VPS (virtual private server) is known as one of the most popular web hosting solutions nowadays. VPS is preferred because it overcomes the shortcomings of shared hosting and dedicated servers.In the following article by VinaHost, let’s find out what is VPS? What are the advantages and disadvantages of VPS? How many types of VPS? How does VPS work and how to choose the most suitable VPS service for your needs! Check it out now!
1. Introduction to VPS
1.1. What is VPS?
What is VPS? VPS stands for Virtual Private Server. It is a virtualized server that acts as a dedicated server within a larger physical server. Multiple virtual servers can coexist on a single physical server, each running its own operating system (OS) and hosting applications independently.
VPS hosting provides users with more control and customization compared to shared hosting, offering a balance between the affordability of shared hosting and the flexibility of a dedicated server. Users can configure their VPS environment, install software, and have dedicated resources (such as CPU, RAM, and storage) allocated to their virtual server.
If you’re looking for an upgrade from shared hosting but don’t need the full power and expense of a dedicated server, VPS could be a great option.
VPS hosting is commonly used for hosting websites, applications, or other online services:
- Websites with moderate to high traffic
- Businesses that need more control over their server environment
- Websites requiring specific software or configurations
- Businesses that are expecting to grow and need scalability
Also Read: What is Linux VPS? | Choosing the Right Linux VPS Provider
1.2. Importance of VPS

The importance of VPS hosting lies in its ability to provide users with a balance between affordability, flexibility, and performance.
- Resource allocation: VPS hosting offers dedicated resources, including CPU, RAM, and storage, ensuring that users have a guaranteed share of resources. This prevents resource contention that can occur in shared hosting environments, leading to more consistent performance.
- Isolation and security: Each virtual private server operates independently within its virtualized environment, providing a level of isolation from other virtual servers on the same physical machine. This isolation enhances security by minimizing the impact of security breaches on neighboring VPS instances.
- Customization and control: VPS users have greater control over their server environment. They can install and configure software, customize server settings, and have more flexibility in managing their hosting environment compared to shared hosting.
- Scalability: VPS hosting allows users to scale resources based on their requirements. As the needs of a website or application grow, users can easily upgrade their VPS plan to access more resources, such as additional CPU cores, RAM, and storage.
- Performance: VPS hosting typically offers better performance compared to shared hosting. Since resources are dedicated to each virtual server, there is less impact from the activities of other users on the same physical server.
- Affordability: While not as expensive as dedicated hosting, virtual private server provides a cost-effective solution for users who need more resources and control than shared hosting but don’t require an entire physical server.
- Hosting multiple websites: VPS hosting is suitable for hosting multiple websites or applications on a single server. Each website or application can have its own isolated environment, ensuring better stability and security.
- Root access:VPS users often have root or administrator access, allowing them to make system-level changes and install software as needed. This level of access is not typically available in shared hosting environments.
- Reliability: VPS hosting offers a higher level of reliability compared to shared hosting. Since each VPS operates independently, issues affecting one VPS are less likely to impact others.
- Dedicated IP address: VPS hosting often includes a dedicated IP address for each virtual server. This is beneficial for tasks such as SSL certificate installation and can improve email deliverability.
2. How Does VPS Work?
What is VPS and how does it work?
Imagine a physical server:
- This server has powerful hardware like CPU, RAM, and storage.
- Traditionally, this server could be used to host one website (dedicated hosting), or be divided into smaller sections for multiple websites (shared hosting).
VPS uses virtualization technology:
- This technology essentially creates virtual partitions within the physical server.
- Each partition acts like a separate, isolated server with its own dedicated resources like CPU, RAM, and storage.
- This allows multiple VPS users to share the physical server, but each user has their own dedicated space and resources.
Here’s what happens when you use VPS:
- You rent a VPS plan from a hosting provider.
- The provider configures a virtual partition on the physical server based on your chosen plan (e.g., amount of RAM, storage).
- You get root access to your virtual partition, giving you complete control over its settings and software.
- You can install your operating system, applications, and configure everything according to your needs.
- Your website runs on your isolated virtual server, unaffected by other users on the physical server.
3. What is the VPS’s Advantages
3.1. Cost-effectiveness
VPS hosting offers a cost-effective solution that strikes a balance between shared and dedicated hosting. Users benefit from dedicated resources without the expense of an entire physical server. This makes it an economical choice for businesses and individuals with varying resource needs.
3.2. Scalability and Flexibility
VPS hosting provides scalability, allowing users to easily adjust resources such as CPU, RAM, and storage based on their requirements. This flexibility ensures that the hosting environment can adapt to the evolving needs of websites or applications, making it suitable for growing
3.3. Enhanced Security
Each VPS operates independently with its own isolated environment. This isolation enhances security by minimizing the impact of security breaches on other virtual servers. Users have control over their security configurations, including firewalls and access controls, contributing to a more secure hosting environment.
3.4. Improved Performance
Dedicated resources allocated to each VPS result in improved performance compared to shared hosting. Since the activities of one VPS do not directly impact others on the same physical server, users experience more consistent and reliable performance. This is particularly beneficial for resource-intensive applications and websites.
Also Read: What is gaming VPS? | Choosing the Right gaming VPS Provider
4. Types of VPS Hosting

4.1. Unmanaged VPS
What is VPS unmanaged? Unmanaged VPS hosting grants users complete control over their virtual server. With the freedom to configure and manage every aspect of the server, it is suitable for those with advanced technical skills. Users take on responsibilities such as server setup, security, and software installations. While providing maximum customization, it requires users to handle server maintenance independently.
Pros:
- Most affordable option
- Full root access and control over the server environment
- Ideal for technically savvy users or businesses with dedicated IT staff
Cons:
- Requires technical expertise to manage and maintain the server
- Responsible for security updates, software installation, and troubleshooting
- Can be time-consuming and complex for non-technical users
4.2. Managed VPS
What is VPS managed? Managed VPS hosting offers a more hands-off approach, making it ideal for users with limited technical expertise. Hosting providers take care of server maintenance, security updates, and troubleshooting, allowing users to focus on their websites or applications. This type of VPS is characterized by professional support and management services, providing a hassle-free hosting experience.
Pros:
- The hosting provider handles server management, maintenance, and updates
- Frees up your time and resources to focus on your website and business
- Often includes basic security monitoring and support
- Ideal for users who prefer a hands-off approach or lack technical expertise
Cons:
- More expensive than unmanaged VPS
- Less control over the server environment compared to unmanaged options
- May have limitations on software installation or customization
Also Read: The difference between Managed VPS and Unmanaged VPS
4.3. Cloud VPS
What is VPS Cloud? Cloud VPS utilizes cloud infrastructure, distributing resources across multiple physical servers. This approach enhances scalability, flexibility, and overall reliability. Cloud VPS hosting allows users to easily scale resources based on demand, providing high availability and redundancy. It is well-suited for applications or websites with fluctuating resource needs.
Pros:
- Highly scalable and flexible resource allocation
- On-demand resource scaling based on traffic spikes or needs
- High availability and fault tolerance due to distributed infrastructure
- Ideal for websites with unpredictable traffic patterns or expecting significant growth
Cons:
- Can be more complex to set up and manage compared to traditional VPS
- May have slightly higher costs depending on resource usage
4.4. SSD VPS
What is VPS SSD? SSD VPS hosting utilizes Solid State Drives (SSDs) for storage, offering faster data access speeds compared to traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs). This results in improved performance for applications and websites. SSD VPS is particularly beneficial for tasks that involve frequent data read and write operations, providing a speed boost that enhances overall responsiveness.
Pros:
- Utilizes Solid State Drives (SSDs) for faster storage access
- Significantly faster loading times and website performance compared to traditional HDDs
- Ideal for websites requiring high I/O operations or dealing with large data volumes
Cons:
- May be slightly more expensive than traditional VPS with HDD storage
- Storage capacity is generally lower than HDD-based VPS options
Also Read: What is SSD VPS Hosting? | Everything You Need to Know
5. Choosing the Right VPS Provider? What is VPS considerations?
5.1. Reliability and Uptime
- Look for providers with a proven track record of high uptime (ideally above 99.9%).
- Check independent reviews and user feedback to gauge their reliability and performance consistency.
- Consider offering redundancy features like backup servers and disaster recovery plans.
5.2. Customer Support
- Evaluate the quality and availability of their customer support. Do they offer 24/7 support via phone, chat, and email?
- Look for responsive and knowledgeable support representatives who can effectively address your technical needs.
- Check the provider’s knowledge base and FAQs for readily available self-help resources.
5.3. Pricing and Plans
- Compare different plans and providers based on your specific resource requirements (RAM, storage, CPU).
- Analyze resource scalability options to accommodate future growth and avoid unnecessary costs.
- Be aware of hidden fees or additional charges associated with certain features or services.
- Consider long-term contracts vs. month-to-month options based on your budget and commitment needs.
5.4. Server Location
- Choose a server location geographically closer to your target audience for faster loading times and improved user experience.
- Consider data privacy regulations and compliance requirements when choosing a server location, especially if you handle sensitive data.
- Some providers offer multi-location hosting options for broader reach and redundancy.
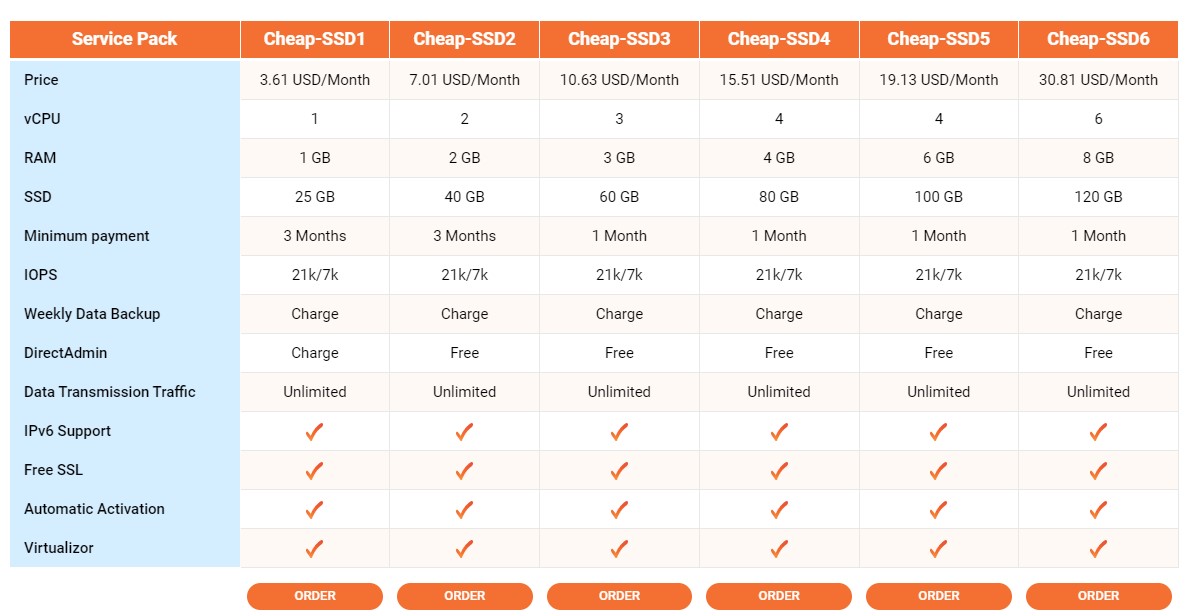
Additionally, we also provide:
| Server Vietnam | Colocation in Vietnam | Server Cambodia | Cloud VPS Cambodia |
| VPS Indonesia | VPS Thailand | VPS Germany | Server Indonesia |
6. Setting Up a VPS
6.1. OS Installation
Choosing and installing the right operating system (OS) is the foundation of setting up a VPS, as it determines the environment for your applications and services.
- Select a compatible OS based on your requirements (Linux distributions like Ubuntu, CentOS, or Windows Server).
- Access the VPS control panel or use command-line tools to initiate the OS installation.
- Follow the installation prompts, configure settings, and set up user accounts.
6.2. Control Panel Configuration
Control panels simplify server management, providing a user-friendly interface to monitor and control various aspects of the VPS.
- Choose a control panel (e.g., cPanel, Plesk, or Webmin) based on your familiarity and requirements.
- Install the control panel using the provided instructions or through command-line tools.
- Configure the control panel settings, including user accounts, security, and server preferences.
Also Read: [UPDATED] TOP 20 Best VPS Control Panel Free & Paid
6.3. Domain and Website Setup
Configuring domains and setting up websites is essential for making your content accessible on the internet.
- Register a domain through a domain registrar or use an existing domain.
- Point the domain’s DNS records to your VPS IP address.
- Set up virtual hosts or server blocks to host multiple websites on the VPS.
- Install and configure a web server (e.g., Apache, Nginx) to handle website requests.
7. Managing a VPS
7.1. Regular Backups

- Implement automated backup schedules to capture critical data and configurations.
- Store backups in secure, offsite locations to prevent data loss in the event of server failures.
- Periodically test the restoration process to ensure the viability of backups.
7.2. Security Updates and Patches
Keeping the VPS up-to-date with the latest security updates and patches is essential for protecting against vulnerabilities and potential exploits.
- Enable automatic updates for the operating system and installed software.
- Regularly check for security advisories and apply patches promptly.
- Implement a vulnerability scanning routine to identify and address potential security issues.
7.3. Monitoring and Optimization
Continuous monitoring helps identify performance issues, potential bottlenecks, and abnormal behavior, allowing for proactive optimization.
- Utilize monitoring tools to track server metrics such as CPU usage, memory consumption, and disk space.
- Set up alerts to notify administrators of unusual activities or resource constraints.
- Conduct regular performance reviews and optimize configurations based on monitoring data.
8. What is VPS Applications?
8.1. Website Hosting
One of the most common uses of VPS is hosting websites. VPS hosting provides more resources and customization options compared to shared hosting, making it suitable for hosting multiple websites, handling increased traffic, and running resource-intensive applications.
Advantages:
- Dedicated resources ensure consistent website performance.
- Customizable server configurations for specific website requirements.
- Ability to host multiple websites on a single VPS.
Also Read:
8.2. Virtual Desktops
VPS can be used to create virtual desktop environments, allowing users to access a virtualized desktop with their preferred operating system and applications. This is especially beneficial for remote work scenarios, enabling users to access their desktop environment from any device.
Advantages:
- Access to a consistent desktop environment from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Enhanced security and data protection compared to traditional desktops.
- Efficient resource utilization for multiple virtual desktop instances on a single VPS.
Also Read: What is a Virtual Dedicated Server? | How does VDS work?
8.3. Development and Testing Environments
VPS serves as an ideal environment for software development and testing. Developers can create isolated development environments, replicate production settings, and test applications in a controlled setting before deployment.
Advantages:
- Isolated environments prevent interference with other development or production systems.
- Customizable configurations to match specific application requirements.
- Ability to quickly provision and de-provision environments as needed.
8.4. Gaming Servers
Gamers often utilize VPS to host private game servers. This allows them to create customized gaming experiences, control access to the server, and host multiplayer games for friends or communities.
Advantages:
- Dedicated resources for optimal gaming server performance.
- Control over server settings and game configurations.
- Ability to host a variety of multiplayer games on a single VPS.
Additional Applications:
- Database servers: Run dedicated MySQL, PostgreSQL, or other database servers for high performance and scalability.
- Media streaming: Host video and audio streaming services for live events, podcasts, or educational content.
- Email servers: Manage your own email infrastructure for secure and reliable communication.
- Machine learning and AI: Train and run machine learning models on your own VPS for specific applications.
- VPN servers: Create a secure connection for remote users to access your network resources.
9. Future Trends of VPS
9.1. Containerization technology
Containerization technologies like Docker and Kubernetes are revolutionizing how applications are deployed and managed on VPS. Containers create isolated environments for applications, ensuring better resource utilization, scalability, and security.
Benefits:
- Improved density: Run more applications on a single VPS, optimizing resource usage and cost efficiency.
- Faster deployments: Simplified application deployment and updates, leading to quicker time-to-market.
- Enhanced portability: Easily move applications across different VPS environments without compatibility issues.
9.2. Serverless Computing
Serverless computing eliminates the need to manage server infrastructure, allowing developers to focus on building and deploying applications. Platforms handle server provisioning, scaling, and maintenance automatically.
Benefits:
- Reduced operational overhead: Developers focus on code, not server management, saving time and resources.
- Pay-per-use model: Only pay for the resources your application uses, leading to cost optimization.
- High scalability: Serverless platforms automatically scale based on demand, ensuring seamless user experience.
9.3. Edge Computing
Edge computing brings processing power closer to users, reducing latency and enhancing performance for applications requiring real-time responsiveness. Virtual private server providers are increasingly offering edge computing capabilities.
Benefits:
- Reduced latency: Faster response times for applications like live streaming, gaming, and IoT devices.
- Improved user experience: Smoother and more responsive applications, leading to higher user satisfaction.
- Reduced bandwidth costs: Processing data closer to users minimizes data transfer across long distances.
Also Read: Top 15 Best VPS Hosting Providers [Updated]
10. What is VPS server? What is Shared Hosting? VPS vs Shared Hosting
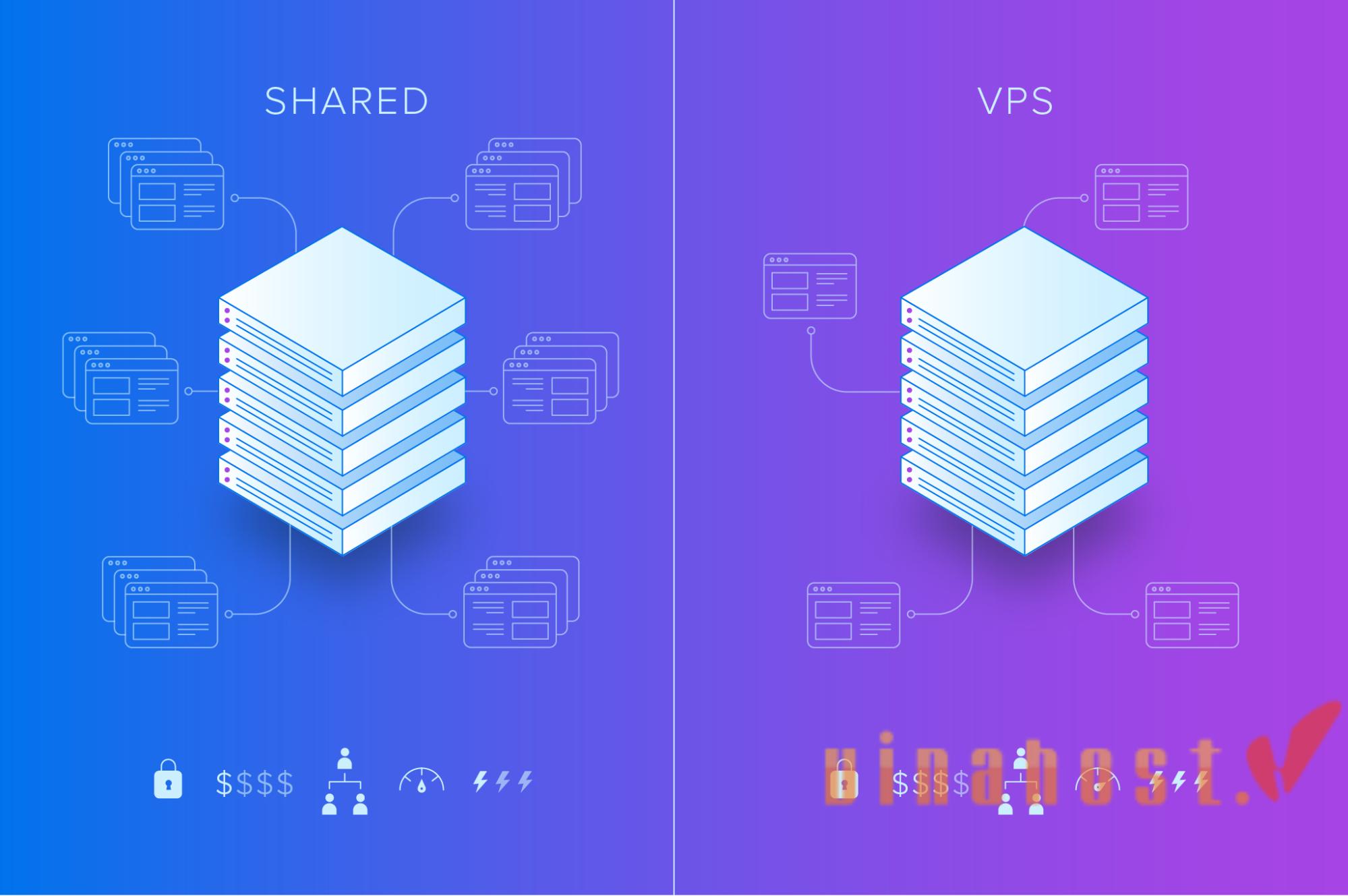
| Feature | What is VPS server? | What is Shared Hosting? |
|---|---|---|
| Resource Allocation | Dedicated resources for each user, including CPU, RAM, and storage. | Shared resources among multiple users on the same server. |
| Performance | More consistent performance as resources are dedicated. Less impacted by other users. | Performance can be variable, influenced by activities of other users on the same server. |
| Customization and Control | More control over server settings, software installations, and choice of operating system. | Limited customization options; control through hosting provider’s control panel. |
| Security | Higher security with isolation between VPS instances, reducing the risk of security breaches from other users. | Potential security risks as activities on one user’s site can impact others on the same server. |
| Scalability | Scalable with the ability to upgrade or downgrade resources based on user needs. | Limited scalability due to shared resources, potential restrictions on resource scaling. |
| Cost | Generally more expensive than shared hosting, reflecting dedicated resources and increased control. | More cost-effective, making it suitable for individuals and small businesses with budget constraints. |
| Isolation | Greater isolation between VPS instances, reducing the impact of one user on others. | Limited isolation; performance of one user’s site can affect others on the same server. |
| Suitability | Ideal for medium to large-sized websites, businesses requiring dedicated resources and customization. | Suitable for smaller websites, personal blogs, or businesses with lower traffic and resource requirements. |
11. What is a VPS server? What is Dedicated Server? VPS vs Dedicated Server

| Feature | What is a VPS server? | What is Dedicated Server? |
|---|---|---|
| Resource Allocation | Dedicated virtualized resources within a physical server, sharing the server with other VPS instances. | Entire physical server dedicated to a single user or entity, providing exclusive access to all resources. |
| Performance | Consistent performance but may be influenced by other VPS instances on the same server. | Highest level of performance as all resources are dedicated solely to the user. No impact from other users. |
| Customization and Control | Customizable configurations with control over server settings, software installations, and choice of operating system. | Maximum control and customization options. Users can tailor the server environment to their specific needs. |
| Security | Higher security than shared hosting, with isolation between VPS instances. Users have their own virtual environment. | Enhanced security with no shared resources. Users have full control over security configurations and measures. |
| Scalability | Scalable with the ability to upgrade or downgrade resources, but limited by the physical server’s capacity. | Highly scalable, allowing users to upgrade components (CPU, RAM, storage) as needed without impacting other users. |
| Cost | More cost-effective than dedicated servers, making it suitable for users with budget constraints who still require dedicated resources. | Generally more expensive due to exclusive access to all server resources. Ideal for businesses with higher resource and performance needs. |
| Isolation | Good isolation between VPS instances, reducing the impact of one user on others. | Complete isolation from other users; no sharing of resources, ensuring maximum performance and security. |
| Management | Managed or unmanaged options available, with varying levels of server management provided by the hosting provider. | Users have full control and responsibility for server management. Requires more technical expertise or the use of a separate management service. |
| Suitability | Suitable for a wide range of businesses and websites requiring dedicated resources, customization, and consistent performance. | Ideal for large-scale websites, applications, or businesses with high traffic and resource-intensive requirements. |
Also Read: What is a Dedicated Server? | How Does a Dedicated Server Work?
12. What is VPS Hosting? What is Cloud Hosting? VPS vs Cloud Hosting

| Feature | What is VPS Hosting? | What is Cloud Hosting? |
|---|---|---|
| Resource Allocation | Dedicated virtualized resources within a physical server, often sharing the server with other VPS instances. | Resources are distributed across a network of interconnected virtual servers, allowing for scalability and flexibility. |
| Performance | Consistent performance, but may be influenced by other VPS instances on the same server. | Scalable performance with the ability to dynamically allocate resources based on demand. Performance can be more consistent due to the distributed nature of cloud infrastructure. |
| Customization and Control | Customizable configurations with control over server settings, software installations, and choice of operating system. | Customization options may vary. Users typically have control over certain aspects, but not the underlying infrastructure. |
| Security | Higher security than shared hosting, with isolation between VPS instances. Users have their own virtual environment. | Security measures vary. Cloud hosting providers often implement robust security features, but users share underlying infrastructure with other cloud users. |
| Scalability | Scalable with the ability to upgrade or downgrade resources, but limited by the physical server’s capacity. | Highly scalable, allowing users to scale resources vertically (upgrading components) or horizontally (adding more virtual servers) based on demand. |
| Cost | Generally more cost-effective than dedicated servers, making it suitable for users with budget constraints who still require dedicated resources. | Cost model is often pay-as-you-go or subscription-based, allowing users to pay for resources consumed. Can be cost-effective for variable workloads. |
| Isolation | Good isolation between VPS instances, reducing the impact of one user on others. | Isolation is achieved through virtualization and network segmentation. Users share physical infrastructure but operate independently. |
| Management | Managed or unmanaged options available, with varying levels of server management provided by the hosting provider. | Cloud hosting often comes with managed services, and users can delegate some infrastructure management tasks to the cloud provider. |
| Reliability | Reliability depends on the hosting provider and infrastructure. | Generally more reliable due to the distributed nature of cloud infrastructure. Redundancy and failover mechanisms enhance reliability. |
| Suitability | Suitable for a wide range of businesses and websites requiring dedicated resources, customization, and consistent performance. | Ideal for businesses with dynamic or unpredictable workloads, requiring scalability and flexibility. Suitable for startups, growing businesses, and applications with variable resource needs. |
13. FAQs
13.1. What is the difference between VPS and shared hosting?
The main difference between VPS and shared hosting lies in resource allocation and control. In shared hosting, multiple users share the same server resources, leading to potential performance fluctuations and limited customization.
In contrast, VPS provides dedicated virtualized resources within a shared physical server, offering more consistent performance and greater control over server settings, software installations, and configurations. VPS is suitable for users requiring dedicated resources and customization, while shared hosting is more cost-effective for smaller websites with lower resource demands.
13.2. Can I upgrade my VPS plan in the future?
Yes, in most cases, you can upgrade your VPS plan in the future. VPS hosting providers typically offer scalability, allowing you to increase resources such as CPU, RAM, and storage based on your evolving needs. The upgrade process usually involves contacting your hosting provider’s support or using their control panel to choose a higher-tier plan.
Keep in mind that the specific upgrade options and procedures may vary among hosting providers, so it’s advisable to check with your provider for their specific policies and instructions regarding VPS plan upgrades.
13.3. Is VPS suitable for e-commerce websites?
Yes, VPS hosting is often highly suitable for e-commerce websites. E-commerce sites, particularly those with medium to high traffic or complex functionalities, benefit from the dedicated resources and increased control that VPS hosting provides.
VPS offers better performance, scalability, and security compared to shared hosting, ensuring a more reliable and responsive online shopping experience for visitors. Additionally, the customization options available with VPS allow e-commerce businesses to tailor their hosting environment to meet specific requirements, integrate specialized software, and implement security measures essential for handling sensitive customer data in a secure manner.
13.4. Can I install any software on my VPS?
Yes, one of the advantages of using a VPS is that you typically have the freedom to install and run a wide range of software applications. VPS hosting provides a level of control and customization that allows you to choose your operating system, configure server settings, and install software based on your specific needs.
Common software installations on a VPS include web servers (e.g., Apache, Nginx), databases (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL), content management systems (e.g., WordPress, Joomla), development tools, and various other applications. However, it’s important to ensure that any software you install complies with the hosting provider’s terms of service and doesn’t violate security or resource usage policies.
13.5. How can I secure my VPS?

- Keep your software updated: Regularly update your operating system, applications, and software with the latest security patches to address known vulnerabilities.
- Strong passwords: Use strong and unique passwords for all accounts and enable two-factor authentication (2FA) wherever possible.
- Secure your SSH connection: Use a secure port and disable root login for SSH access. Consider using key-based authentication instead of password-based authentication.
- Firewall: Implement a firewall to restrict unauthorized access to your server.
- Regular backups: Back up your data regularly to a secure location in case of emergencies.
- Monitor your server: Monitor your server activity for suspicious behavior and log events for troubleshooting and security analysis.
- Security software: Consider installing security software like malware detection and intrusion detection systems for added protection.
- Control panel security: Ensure your control panel is configured securely and update it regularly.
- User permissions: Grant users only the minimum permissions they need to perform their tasks.
- Vulnerability scanning: Regularly scan your server for vulnerabilities and address them promptly.
- Keep sensitive data encrypted: Encrypt sensitive data like passwords and credit card information to protect it even if it’s compromised.
Additional tips:
- Choose a reputable VPS provider: Look for providers with a good track record of security and reliable customer support.
- Stay informed: Keep yourself updated on the latest security threats and best practices.
- Be proactive: Don’t wait for a security breach to happen. Take preventive measures to secure your server from the start.
Also Read: What is VPS Security? | 13 Best Practices for VPS Security
13.6. Is VPS more secure than shared hosting?
13.7. How does VPS hosting impact website loading speed?
13.8. Can I install any software on my VPS?
Yes, you generally have the flexibility to install and run a wide range of software on your VPS (Virtual Private Server). This includes operating systems, web servers, databases, content management systems, development tools, and various applications.
The ability to install software is one of the advantages of using a VPS, as it provides a level of control and customization over your hosting environment. However, it’s important to ensure that any software installations comply with the terms of service of your hosting provider and do not violate security or resource usage policies.
Also Read: What is Windows VPS? | Who Should Use a Windows VPS?
14. Conclusion
Virtual Private Servers is a powerful and versatile hosting solution that bridges the gap between shared hosting and dedicated servers.
Through this article, we have delved into the essence of VPS, understanding what is VPS, unraveling its advantages and potential drawbacks, and gaining insights into its operational dynamics.
This technology empowers users with dedicated resources, scalability, and customization options, making it an ideal choice for businesses and individuals seeking a flexible and efficient hosting environment.
Whether you’re a budding entrepreneur, a seasoned developer, or simply seeking a reliable platform for your online presence, VPS offers a perfect blend of performance, control, and scalability to meet diverse hosting needs.
Find out more articles at our Blog and don’t hesitate to contact us for support:
- Email: support@vinahost.vn
- Hotline: 1900 6046
- Livechat: https://livechat.vinahost.vn/chat.php
Read More:
What is Cambodia VPS Hosting? | Everything you need to know
What is Thailand VPS Hosting? Top 8 benefits of Thailand VPS Hosting
What is VPS Indonesia? Experience in Choosing the Best VPS Indonesia
What is NVMe VPS? | The Difference between NVMe VPS vs SSD VPS


 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt English
English 简体中文
简体中文