting in website accessibility
Web hosting plays a crucial role in website accessibility, impacting how easy it is for everyone to find, understand, and navigate your website.
Performance and reliability:
- Fast loading times: A reliable web host service with sufficient resources ensures your website loads quickly and consistently, preventing frustration for users with slower internet connections or disabilities.
- Uptime: Consistent uptime minimizes interruptions and ensures your website is accessible whenever users require it. Downtime due to hosting issues can be particularly detrimental for users who rely on your content for daily tasks or communication.
Technical compatibility:
- Code and server compliance: The host environment should be compatible with the technologies and standards used to build your website, including HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and assistive technologies (AT). Using an outdated or non-compliant hosting platform can lead to rendering issues and difficulties for users with disabilities.
- Accessibility features: Some host providers offer built-in tools or plugins that can help improve your website’s accessibility, such as alt text generation for images, keyboard navigation optimization, and screen reader compatibility testing.
Security and scalability:
- Secure access: Secure hosting with strong encryption and authentication protocols protects user data and ensures secure navigation, especially for websites handling sensitive information.
- Scalability: As your website’s traffic grows, your host plan should be able to scale accordingly to maintain performance and accessibility. Overloaded servers can slow down page loading and potentially crash, hindering access for all users.
Resource management:
- Bandwidth and disk space limitations: Ensure your hosting plan provides enough bandwidth and disk space to accommodate your website’s content and expected traffic. Inadequate resources can lead to slow loading times and limit accessibility for users with data limitations.
- Content optimization: Consider optimizing your website’s content by compressing images and using efficient coding practices to reduce resource usage and improve accessibility for users on limited bandwidth connections.
2. Types of Hosting
2.1. Shared hosting
Shared hosting is a common and cost-effective hosting solution where multiple websites share resources on a single server. Each website has its own domain but shares server resources such as CPU, RAM, and storage with other websites on the same server.
Advantages:
- Cost-effective: Shared host is often the most affordable option for individuals and small businesses.
- Easy to manage: Host provider takes care of server maintenance and administration.
- Suitable for beginners: Ideal for those new to website host and with moderate traffic.
2.2. Virtual Private Server (VPS) hosting
VPS provides a virtualized environment within a dedicated server. Each VPS operates as an independent virtual machine with its own dedicated resources. It offers you with more control as well as customization compared to shared hosting.
Advantages:
- Enhanced control: Users have more control over server configurations and can install custom software.
- Dedicated resources: Dedicated portions of CPU, RAM, and storage provide better performance.
- Scalability: Easily scalable with the ability to adjust resources based on website needs.
2.3. Dedicated hosting
Dedicated hosting offers an entire physical server exclusively for one user or organization. This type of host provides the highest level of control, performance, and customization.
Advantages:
- Full server access: Complete control over server settings and configurations.
- High performance: Dedicated resources ensure optimal performance for high-traffic websites.
- Customization: Users can install and configure any software based on their specific requirements.
2.4. Cloud hosting
Cloud hosting utilizes a network of interconnected virtual and physical servers to distribute resources and ensure reliability. Websites hosted on the cloud can dynamically scale resources based on demand.
Advantages:
- Scalability: Resources can be scaled up or down based on website traffic and demand.
- Reliability: Redundant server architecture minimizes downtime and enhances reliability.
- Pay-as-You-Go Pricing: Users pay for the resources they use, making it cost-effective.
3. How Does Web Hosting Works
Web host works through the interplay of domain names and IP addresses, name servers facilitating DNS resolution, and the client-server relationship. This intricate process ensures that users can access websites seamlessly by typing in user-friendly domain names, initiating a series of steps that lead to the retrieval and display of web content.

3.1. Domain names and IP addresses
Domain names: Users access websites through domain names (e.g., www.vinahost.vn). These names are easier for humans to remember than IP addresses.
IP addresses: Each domain name corresponds to a unique IP address, which is a numerical identifier for a server on the internet. IP addresses are used by computers to locate and communicate with each other.
Also read: What is Domain & How It Impacts Your Online Presence
3.2. What is hosting Name Servers and DNS resolution?
Name servers: When a user enters a domain name in a web browser, the request is sent to a domain’s designated name servers. Name servers are specialized servers that store DNS (Domain Name System) records, including the mapping of domain names to IP addresses.
DNS resolution: The name servers respond with the corresponding IP address for the requested domain. This process, known as DNS resolution, translates human-readable domain names into machine-readable IP addresses, allowing the browser to locate the server hosting the website.
Also read: What is DNS Record: The Key to Unlocking the Internet
3.3. The client-server relationship
Client: The client is the user’s device (computer, smartphone, etc.) that requests a web page. The client uses a web browser to send a request to the server for a specific website.
Server: The server is a powerful computer, often hosted by a web hosting provider, that stores website files, databases, and other resources. When a server receives a request from a client, it processes the request and sends back the requested web page or content.
HTTP/HTTPS Protocol: The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) or its secure version, HTTPS, is used for communication between the client and server. The client’s browser sends an HTTP/HTTPS request to the server, and the server responds with the requested web page or resource.
Rendering the Web page: Once the client receives the response from the server, it interprets the HTML, CSS, and other files to render the web page. The rendered page is then displayed on the user’s device.
4. Choosing the Right Web Hosting Provider
There’s no one-size-fits-all solution. Prioritize factors most critical to your website’s needs, budget, and technical expertise. So that you need to research thoroughly, compare options, and don’t hesitate to contact potential providers for clarification before making your decision.
4.1. Factors to consider
- Type of host: Understand your host needs—shared, VPS, dedicated, or cloud host. Choose a type that aligns with your website’s size, traffic, and complexity.
- Website traffic: Estimate your current and projected traffic volume. Shared host may suffice for low traffic, while VPS or dedicated servers are better for high traffic.
- Resource needs: Consider disk space, bandwidth, CPU, and RAM requirements based on your website’s content and applications.
- Budget: Shared host is the cheapest, while dedicated servers are the most expensive. VPS and cloud hosting fall in between.
- Technical skills: Shared and cloud host are easiest to manage, while VPS and dedicated servers require technical knowledge.
- Control needs: Shared host offers least control, dedicated hosting offers most control over server environment and settings.
- Features: Look for features like email accounts, backups, security tools, and customer support options.
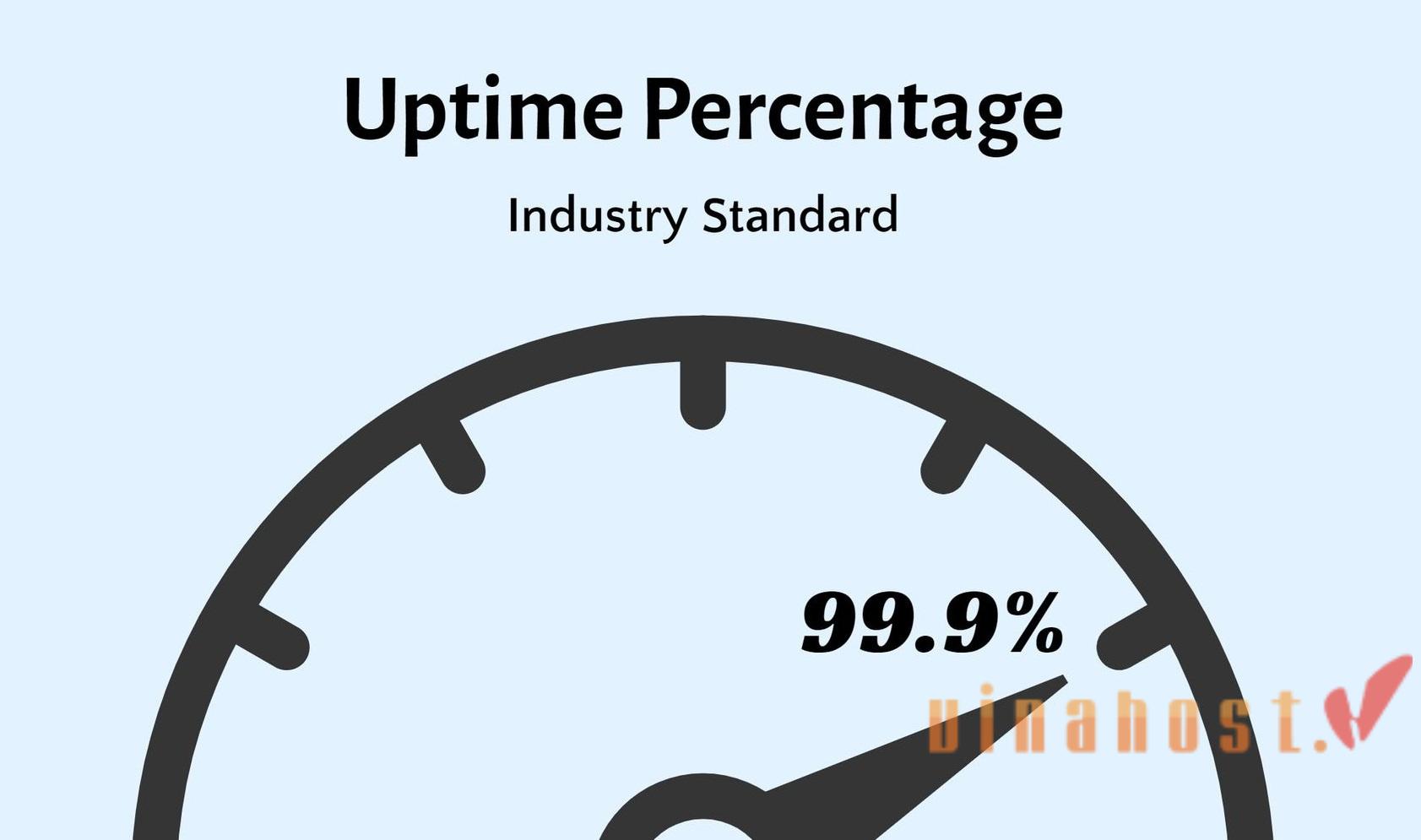
- Uptime guarantee: Look for providers offering a high uptime guarantee (99.9% or above). Consistent availability is essential for a reliable online presence.
- Scalability and growth potential: Consider if the provider offers easily upgradeable plans or flexible options like cloud hosting to accommodate future growth.
- Tech support and customer care: Opt for providers with responsive support through various channels, including live chat, email, and phone.
- User-Friendly control panel: A user-friendly control panel (e.g., cPanel, Plesk) simplifies website management. Check if the hosting provider offers an intuitive interface for easy administration.
4.2. Evaluating performance and reliability
- Reviews and reputation: Read reviews and testimonials from existing customers. A positive reputation for performance and reliability is a good indicator of a host provider’s capabilities.
- Server peed: Opt for a hosting provider with fast server speeds. Faster loading times can contribute to a good user experience and may positively impact SEO rankings.
- Uptime guarantees: Look for providers offering uptime guarantees to ensure minimal downtime and consistent website access.
- Server location: Choose a provider with server locations close to your target audience. Proximity reduces latency and ensures faster access for users.
- Performance benchmarks: Utilize online tools to compare server response times and performance metrics for different providers.
4.3. Scalability and growth potential
- Plan flexibility: Check if the provider offers various host plans with easily upgradeable resources to accommodate future growth.
- Cloud hosting options: Consider cloud hosting for automatic scaling based on traffic fluctuations, avoiding resource limitations or overpaying.
- Migration support: Choose a provider offering easy website migration if you switch from another provider in the future.
- Additional services: Explore additional services offered, such as content delivery networks (CDNs) or automatic scalability features. These can enhance performance and accommodate growth.
5. Shared Hosting: The Community of Websites
Shared hosting is an ideal choice for those seeking a budget-friendly option to establish an online presence. It strikes a balance between cost-effectiveness and ease of use, making it accessible for individuals and small businesses entering the digital landscape.
As your website grows, you can reassess your host needs and consider more advanced solutions tailored to accommodate increased traffic and resource requirements.
5.1. Sharing resources and limitations
Server resources: In shared hosting, multiple websites share the same physical server and its resources, including CPU, RAM, and storage. This communal sharing allows hosting providers to offer affordable plans as the costs are distributed among users.
Limitations: The main limitation is that the resources are shared. If one website on the server experiences a spike in traffic or resource usage, it may temporarily affect the performance of other websites on the same server. However, reputable hosting providers implement measures to mitigate these potential impacts.
5.2. Cost-effectiveness for small websites
Affordability: Shared host is one of the most cost-effective host solutions, making it an attractive choice for small websites, personal blogs, or startups with limited budgets. The shared nature of resources enables providers to offer lower prices.
Ease of management: Shared hosting plans often come with user-friendly control panels, such as cPanel or Plesk, making it easy for individuals with little technical expertise to manage their websites, email accounts, and other host settings.
Suitability for low to moderate traffic: Shared host is well-suited for websites with low to moderate traffic. If your website is just starting or doesn’t anticipate a large influx of visitors, shared hosting provides a cost-effective solution without the need for extensive resources.
Scalability considerations: While shared hosting is an excellent starting point, websites with significant growth or resource-intensive needs may eventually outgrow shared plans. In such cases, transitioning to a more robust hosting solution like VPS or dedicated host becomes necessary.

Also read: BEST – Cheap VietNam Hosting Full SSD | VinaHost.VN
6. VPS Hosting: The Virtual Private Sanctuary
VPS hosting carves out a virtual server within the physical server, granting you exclusive access to a portion of its CPU, RAM, and disk space. It’s like having your own floor or wing within a building, free from the resource fluctuations and performance impacts of other websites.
It provides a scalable and flexible solution, offering the benefits of isolated resources and enhanced performance without the costs associated with dedicated hosting.
This leads to:
6.1. Isolated resources and enhanced performance
Virtualization technology: VPS (Virtual Private Server) hosting involves the use of virtualization technology to create isolated virtual environments within a physical server. Each VPS operates independently, with its own dedicated resources such as CPU, RAM, and storage.
Resource allocation: Unlike shared hosting, where resources are shared among multiple users, VPS hosting ensures that the allocated resources are dedicated to a specific VPS. This isolation prevents the performance of one VPS from affecting others on the same server.
Customization: Users have greater control over the server environment, allowing for customization of software configurations, installation of specific applications, and more. This flexibility contributes to enhanced performance.
6.2. Ideal for growing websites with moderate traffic
Scalability: VPS hosting is highly scalable, making it an excellent choice for growing websites. As the traffic and resource demands increase, users can easily scale their VPS by adjusting CPU, RAM, and storage allocations to accommodate the growth.
Performance stability: The isolation of resources ensures more stable and consistent performance for websites. Growing websites with moderate to high traffic benefit from the dedicated resources and reduced impact from neighboring virtual environments.
Advanced features: VPS hosting often comes with advanced features such as root access, which provides full control over the server. This is valuable for users with specific technical requirements or those seeking a hosting environment with more capabilities.
Affordability and performance balance: VPS hosting strikes a balance between the enhanced performance of dedicated hosting and the cost-effectiveness of shared hosting. It offers a cost-effective solution for websites that have outgrown shared hosting but don’t require the full resources of a dedicated server.

7. Dedicated Hosting: The Grand Estate of Websites
Dedicated hosting represents the pinnacle of hosting solutions, offering a virtual grand estate for websites and applications with the most demanding requirements. It caters to users seeking maximum control, exclusive access to resources, and uncompromised performance.
While it comes with a higher cost compared to shared or VPS hosting, the benefits of dedicated hosting are invaluable for those with high-traffic websites, complex applications, or specific security and customization needs. It provides a hosting environment that truly mirrors the grandeur and exclusivity of a private estate for your online presence.
Dedicated hosting grants you the entire physical server, akin to owning a sprawling mansion where every aspect is catered to your website’s specific needs. No sharing, no limitations, just absolute dominion over CPU, RAM, disk space, and software configurations. This absolute power brings:
7.1. Full control and exclusive resources
- Exclusive server: In dedicated hosting, a user leases an entire physical server exclusively for their website or application. This means all server resources, including CPU, RAM, storage, and bandwidth, are dedicated to that user’s needs.
- Complete server access: Users have full administrative access and control over the server. This level of control allows for advanced customizations, installation of specific software, and configuration adjustments tailored to the unique requirements of the website or application.
7.2. Perfect for high-traffic websites and complex applications
- High performance: Dedicated hosting provides unparalleled performance, making it ideal for high-traffic websites that demand robust processing power and fast response times. Exclusive access to resources ensures optimal performance even during traffic spikes.
- Resource intensive applications: Complex applications, databases, and resource-intensive tasks benefit from the dedicated resources of a server. Dedicated host is well-suited for applications with extensive computational requirements, such as large-scale e-commerce platforms, streaming services, or data-intensive applications.
- Custom security measures: Dedicated hosting allows users to implement custom security measures, enhancing the overall security of the server. This is particularly important for websites handling sensitive data or requiring specific security configurations.
- Scalability: While dedicated hosting provides ample resources, it also allows for scalability. Users can upgrade server components or add more servers to their infrastructure to accommodate future growth.

8. Cloud Hosting: The Dynamic Web Oasis
Cloud hosting stands out for its dynamic and flexible nature, providing an oasis of resources for websites and applications.
The scalability, distributed infrastructure, and redundancy make it an excellent choice for businesses and websites with varying workloads, ensuring optimal performance, high availability, and efficient resource utilization.
The cloud hosting model aligns well with the evolving needs of modern web applications and the demand for a reliable, scalable, and cost-effective host solution.
8.1. Scalability and flexibility
- Dynamic resource allocation: Cloud hosting utilizes a network of interconnected servers to distribute resources dynamically. This allows for on-demand scaling of resources based on website traffic and requirements. Resources, such as CPU, RAM, and storage, can be easily adjusted to accommodate changing needs.
- Pay-as-You-Go model: Cloud host often operates on a pay-as-you-go model, where users only pay for the resources they consume. This flexibility is beneficial for businesses with fluctuating workloads, as they can scale up during peak times and scale down during quieter periods.
- Easy deployment and management: Cloud providers manage the underlying infrastructure, freeing you to focus on website development and content creation, minimizing technical complexities.
8.2. Distributed infrastructure and redundancy
- Distributed servers: Cloud hosting relies on a distributed infrastructure, meaning that websites are not hosted on a single physical server but are distributed across a network of interconnected servers. This distribution enhances reliability and performance.
- High availability and uptime: With data and services mirrored across multiple servers, website outages become a distant memory. Even if one server experiences an issue, your website remains accessible and operational.
- Redundancy for high availability: Cloud host providers implement redundancy measures to ensure high availability. If one server or component fails, the workload is seamlessly transferred to another available server, minimizing downtime and ensuring continuous operation.
- Load balancing: Load balancing is often employed in cloud environments to evenly distribute incoming traffic across multiple servers. This optimizes resource utilization and prevents individual servers from being overwhelmed.
- Data mirroring and backups: Cloud hosting providers typically employ data mirroring and regular backups to enhance data integrity and disaster recovery. Data is often mirrored across multiple servers and locations to prevent data loss in case of hardware failures.

Also read: [TOP] – VPS VietNam FREE Trial 7 Days | VinaHost.VN
9. Managed Hosting: The Supportive Backbone
Managed hosting acts as a supportive backbone by handling the technical intricacies of server management, allowing website owners to concentrate on creating valuable content and driving growth.
The comprehensive support provided by managed host services not only ensures the smooth operation of websites but also contributes to a secure, high-performing, and scalable online presence. It’s an excellent option for those who prioritize assistance, reliability, and a focus on content and business development.
Managed host comes at a premium compared to unmanaged options, requiring careful consideration of your budget and technical needs. Additionally, while some providers offer platform-specific host (WordPress, Drupal), others have broader expertise.
If you value technical expertise, prioritize continuous support, and desire to devote your energy to creative pursuits, managed host provides the ideal backbone for your website’s journey. Weigh the benefits against the cost and choose a provider that aligns with your technical proficiency and platform needs.
9.1. Technical assistance and maintenance
- Proactive support: Managed hosting providers offer proactive technical assistance and support. This includes server maintenance, security updates, and performance optimizations handled by the host provider’s team of experts.
- 24/7 monitoring: Continuous monitoring of server health, security, and performance ensures early detection of issues. Managed hosting providers often offer 24/7 monitoring, allowing prompt resolution of any potential problems.
- Security measures: Managed host services include robust security measures, such as firewall configurations, regular security audits, and malware scanning.
9.2. Focus on content creation and growth
- Content management: With technical aspects managed by the host provider, website owners can focus more on content creation and development. This is particularly beneficial for bloggers, content creators, and businesses aiming to grow their online presence.
- Scalability and resource management: Managed host providers assist in managing resources and scaling server configurations based on website growth. This ensures that the host environment remains aligned with the evolving needs of the website.
- Performance optimization: Providers optimize server configurations for performance, ensuring that websites load quickly and deliver a seamless user experience. This is crucial for retaining visitors and improving search engine rankings.
- Regular backups and recovery: Managed host services often include automated regular backups, ensuring that website data is securely stored. In the event of data loss or unexpected issues, quick data recovery options are available.

10. The Importance of Uptime and Performance
Uptime and performance are critical factors for the success of a website. Downtime can lead to negative consequences, affecting user experience, SEO rankings, and overall business goals.
Choosing a hosting provider with reliable uptime guarantees, a strong reputation, and proactive measures for monitoring and redundancy is essential for maintaining a consistently accessible and high-performing website.
10.1. Downtime and its impact
Downtime refers to the period during which a website is not accessible or experiences disruptions in service. This can be due to server issues, maintenance, or other unforeseen events.
- Impact on user experience: Downtime negatively affects the user experience, as visitors may be unable to access the website, resulting in frustration. For businesses and e-commerce sites, downtime can lead to lost sales, revenue, and damage to the brand’s reputation.
- SEO consequences: Search engines consider website uptime when determining search rankings. Frequent downtime may lead to a drop in search engine rankings, reducing the visibility of the website.
10.2. Choosing hosting with reliable uptime guarantees
- Uptime guarantees: Host providers often offer uptime guarantees as a commitment to the reliability of their services. Look for providers with high uptime guarantees, commonly expressed as a percentage (e.g., 99.9% uptime).
- Reputable hosting providers: Reputable host providers invest in robust infrastructure, redundant systems, and proactive monitoring to minimize downtime. Reading reviews and assessing the reputation of host providers can provide insights into their historical uptime performance.
- Service level agreements (SLA): A host provider’s SLA typically includes details about uptime guarantees and compensation in case of failures to meet those guarantees. It’s essential to review and understand the SLA before selecting a host provider.
- Monitoring and notifications: Choose a host provider that offers monitoring services and notifications in case of potential issues. Proactive monitoring allows for quick identification and resolution of problems before they impact the website’s performance.
- Load balancing and redundancy: Host providers that implement load balancing and redundancy measures distribute website traffic across multiple servers. This not only enhances performance but also minimizes the impact of potential server failures on uptime.
Also read: [TIPS] How to reduce Vietnam Server response time for WordPress
11. Security and Hosting
In the vast online landscape, where data flows freely and threats lurk, website security is not just an option, it’s a necessity. Just like a sturdy castle protects its inhabitants, secure hosting builds a robust defense against cyber threats, safeguarding your website and its valuable assets.
By implementing a combination of preventive measures, regular audits, and robust encryption protocols, you can create a secure hosting environment that safeguards your website from cyber threats.
Let’s explore two key pillars of secure hosting:
11.1. Protecting your website from cyber threats
- Firewall protection: Implementing a robust firewall is the first line of defense against unauthorized access and cyber threats. Firewalls monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic, safeguarding your website from malicious activities.
- Regular security audits: Conducting regular security audits helps identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in your website’s infrastructure.
- Secure file permissions: Set proper file permissions to restrict access to sensitive files and directories. This ensures that only authorized users or processes can modify or access critical components of your website.
- Malware scanning and pemoval: Regularly scan your website for malware, viruses, and other malicious code. Hosting providers often offer malware scanning tools, and integrating third-party security solutions can provide an additional layer of protection.
- Backup and disaster recovery: Regularly back up your website’s data, and ensure you have a comprehensive disaster recovery plan in place.
11.2. SSL certificates and data encryption
- SSL certificates: SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificates are crucial for encrypting data transmitted between the user’s browser and your server. This encryption ensures that sensitive information, such as login credentials, personal details, and payment information, remains secure during transit.
- HTTPS protocol: Implementing HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) ensures that your website uses SSL/TLS encryption. Websites with HTTPS provide a secure and encrypted connection, fostering trust among users and contributing to improved search engine rankings.
- Data encryption at rest: In addition to securing data in transit, hosting providers may offer encryption for data at rest. This ensures that stored data, such as databases and files, remains protected against unauthorized access.
- Multi-Layered security: Employing a multi-layered security approach involves combining various security measures, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security updates. This comprehensive strategy helps address security threats from multiple angles.
- Security certifications and compliance: Hosting providers adhering to industry security standards and certifications, such as ISO 27001 or SOC 2, demonstrate a commitment to maintaining a secure hosting environment. Compliance with these standards ensures that security protocols are consistently followed.

12. Website Migration and Hosting Transfers
Just like packing up your belongings and shifting houses, website migration involves transferring your website’s files, databases, and configurations to a new hosting provider.
It can be a daunting task, but with careful planning and execution, you can ensure a smooth transition and avoid frustrating downtime or data loss. Let’s explore the crucial steps and considerations for a successful website migration:
12.1. Moving your website to a new host
- Selecting a new hosting provider: Choose a hosting provider that aligns with your website’s requirements in terms of performance, features, and support. Consider factors such as server specifications, scalability options, and customer reviews.
- Backup your website: Before initiating the migration, create a comprehensive backup of your website’s files, databases, and any essential configurations. This backup ensures that you have a restore point in case of any unforeseen issues during the migration process.
- Replicating DNS records: Replicate the DNS (Domain Name System) records of your domain on the new hosting provider. This includes updating the nameservers or pointing the domain to the new hosting provider’s IP address.
- Transferring files and databases: Move your website’s files and databases to the new hosting environment. This can be done using various methods, such as FTP (File Transfer Protocol) for files and exporting/importing databases for data.
12.2. Ensuring a smooth transition
- Testing on a staging environment: Before making the final DNS changes, set up a staging environment on the new host to test your website’s functionality. This allows you to identify and address any issues or compatibility issues that may arise in the new hosting environment.
- Monitoring uptime and performance: Monitor your website’s uptime and performance during and after the migration. Tools like website monitoring services can help track the transition and detect any potential issues affecting accessibility or speed.
- Updating configuration settings: Review and update any configuration settings, such as file paths, database connection details, and other environment-specific configurations, to ensure compatibility with the new hosting environment.
- Communicating with stakeholders: If your website has regular visitors or users, communicate the migration plan and potential downtime to minimize disruption. Provide updates on the progress and inform stakeholders once the migration is successfully completed.
- Addressing post-migration tasks: After the migration, update any internal or external links, configure email settings if applicable, and address any post-migration tasks specific to your website’s functionalities.
- Monitoring for post-migration issues: Keep a close eye on your website’s performance, user feedback, and any potential issues that may arise after the migration. Address any reported issues promptly to ensure a seamless user experience.

Also Read: What is Addon Domain – A Gateway to Website Expansion
13. Cost Considerations and Budgeting
Balancing features and affordability is key to selecting a hosting plan that meets your website’s needs while staying within your budget. Additionally, understanding the long-term cost implications, including renewal rates and potential scalability costs, allows for effective budgeting and ensures a sustainable hosting solution for your online presence.
Remember, the cheapest option isn’t always the best. Strike a balance between features you need and your budget:
13.1. Balancing features and affordability
- Identifying hosting needs: Start by assessing the specific needs of your website. Different types of websites (e.g., personal blog, business site, e-commerce platform) have varying requirements. Consider factors such as storage space, bandwidth, performance, and support features.
- Comparing hosting plans: Hosting providers offer a range of plans with different features and pricing tiers. Compare plans to find the one that best aligns with your website’s requirements while staying within your budget.
- Evaluating additional costs: Beyond the base hosting fee, consider additional costs such as domain registration, SSL certificates, and any add-on services you may need. Some hosting providers include these features in their plans, while others may charge separately.
- Promotionalpricing vs. renewal rates: Be mindful of promotional pricing offered by hosting providers, as they may increase significantly when the plan renews. Understand the renewal rates to anticipate the long-term cost of hosting.
13.2. Long-term cost implications
- Renewal costs: Hosting providers often offer discounted rates for the initial term, which increases upon renewal. Consider the long-term cost implications and evaluate whether the hosting provider’s renewal rates fit your budget.
- Scalability and upgrades: Anticipate the future growth of your website. Choose a hosting provider that offers scalability and consider the potential costs associated with upgrading to a higher-tier plan or a different hosting type as your website expands.
- Contract length: Hosting vendors can provide promotions for longer billing cycles. While this can be cost-effective, consider your commitment level and potential changes in hosting needs over time.
- Hidden fees and add-ons: Be aware of any hidden fees or additional charges that may apply. Some hosting providers charge extra for services like website backups, security features, or premium support. Understand the full cost structure to avoid surprises.
- Evaluating value for money: Instead of solely focusing on the lowest cost, evaluate the overall value for money. Consider the hosting provider’s reputation, customer support, performance, and the inclusion of essential features in their plans.
14. Scaling and Growing with Your Hosting
Upgrading hosting isn’t just about adding more space. It’s about ensuring your website has the right foundation to support its growth. Don’t wait until you hit resource limitations; proactive planning and timely upgrades prevent bottlenecks and maintain a seamless user experience.
14.1. Planning for future expansion
- Assessing website growth: Evaluate your website’s current and potential future growth. Consider factors such as increasing traffic, content expansion, and additional features or functionalities. Understanding the trajectory of your website helps in planning for scalability.
- Scalable hosting solutions: Choose a host provider and plan that offers scalability. Scalable solutions, such as VPS (Virtual Private Server) or cloud host, allow you to easily increase resources (CPU, RAM, storage) as your website grows.
- Monitoring resource usage: Regularly monitor your website’s resource usage to identify trends and potential bottlenecks. Utilize tools provided by host providers or third-party monitoring services to track performance metrics.
- Flexible hosting features: Opt for hosting plans that provide flexibility and room for expansion. Features like easy upgrades, additional domains, and the ability to install custom applications contribute to a scalable hosting environment.
14.2 Upgrading hosting plans
- Assessing current host needs: Regularly assess your website’s performance and resource requirements. If your website experiences slow loading times or if you anticipate increased traffic, it may be time to consider upgrading your host plan.
- Types of upgrades: Host providers typically offer various types of upgrades, including transitioning from shared hosting to VPS or dedicated hosting, or upgrading to higher-tier plans within the same host type. Evaluate the options based on your website’s specific needs.
- Consideration for E-commerce: If your website involves e-commerce and experiences growth in transactions and data, ensure that your hosting plan can handle the increased load. Upgrading to a plan with more resources and enhanced security features may be necessary.
- Database optimization: For websites heavily reliant on databases, optimizing database performance is crucial. Consider hosting plans that offer database-specific optimizations or explore managed database services to improve efficiency.
- Backup and security enhancements: As your website grows, prioritize backup solutions and security enhancements. Upgrading to plans that include automated backups, enhanced security measures, and SSL certificates contributes to the overall stability and protection of your website.
Also read: [NOTE] Migrating from a Dedicated Vietnam server to a Cloud Hosting
15. FAQ
15.1. Can I host my website for free?
15.2. What is hosting in website and what types of hosting are available?
Several types of host are available to cater to different website needs.
- Shared host involves multiple websites sharing resources on a single server, making it cost-effective for smaller websites.
- VPS offers dedicated virtual environments within a shared server, providing more control and resources.
- Dedicated host provides an entire physical server exclusively for one website, offering maximum control and performance.
- Cloud host utilizes a network of interconnected servers, allowing dynamic resource allocation and scalability.
- Managed host includes technical assistance and maintenance services, easing the burden on website owners.
Each type of hosting has its advantages, making it crucial to choose based on your website’s size, traffic, and specific requirements.
15.3. Can I change my web hosting provider without affecting my website?
15.4. Does web hosting require technical expertise?
15.5. Is it possible to upgrade my hosting plan in the future?
15.6. How can I ensure the security of my website with web hosting?
Website security starts with choosing a reliable web host provider that offers robust security features. Prioritize providers with:
- Strong uptime guarantees and server redundancy: minimized downtime and resilience against outages.
- Firewalls and malware scanning: active protection against malicious attacks and potential threats.
- Regular software updates and patching: ensures vulnerabilities are addressed promptly.
- SSL certificates: encrypts data transfer between your website and users, building trust and protecting sensitive information.
- Access control and user management: restricts unauthorized access to your website and data.
16. Conclusion
So, now you know what is web hosting, what is hosting for a website and how it works. It is the secret key, the unsung hero that empowers every website to rise and shine. Whether you’re a budding blogger or a seasoned business owner, understanding this core principle is key to navigating the online world with confidence.
Start exploring hosting options, choose the right platform for your needs, and unleash the true potential of your website. Remember, in the vast digital landscape, a solid foundation built on secure and reliable hosting is your key to standing out and thriving.
Find out more articles at our Blog and don’t hesitate to contact us for support:
- Email: support@vinahost.vn
- Hotline: 1900 6046
- Livechat: https://livechat.vinahost.vn/chat.php
Read more:
What is a Parked Domain: What You Need to Know
What is a Subdomain? Exploring the Difference Between Domains & Subdomains