A Virtual Private Server (VPS) provides dedicated resources within a shared hosting environment, offering a balance between performance and cost-efficiency. However, with increased control and customization capabilities comes the responsibility of ensuring robust security measures. VPS security encompasses a range of practices and strategies designed to protect your server from potential threats, including malware, unauthorized access, and data breaches. By adopting the practices in this VinaHost‘ article, you can minimize vulnerabilities, protect sensitive data, and maintain the integrity and availability of your online services.
1. What is VPS Security?
VPS security is a set of practices and tools used to safeguard your VPS from unauthorized access, data breaches, malware, and other cyber threats. While VPS offers isolation and more control compared to shared hosting, it’s not completely secure like a dedicated server. Therefore, implementing these security measures helps mitigate risks and maintain a secure hosting environment.
Also Read: What is VPS? | Unveiling the Power Behind Virtual Private Servers
2. Why is VPS Security Important?

VPS security is important for many reasons as follows:
Protects your website and data:
- Security measures help protect sensitive information, such as personal data, financial records, and proprietary business information, from unauthorized access and breaches.
- Ensuring that data is not tampered with or altered by unauthorized parties is vital for maintaining the accuracy and reliability of your information.
- Effective security prevents unauthorized users from accessing your server and data, reducing the risk of data theft, vandalism, and other malicious activities.
- By securing your VPS, you enhance your business’s resilience against cyber threats, helping to sustain operations and recover quickly from potential disruptions.
Maintaining service availability:
- Security measures protect your VPS from attacks such as Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, which can disrupt services and make your website or application unavailable to users.
- By preventing security breaches and minimizing downtime, you ensure that your services remain consistently available to your users and customers.
Preserves reputation:
- A secure VPS hosting helps build and maintain trust with your customers and users, who expect their data to be handled securely.
- Avoiding security incidents protects your brand’s reputation, as breaches can lead to negative publicity and loss of customer confidence.
- For businesses that rely on proprietary software, algorithms, or content, securing the VPS is essential to protect intellectual property from theft or unauthorized use.
Financial protection:
- Security breaches can lead to significant financial losses due to downtime, data loss, legal fees, and remediation costs.
- Investing in VPS security helps prevent costly incidents, providing long-term savings by avoiding the fallout from security breaches.
- Security measures are a critical part of business continuity planning, ensuring that your operations can continue even in the face of security threats.
Compliance and legal requirements:
- Regulations: A wide range of industries must comply with rigorous data protection regulations, such as GDPR and HIPAA. Ensuring your VPS is secure helps you comply with these legal requirements and avoid penalties.
- Standards: Adhering to security standards and best practices is often necessary for certifications and customer trust.
Also read: What is Linux VPS? | Choosing the Right Linux VPS Provider
3. Best Practices for VPS Security

In this part, VinaHost will show you how to secure VPS with common practices as follows:
3.1. Choosing a Reputable VPS Provider
Choosing a reputable VPS provider is necessary for ensuring the security and reliability of your hosting environment. You can start by evaluating providers based on their robust security measures, including data center security, network protection, and encryption protocols.
After that, you need to assess the reliability of their infrastructure, ensuring they use enterprise-grade hardware and have redundant systems to minimize downtime. Responsive support is also vital; look for 24/7 customer service with a knowledgeable technical team.
Additionally, you should review the provider’s security policies for compliance with industry standards and regular audits. Uptime guarantees should be examined through their Service Level Agreements (SLA) and historical performance data.
Finally, you have to consider customer reviews and testimonials to gauge the provider’s reputation and reliability. By carefully selecting a provider based on these criteria, you can establish a secure and dependable VPS hosting environment.
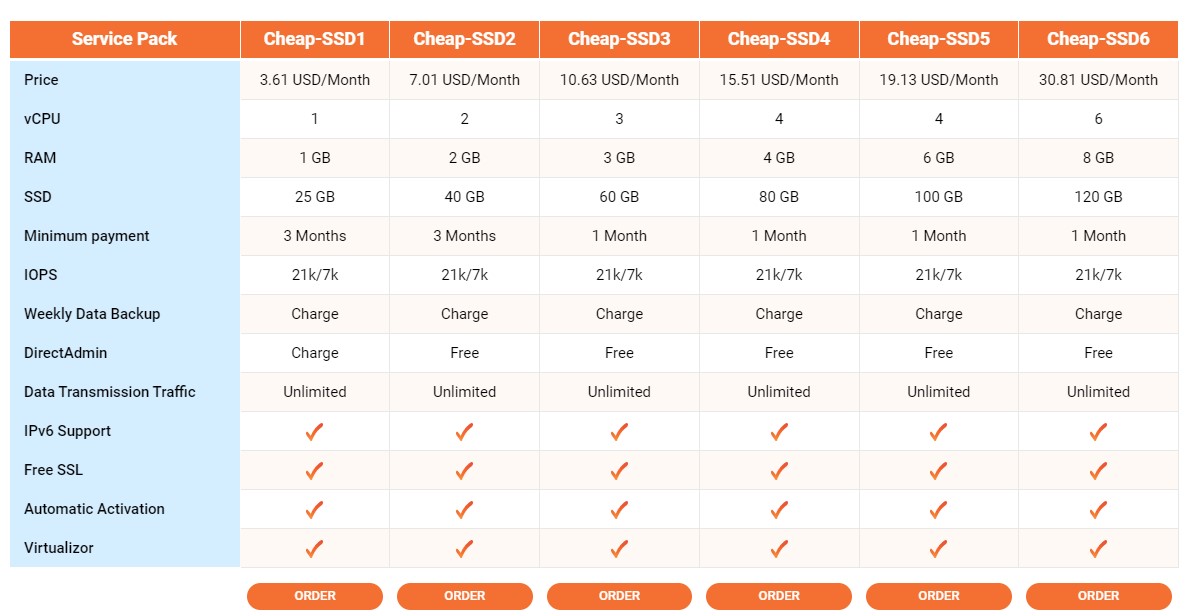
Additionally, we also provide:
3.2. Disable root logins
We all know that the root account, with its unrestricted access, is a common target for attackers. By disabling direct root logins, you significantly reduce the risk of exploitation.
Instead, you can create a separate user account with sudo privileges to perform administrative tasks. This approach limits the potential damage of compromised accounts, as the sudo user has specific permissions rather than full root access.
Besides, using sudo allows for logging and monitoring of administrative activities, enhancing accountability and auditability. Implementing this practice, along with two-factor authentication for the sudo user, strengthens the security of your VPS and helps maintain a secure hosting environment.
3.3. Firewall

A firewall acts as a barrier between your server and potential threats, blocking unauthorized access while permitting legitimate connections. You can define rules that specify which ports and IP addresses are allowed to communicate with your server, thereby mitigating the risk of unauthorized intrusions and attacks by setting up a firewall.
Tools like iptables and UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall) offer robust and flexible options for managing firewall rules, enabling you to tailor security settings to your specific needs.
There are many VPS providers offering integrated firewall services that simplify the configuration process and provide a user-friendly interface for managing security policies. Implementing a firewall not only protects your server from malicious traffic but also enhances overall network security, ensuring that only trusted and necessary connections are maintained.
Also read: What is SSD VPS Hosting? | Everything You Need to Know
3.4. Keep Your Software Up-to-Date
We think that neglecting the software updates can leave your server exposed to cyber threats and potential breaches.
Software developers continuously release updates to address security flaws, enhance performance, and add new features. You need to keeping your software up-to-date by regularly updating the operating system, control panels, and all installed applications with the latest security patches and updates.
This will help you maintain a robust defense against emerging threats and ensure the overall stability and security of your VPS environment. Don’t worry because automated update tools and regular maintenance schedules can help ensure that your system remains current and secure.
By doing so, you protect your server from known vulnerabilities and exploits that attackers could use to gain unauthorized access or disrupt services.
3.5. User Management
Effective user management will help you to maintain the security of your VPS.
You have to implement the principle of least privilege involves creating user accounts with only the necessary permissions required for their specific roles. This minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and potential damage from compromised accounts.
Besides, you should regularly review and update user access to ensure that only authorized personnel have access to critical systems and resources, further reducing the risk of insider threats and unauthorized activities.
By restricting permissions to the minimum necessary, you can limit the potential impact of security breaches and maintain a more secure and manageable server environment. Additionally, maintaining detailed records of user access and changes can help in auditing and tracking user activities, contributing to overall security and compliance efforts.
3.6. Backups
Implementing a robust backup strategy, including off-site or cloud backups, adds an additional layer of protection, safeguarding your data against local disasters or systemic failures.
By scheduling automated backups, you can ensure that all important data and system configurations are consistently saved to secure locations, minimizing the risk of data loss due to hardware failures, cyber attacks, or human error.
You need to test these backups periodically to confirm that they can be restored quickly and accurately in the event of data loss or corruption. This not only guarantees the integrity of your backup process but also ensures that your business operations can resume with minimal downtime and disruption.
3.7. Install an antivirus

Install and maintain reliable antivirus software on your VPS to detect and remove malicious software. You should regularly scans and real-time protection can help prevent infections and compromises.
While installing antivirus software on a VPS might seem intuitive, it’s not the most effective solution. Antivirus programs are designed for personal computers and may not be optimized for the specific threats on a VPS.
Instead, you need to choose intrusion detection systems to monitor for suspicious activity, keep your software updated to patch vulnerabilities malware exploits, and utilize firewalls to filter traffic. In some limited cases, like managing user-uploaded files, an antivirus might offer extra protection, but you should focus on core security measures first.
3.8. Use a malware scanner
By implementing reliable malware scanning solutions and scheduling regular scans, you can promptly address security issues and ensure that your server remains secure and operational.
Malware scanners work by identifying and removing malicious software that can compromise your server’s functionality and security.
They help to prevent data breaches, unauthorized access, and other cyber threats by continuously monitoring your system for signs of infection or abnormal behavior.
You need to regularly scan your server for malicious code, vulnerabilities, and suspicious activities allows for early detection and mitigation of potential threats.
Additionally, integrating these tools with your overall security strategy enhances your ability to maintain a robust and resilient hosting environment.
3.9. Use SFTP(Secure File Transfer Protocol)
Utilizing SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol) is a fundamental aspect of VPS security, providing a secure method for transferring files between your local system and the server.
Unlike traditional FTP, which sends data in plaintext, SFTP encrypts data during transmission, protecting it from interception and unauthorized access.
By using SFTP for file transfers, you ensure that sensitive information, such as login credentials, configuration files, and user data, remains secure. SFTP also supports key-based authentication, further enhancing security by eliminating the need to transmit passwords over the network.
Implementing SFTP as the preferred method for file transfers helps safeguard your VPS against potential attacks, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of your data exchanges. Additionally, many modern FTP clients and server configurations support SFTP out of the box, making it easy to adopt as part of your security practices.
3.10. Install SSL certificates
Installing SSL certificates is not only a best practice for VPS security but also essential for complying with industry regulations and meeting user expectations regarding data privacy and security.
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificates encrypt data transmitted between the server and users’ web browsers, ensuring confidentiality and integrity. This encryption prevents malicious actors from intercepting and deciphering the information exchanged, safeguarding sensitive details like login credentials, payment information, and personal data.
Besides, SSL certificates authenticate the identity of your server, reassuring users that they are connecting to a legitimate and trustworthy website or application.
By encrypting data in transit and verifying server authenticity, SSL certificates foster trust among users and protect against various forms of cyber threats, including man-in-the-middle attacks and data breaches.
3.11. Use strong passwords
Using strong passwords is a fundamental yet effective measure for enhancing the security of your VPS. Strong passwords are characterized by their complexity, length, and uniqueness, making them resilient against brute-force attacks and password guessing techniques employed by hackers.
When creating passwords for user accounts, administrative access, or database credentials, adhere to the following best practices:
- Complexity: Include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters to increase the complexity of the password.
- Length: Opt for longer passwords, ideally consisting of 12 characters or more, as longer passwords are inherently more secure against cracking attempts.
- Uniqueness: Avoid reusing passwords across multiple accounts or services to prevent a compromised password from compromising other accounts.
- Avoid Common Patterns: Refrain from using easily guessable patterns, such as sequential numbers or common words found in dictionaries, as these are vulnerable to dictionary attacks.
Implementing strong passwords across your VPS environment significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access and strengthens your overall security posture. You should consider using password management tools to generate, store, and securely manage complex passwords for different accounts and services, further enhancing password security and convenience.
3.12. Enable two-factor authentication (2FA)
3.13. Monitor server logs
4. FAQs
4.1. Is VPS security too complicated?

VPS security can seem complex for those who do not have technical skills due to the range of security measures and techniques involved, but it doesn’t have to be overwhelming.
You can break down security tasks into manageable steps, such as implementing strong passwords, enabling firewalls, and keeping software updated
Leveraging managed hosting services or security-focused VPS providers can help you alleviate much of the burden by offering built-in security features, automated updates, and expert support.
Ultimately, while securing a VPS requires understanding various concepts and implementing multiple layers of protection, there are many resources, tools, and best practices are available to simplify the process.
4.2. How can I monitor activity on my VPS?
You can monitor activity on your VPS using various tools and techniques:
- Server logs: Regularly review system logs, including access logs, error logs, and authentication logs, to track user activity, network traffic, and system events.
- Monitoring software: Install server monitoring software like Nagios, Zabbix, or Prometheus to track system performance metrics, such as CPU usage, memory usage, disk space, and network activity, in real-time.
- Security information and event management (SIEM) tools: SIEM tools like Splunk or ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) aggregate and analyze log data from multiple sources, enabling you to detect security incidents and anomalies.
- Intrusion detection systems (IDS): Deploy IDS solutions like Snort or Suricata to monitor network traffic for signs of malicious activity, including intrusion attempts, malware, and suspicious behavior.
- File integrity monitoring (FIM): Use FIM tools like Tripwire or OSSEC to monitor changes to critical system files and directories, helping to detect unauthorized modifications or tampering.
- User activity monitoring: Implement user activity monitoring tools or audit trails to track user logins, commands executed, and file access, enabling you to identify suspicious or unauthorized activities.
- Alerting and notifications: Set up alerts and notifications for critical events, such as high CPU usage, disk space exhaustion, or security incidents, to receive timely notifications and respond proactively to potential issues.
Also Read: What is Linode VPS? | Everything You Need to Know
4.3. What is the difference between a firewall and an IDS/IPS?

Firewalls, IDS, and IPS all play important roles in VPS security, but they function in distinct ways.
Firewalls primarily focus on access control and traffic filtering, while IDS/IPS solutions focus on detecting and responding to security threats and anomalies within the network. Combining both technologies in a layered security approach provides comprehensive protection against a wide range of cyber threats.
- Firewall: A firewall acts as the first line of defense, controlling incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined security rules. It allows authorized traffic (like legitimate website visitors) and blocks unauthorized traffic (like malicious attacks). Firewalls typically filter traffic based on factors like IP addresses, ports, and protocols.
- Intrusion Detection System (IDS): An IDS monitors network traffic and server activity for signs of potential security breaches or attacks. It can detect suspicious patterns, anomalies, or attempts to exploit vulnerabilities. However, unlike a firewall, an IDS doesn’t actively block threats. It typically generates alerts and logs suspicious activity, requiring further investigation or manual intervention.
- Intrusion Prevention System (IPS): An IPS combines the functionalities of a firewall and an IDS. An IPS not only detects suspicious activity but also actively takes steps to prevent it. This might involve blocking traffic, dropping packets, or resetting connections. IPS systems offer a more proactive approach to security compared to IDS.
You can choose the Right Security solution in a simple way:
- Firewalls: Essential for all VPS setups. They provide a basic layer of security by filtering traffic.
- IDS: Effective for detecting a wider range of threats and potential vulnerabilities.
- IPS: Offers a more proactive approach but can be more complex to configure and might introduce performance overhead.
4.4. What are some common VPS security threats?
There are some common VPS security threats as follows:
- Unauthorized access: Unauthorized access attempts, such as brute-force attacks, password guessing, or exploiting weak authentication mechanisms, can lead to unauthorized users gaining access to your VPS.
- Malware and viruses: Malicious software, including viruses, worms, Trojans, and ransomware, can infect your VPS, compromising data, disrupting services, and causing financial losses.
- Zero-day vulnerabilities: These are previously unknown software flaws that attackers exploit before a security patch is available. Keeping software updated helps minimize the window of vulnerability.
- Denial of Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks: DoS and DDoS attacks aim to overwhelm your server with excessive traffic, rendering it inaccessible to legitimate users and disrupting services.
- Data breaches: Data breaches occur when sensitive information, such as user credentials, financial data, or personal information, is accessed or stolen by unauthorized parties, often resulting in identity theft, financial fraud, or reputational damage.
- SQL injection: SQL injection attacks exploit vulnerabilities in web applications to execute malicious SQL queries against databases, potentially leading to data leakage, data manipulation, or unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Cross-Site scripting (XSS): XSS attacks inject malicious scripts into web pages viewed by other users, allowing attackers to steal session cookies, redirect users to malicious sites, or perform unauthorized actions on behalf of legitimate users.
- Phishing and social engineering: Phishing attacks use deceptive emails, messages, or websites to trick users into revealing sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial details, which can be used for identity theft or further attacks.
- Insider threats: Insider threats involve malicious actions or negligence by authorized users, such as employees or contractors, who misuse their privileges to steal data, disrupt services, or sabotage systems.
- Insecure configurations: Poorly configured server settings, outdated software, misconfigured permissions, or default passwords can create security vulnerabilities that attackers exploit to gain unauthorized access or escalate privileges.
- Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks: MitM attacks intercept and manipulate communication between two parties, allowing attackers to eavesdrop on sensitive information, modify data in transit, or impersonate legitimate users or servers.
4.5. What are the benefits of using a managed VPS service?

Managed VPS services are a good option for businesses or individuals who:
- Lack the technical expertise to manage a VPS themselves.
- Optimize their time and focus on core business activities.
- Have high security requirements and want a proactive approach to security management.
- Require reliable and high-performing VPS hosting with technical support readily available.
While there is an added cost associated with managed VPS services, the benefits can outweigh the cost for many users, especially those who prioritize security, performance, and ease of management:
- Expert support: Managed VPS providers offer expert technical support, including 24/7 monitoring, troubleshooting, and assistance with server management tasks. This allows you to focus on your business without worrying about server maintenance or technical issues.
- Proactive security management: Managed VPS providers typically have dedicated security teams responsible for implementing and maintaining security measures, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and vulnerability scanning. This proactive approach helps to identify and address potential security threats before they can cause damage.
- Reliability: Managed VPS providers typically operate high-performance infrastructure with redundant hardware, network connectivity, and data backups, minimizing the risk of downtime and ensuring reliable service availability for your websites and applications.
- Scalability: Managed VPS services offer flexible scalability options, allowing you to easily upgrade or downgrade your server resources as your business needs evolve. This ensures that your server can accommodate changes in traffic, workload, or resource requirements without interruption.
- Simplified VPS management: Managed VPS services often include user-friendly control panels or management interfaces that simplify server administration tasks, such as deploying applications, managing domains, and configuring server settings. This makes it easier for non-technical users to manage their VPS environment.
- Performance optimization: Managed VPS providers optimize server performance by fine-tuning server configurations, optimizing software settings, and implementing caching mechanisms to enhance website speed and responsiveness.
- Backup and disaster recovery: Managed VPS services typically include automated backup and disaster recovery solutions, ensuring that your data is regularly backed up and can be quickly restored in case of data loss, corruption, or server failure.
Also Read: What is gaming VPS? | Choosing the Right gaming VPS Provider
5. Conclusion
In closing, ensuring robust security for your Virtual Private Server (VPS) is crucial in protecting your digital assets and maintaining the integrity and availability of your online services.
VPS security is an ongoing process, not a one-time fix. By adhering to the best practices outlined above and staying vigilant, you can create a robust defense system for your VPS and safeguard your website’s integrity.
Find out more articles at our Blog and don’t hesitate to contact us for support:
- Email: support@vinahost.vn
- Hotline: 1900 6046
- Livechat: https://livechat.vinahost.vn/chat.php
>>> Read more:
What is GPU VPS? | Choosing the Right GPU VPS Provider
What is the difference between VPS and Shared Hosting


 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt English
English 简体中文
简体中文