VPS and VPN are two concepts that are often easily confused because they are both quite similar acronyms. However, these are two completely separate concepts and are used for different purposes. VinaHost will help you distinguish the differences between these two services through this article. Let’s find out!
1. Overview of Virtual Private Server(VPS)
1.1. What is a VPS?
VPS stands for “Virtual Private Server”. This is a form of web hosting where a physical server is divided into multiple independent virtual servers, each of which runs the same operating system and software as a separate server.
Each virtual server has its own resources, including memory, CPU, storage and bandwidth, helping to ensure that users are not affected by other servers on the same system. Administrators have root (or admin) access and complete control over their virtual server.
VPS is often used to deploy and manage web applications, websites, databases and many other purposes, being an intermediate choice between shared hosting services and private servers.

Also Read: What is SSD VPS Hosting? | Everything You Need to Know
1.2. How does a VPS work?
Virtual private servers (VPS) use virtualization technology to divide a physical server into multiple virtual servers. Each virtual server operates independently, just like a dedicated physical server. Here’s how VPS works:
- Physical server: This is a powerful server with many resources such as CPU, RAM, storage capacity and network bandwidth.
- Hypervisor: Is a software called hypervisor or Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM), running on a physical server. Hypervisor creates and manages virtual servers, ensuring they operate independently of each other. Popular hypervisors are VMware, KVM, Hyper-V, and Xen.
- Virtual Server (VPS): Each VPS is a separate virtual environment created by the hypervisor. It has its own share of resources from the physical server (CPU, RAM, disk space, etc.). Even though they share physical hardware, these virtual servers are still completely separate and do not affect each other.
- Operating system: Each VPS runs its own operating system, which may be different from the host operating system or other VPSs on the same physical server. This allows users to have root access and configure the server as desired, install software and host websites or applications.
- Resource Allocation: Hypervisor allocates specific amounts of CPU, RAM, storage, and network bandwidth to each VPS. This allocation ensures each VPS has its fair share of resources and can be adjusted as needed.
- Management and control: Users can manage their VPS via control panel or command line interface. They can start, stop, restart, and configure their VPS as they would manage a physical server.
1.3. Types of VPS Hosting?
VPS hosting can be classified based on factors such as management level, virtualization technology, and specific use cases. Here are the main types of VPS hosting:
Linux VPS Hosting
- Features: Runs on the Linux operating system, famous for its flexibility, security and reasonable cost. Supports many distributions such as Ubuntu, CentOS, Debian and Fedora.
- Who is it suitable for: People who need a stable and cost-effective server environment, suitable for many different types of applications.
Windows VPS Hosting
- Features: Runs on Windows operating system, suitable for applications that require Windows environment such as ASP.NET, Microsoft SQL Server, and other Windows-based software.
- Who is it suitable for: People who need to use Windows-specific applications and software.
VPS NVMe
- Features: VPS NVMe is a type of Virtual Private Server (VPS) that uses NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) hard drives, a modern storage protocol designed to optimize performance and reduce latency during data transfers.
- Who is it suitable for: People who need fast data access speed and high performance.
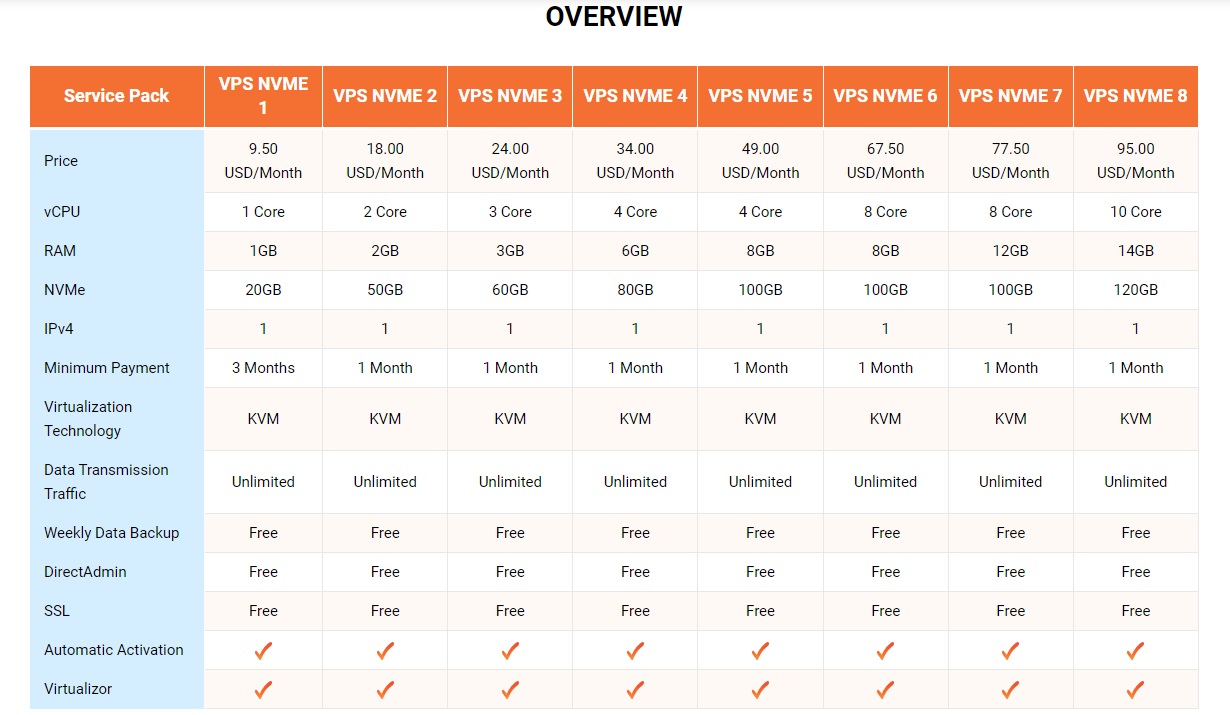
Managed VPS Hosting
- Features: The hosting provider will manage all server-related tasks, including maintenance, updates, security, and backups.
- Who’s it for: People who want to focus on their apps and websites without worrying about server management.
Unmanaged VPS Hosting
- Feature: Users manage all server-related tasks themselves. The provider only supports basic hardware and network issues.
- Who’s it for: Users with technical expertise who want complete control over their server environment.
Not only based on features, VPS is also categorized by geographic location. At VinaHost, we offer VPS solutions:
Choosing the right type of VPS hosting depends on your specific needs, your technical capabilities, and the nature of the application or website you want to host.
Also Read: The difference between Managed VPS and Unmanaged VPS
1.4. Pros of VPS Hosting
Virtual servers bring many advantages to users, including:
- High performance: Each virtual server has separate resources such as CPU, RAM, SSD to help increase performance compared to shared hosting services.
- Maximum control: Users have root (or administrator) access on the virtual server, which provides complete control over the operating system and configuration.
- Flexibility: VPS allows users to customize the system configuration to their specific needs and install their own applications and software.
- Secure and private: Since each virtual server operates independently of the others, it provides a more secure and private environment than shared hosting.
- Scalability: Users can easily expand resources such as CPU, RAM, and storage as needed without affecting other servers.
- Cost savings: VPS is a more cost-effective option than traditional physical servers. This is because users only need to pay for the resources they use.
- Good support: Many virtual server providers provide professional and fast technical support, helping users solve problems effectively.
1.5. Cons of VPS Hosting
VPS service is not perfect in all aspects. In fact, you should only consider using a virtual server when you want to upgrade from shared hosting. At that time, you will have more space and flexibility to manage (websites, for example). Below are some disadvantages when using VPS.
- Cost: Compared to shared hosting services, virtual servers can be more expensive and require more technical knowledge, which can increase cost and difficulty for beginners.
- Management and maintenance: Due to the high level of control, virtual server management requires extensive technical knowledge. Users need to know how to manage the operating system, install and update software, and handle security issues.
- Storage capacity: Although resources can be expanded, VPS storage capacity is often limited compared to physical servers. This can become a limitation for large projects with massive storage needs.
- Shared performance: Although each VPS has its own resources, it still shares physical resources with other virtual servers on the same server. If one VPS overuses resources, it can affect the performance of other VPSes.
- Depends on the provider: VPS performance and service quality depends heavily on the provider. If the provider has infrastructure or technical support problems, users may encounter difficulties.
- High technical requirements: To take full advantage of virtual servers, users need to have enough technical knowledge to manage and optimize their system. This can be challenging for beginners.
1.6. When to Choose a VPS
If you need a cost-effective, flexible, and secure server solution, virtual servers are a great choice. You may consider using virtual servers in the following situations:
- High resource requirements: When you need resources beyond the capabilities of shared hosting, such as powerful CPUs, large amounts of RAM, or special storage capacity.
- Concurrent use of multiple applications: If you deploy and manage multiple applications or projects on the same server and want better control over resources.
- High flexibility: When you need flexibility in configuring the system and choosing software and operating systems that suit the specific requirements of the project.
- High security: When you need a high level of security and complete control over your system, virtual servers provide a good environment to deploy advanced security measures.
- Fast-growing projects: When your project is growing rapidly and you need the flexibility to scale to meet demand.
- Sufficient technical knowledge: When you have sufficient technical knowledge to manage and maintain a virtual server environment.
- High control requirements: When you need complete control over system configuration and want a higher level of security than shared hosting.
- Testing and development: VPS is a great environment for testing and developing new applications.
- Sandbox environment: VPS can be used as a sandbox environment to test new applications or services without affecting the main server environment.

Also Read: [HOT] Top 15 Best VPS Hosting Providers [Updated]
2. Overview of Virtual Private Network(VPN)
2.1. What is a VPN?
VPN stands for “Virtual Private Network”. This is a technology designed to create a secure and private connection on the internet, allowing users to securely access and send data over a public network such as the internet.
When connecting via a virtual private network, data is encrypted, helping to protect personal information and prevent outside tracking. VPN creates a secure “tunnel” between the user’s device and the VPN server, through which information can be transmitted safely without worrying about the risk of loss or outside interference.
Common applications of virtual private networks include protecting internet privacy, avoiding surveillance, and allowing access to information sources or services that may otherwise be geographically restricted.
Also Read: What is VPN & What does it do? | Different Types of VPNs
2.2. How does a VPN work?
A virtual private network (VPN) creates a secure and encrypted connection between your device and a remote server. This helps hide your IP address and encrypt your internet traffic, ensuring privacy and security. Here’s a simple explanation of how a VPN works:
- VPN Software: You install the VPN software on your device (computer, phone, tablet). This software establishes and manages VPN connections.
- Connect to a VPN Server: When you open the software and connect to a VPN, the software connects to a VPN server, usually in a different location.
- Data Encryption: VPN software encrypts your internet traffic before it leaves the device. This encryption turns data into an unreadable form, helping to protect your information.
- Create a Secure Tunnel: Encrypted data is sent through a secure tunnel to the VPN server. This tunnel uses protocols such as OpenVPN, L2TP/IPsec or WireGuard to ensure a secure connection.
- VPN Server: When the data reaches the VPN server, it will be decrypted. The VPN server then forwards your traffic to the website or service you want to access using the VPN server’s IP address.
- Hide Your IP Address: Because traffic is forwarded through the VPN server, the website or service you visit only sees the VPN server’s IP address, not the actual IP address your. This hides your real location and identity.
- Data Return: When a website or service sends data back (like a web page or file), the data goes to the VPN server first. The VPN server encrypts the data and sends it back through a secure tunnel to your device, where the VPN software decrypts it so you can view or use it.
2.3. Types of VPN?
There are different types of VPNs designed to serve different purposes and use cases:
Remote Access VPN (Remote Access VPN)
Allows individual users to remotely connect to a private network and access the network’s internal resources. Commonly used for remote employees to securely connect to the company’s internal network.
Site-to-Site VPN (Or Router-to-Router VPN)
Connect the entire network of offices or branches together securely via the internet. Used by businesses to connect offices and branches safely and effectively.
VPN Client-to-Site
Allows personal devices to remotely connect to a specific server on the network. Typically used when a user wants to remotely connect to a specific server instead of accessing the entire network.
VPN L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol)
Uses layer 2 tunneling protocol to create a secure connection between client and server. Often combined with IPsec to provide security for data transmitted through the tunnel.
VPN IPsec (Internet Protocol Security)
Use the IPsec protocol suite to secure information transmitted over the Internet Protocol (IP). Often widely used to protect remote and site-to-site connections.
SSL VPN (Secure Socket Layer VPN)
Use SSL or TLS protocol to create a secure and encrypted connection between client and server. Typically used for remote access via a web browser without the need for special client software.
VPN PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol)
Uses a point-to-point tunneling protocol to create a secure connection. However, due to security holes, it is no longer recommended for use in modern solutions.
OpenVPN
Is an open source VPN protocol that uses custom security protocols based on SSL/TLS for key exchange. Famous for its security, reliability and high configurability.
WireGuard
Modern VPN protocol, designed for simplicity and improved performance compared to other traditional protocols like OpenVPN.
Mobile VPN
Optimized for mobile devices, helping to maintain a continuous and secure connection when the mobile device switches networks or changes IP addresses.
Each type of VPN has unique characteristics and is suitable for different usage needs.

2.4. Pros of VPN
The outstanding advantage of a virtual private network is that it meets the high security needs of users. In addition, virtual private networks have many other advantages such as:
- Data security: Virtual private networks encrypt data between your computer or device and the server, making it difficult for attackers to read or understand information transmitted over the network.
- Protects privacy: VPNs help keep your online activity protected and hidden from those who want to track you, including your ISP (Internet Service Provider).
- Access most content, such as geo-restricted content: You can access websites and online services that may be geo-restricted, because a VPN allows you to connect from another virtual location.
- Stay safe when using public Wi-Fi: When using public Wi-Fi, a virtual private network helps protect personal information from being stolen.
- Avoid geo-targeted advertising: Virtual private networks help you “switch geolocation” and view online content from other areas, which can avoid geo-targeted advertising.
- Secure remote work: Enables remote workers to securely connect to the corporate network and access internal resources without worrying about security.
- Avoid surveillance tools: Virtual private networks help prevent online surveillance and tracking tools, protecting user privacy.
2.5. Cons of VPN
Using a virtual private network is an ideal choice for users accessing the Internet. However, virtual private networks also have some limitations.
- Slow in use: Data encryption and decryption can cause connection speeds to decrease, especially when using free VPN services.
- Limited by capacity and speed: Free VPN services often limit capacity and speed, which can affect the usage experience.
- Sometimes not safe: Some untrusted virtual private network services may store and share your personal information, posing information security risks.
- Likely to be blocked: Some organizations and websites may detect and block users from using VPNs to access content.
- Dependence on third-party services: Dependence on a virtual private network service can increase risk, especially if that service crashes or stops working.
- IP address spoofing: VPNs can be used to spoof IP addresses, which could lead to abusive use or legal liability.
- Must pay if you want to use advanced services: If you want to use a quality and full-featured virtual private network service, you may need to pay a fee, which increases the cost of using a virtual private network.
2.6. When to Choose a VPN
You should be able to apply a virtual private network in the following cases
- When using public Wi-Fi: Public Wi-Fi is often not secure and your data can be stolen. A VPN will help protect your data from being stolen or eavesdropped.
- When working remotely: A VPN will allow you to securely access your company’s intranet remotely.
- When using highly secure online applications or services: A VPN will help protect your data when you are using highly secure online applications or services, such as online banking online or pay online.
- When you want to protect your privacy: A VPN will help hide your IP address, helping you browse the web anonymously.
- Access geo-restricted content: If you want to access geo-restricted online content or services (e.g. international TV content), a VPN can help you bypass restrictions.
- When you want to avoid blocking or censorship: If you are in a country or network where access to certain websites or services is blocked, a VPN can help you avoid this censorship.
- When you need to ensure safe content downloads: When downloading content from the internet, a virtual private network can help protect your computer from cyber threats and increase safety.
Also Read: What is Linode VPS? | Everything You Need to Know
3. What is the difference between VPS and VPN
Purpose
- VPN: Used to create a virtual private network on the Internet, helping to protect personal information and increase security when accessing the Internet from public places.
- VPS: Is a virtual server running on a physical server, used to host websites, applications, or online services.
Security and anonymity
- VPN: Increases security and anonymity by encrypting data and hiding IP addresses, helping users avoid tracking and keep personal information safe.
- VPS: Provides an independent environment from other servers, but does not have the function of hiding IP addresses or encrypting data.
Application range
- VPN: Often used for secure web browsing, accessing censored content, or remotely connecting to a corporate network.
- VPS: For deploying and managing applications, websites, and online services.
Performance and resources
- VPN: Requires few system resources, suitable for personal use or small businesses.
- VPS: Provides independent system resources, suitable for applications that require a lot of resources such as websites with large traffic.
Management and control
- VPN: Easy to use and does not require deep technical knowledge. Users usually just need to enable and disable the connection.
- VPS: Requires technical knowledge to manage, configure, and maintain a virtual server environment.
Expense
- VPN: Usually has a lower cost, especially for public virtual private network services.
- VPS: May cost more, depending on configuration and resources provided.
Here is a comparison summarizing the differences between VPN and VPS:
| VPN | VPS | |
| Purpose | Security and privacy | Independent, economical, flexible and secure storage |
| How it works | Create a secure “tunnel” between computers | Share resources from a physical server |
| Advantages | Protects data from theft or eavesdropping, hides IP address | Cost-effective, flexible, scalable, secure |
| Disadvantages | Can reduce internet speed, requires software installation | Can be complicated to manage, not suitable for applications with high performance requirements |
| Application | Remote access, data protection, privacy protection | Run applications, data storage, testing and development, sandbox environment |

4. FAQs
4.1. Do I need both a VPS and a VPN?
In some cases, using both VPS and VPN may be necessary to meet different requirements and uses:
- Example 1: If you are primarily interested in hosting websites, applications or game servers with specific resource requirements, then VPS is a must. A VPN may not be necessary if you don’t have a special need for secure remote access or high privacy protection for administrative operations.
- Example 2: If you care about privacy, online security, and accessing geo-restricted content, then a VPN is important. In this case, VPS may not be necessary unless you also need to host special applications or services that require dedicated resources.
- Example 3: For businesses or individuals with diverse needs, using both VPS and VPN can complement each other. For example, you can use a VPS to host business applications and use a VPN for secure remote access, while increasing the level of security and privacy for network activities. These tools work together to ensure a secure and efficient network environment.
4.2. Can a VPS replace a VPN, or vice versa?
VPS (Virtual Private Server) and VPN (Virtual Private Network) have different roles and functions and are usually not interchangeable because of the unique features of each:
VPS (Virtual Private Server)
VPS is mainly used to host websites, applications or services in a dedicated virtual environment.
Function:
- Provides dedicated resources such as CPU, RAM, storage to run applications and services.
- Allows customization of server configuration, software installation and server management.
- Isolate your applications and data from other users on the same physical server.
In case of used:
- Hosting websites, blogs, online stores.
- Run business applications or databases.
- Host game servers like Minecraft.
- Development and testing environment.
VPN (Virtual Private Network)
VPN is used to create a secure and encrypted connection between your device and a remote server, enhancing privacy, security, and access.
Function:
- Encrypted internet traffic to protect from third parties (e.g. hackers, ISPs).
- Hide your IP address and location by routing the connection through a remote server.
- Allows access to geo-restricted content.
- Provides secure remote access to corporate intranet resources.
In case of used:
- Increase your privacy and security online, especially on public Wi-Fi networks.
- Bypass geo-restrictions to access streaming services or sites.
- Secure remote access for employees to company resources.
A VPS cannot completely replace a VPN because it does not provide encryption, privacy, and security like a VPN. If your main concern is privacy, online security or overcoming geo-restrictions, a VPN is indispensable.
A VPN cannot replace a VPS because it does not provide resources (CPU, RAM, storage) or the ability to host websites, applications or services. While a VPN enhances privacy and security, it does not provide the dedicated environment needed for server-side applications or managing storage needs.
Also Read: What is GPU VPS? | Choosing the Right GPU VPS Provider
4.3. Is a VPS secure without a VPN?
While a VPS provides inherent security through isolation, network security, and access controls, using a VPN can add additional security and privacy features. The decision to use a VPN with VPS depends on your specific security requirements, data sensitivity level, and how you want to ensure the security of accessing and managing your server.
4.4. How much does a VPS or VPN cost?
The cost of VPS (Virtual Private Server) and VPN (Virtual Private Network) can vary due to many factors such as the provider, specifications, features, and additional services included. Below is an easy-to-understand overview of common costs for each type of service:
VPS (Virtual Private Server)
Basic VPS Package
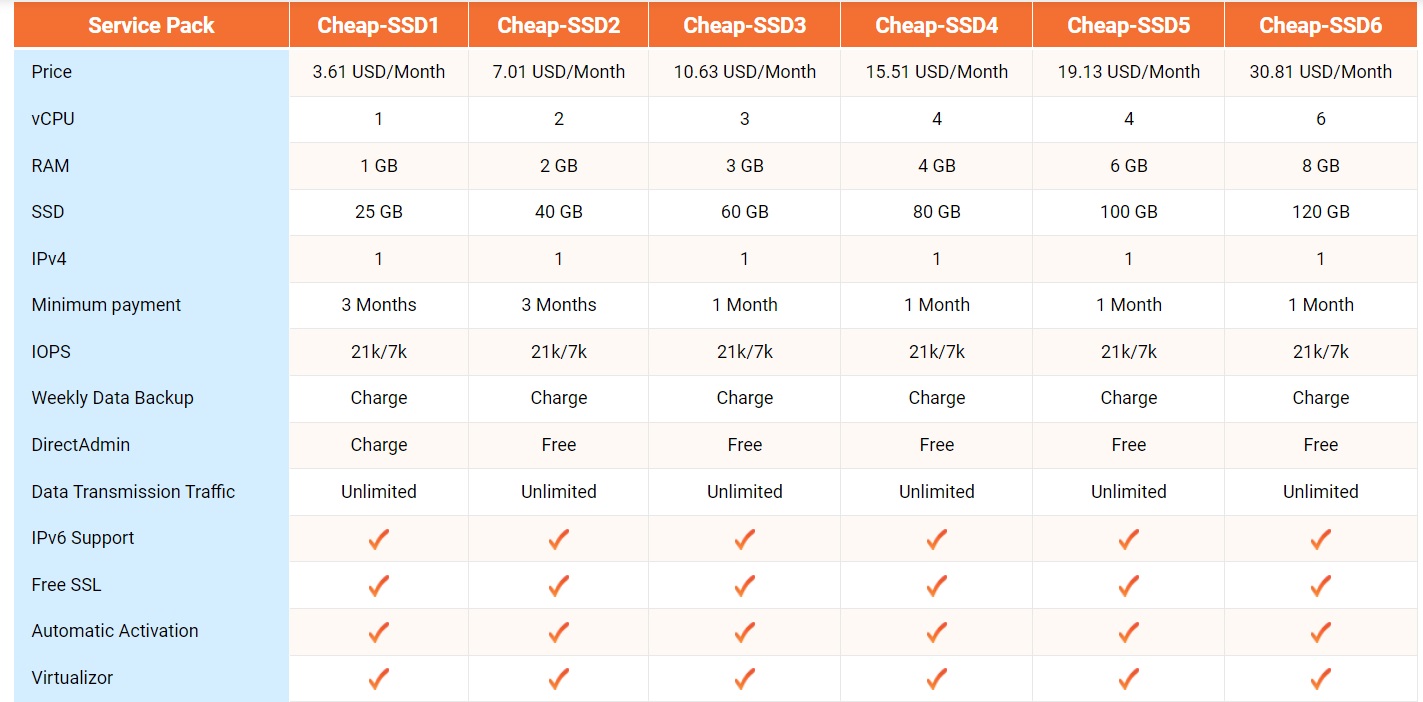
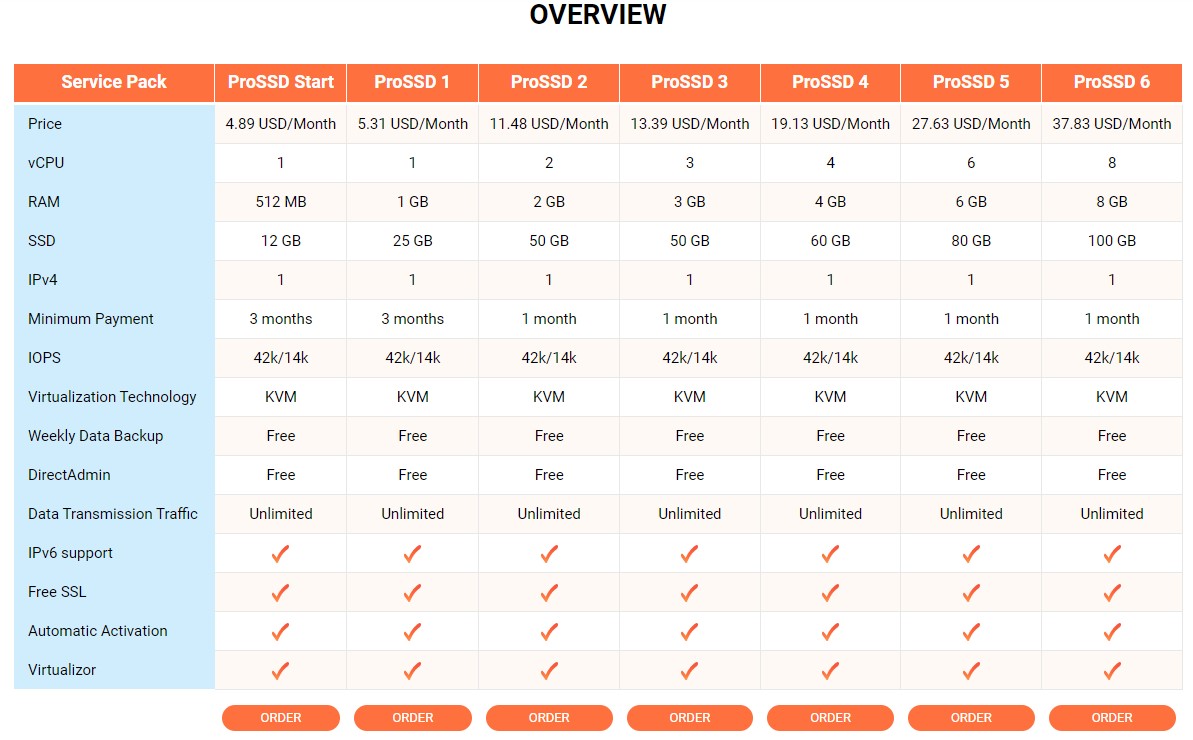
- Basic level VPS: Price ranges from $5 to $20 per month. These plans are typically suitable for small websites or simple applications, with resources like 1 CPU core and 1GB of RAM.
- Mid-range VPS: Price from $20 to $50 per month. These are plans suitable for average websites, e-commerce stores, with resources ranging from 2-4 CPU cores and 4-8GB of RAM.
- High Performance VPS: Pricing can exceed $50 per month, catering to large applications that require more resources like multiple CPU cores, high RAM, and SSD storage.
Additional costs
- Managed Services: Managed plans include monitoring, backups, and security updates, often at an additional cost.
- Optional features: Includes expanded memory, bandwidth, private IP address, and special software licenses that may increase cost.
VPN (Virtual Private Network)
Subscription package
- Monthly Plans: Prices range from $5 to $15 per month for individual subscriptions. Enterprise plans may cost more, depending on features and number of users.
- Annual Plans: Discounted annual plans from $30 to $100 for individual users.
4.5. Where can I find a good VPS or VPN provider?
Finding a good VPS or VPN provider involves considering several factors such as reliability, performance, security features, customer support, pricing, and specific needs like server locations or compatibility with your devices.
- Security and Privacy Features: Look for VPN providers with strong encryption protocols (e.g., AES-256), no-logs policies, and additional security features like kill switch and DNS leak protection.
- Server Locations and Coverage: Ensure the VPN provider offers servers in locations that meet your needs (e.g., accessing geo-restricted content, minimizing latency).
- Customer Support: Reliable customer support with responsive service channels (e.g., live chat, email, phone) can be crucial for resolving issues promptly.
- Price and Value: Consider pricing plans, discounts for longer subscriptions, and additional features offered to assess the overall value of the service.
Some VPN Providers such as: ExpressVPN, NordVPN, CyberGhost, Surf Shark, Private Internet Access (PIA). Vinahost’s VPS service is one of the popular choices for users in Vietnam, with many outstanding advantages as follows:
- Diverse service packages: Vinahost offers a variety of VPS packages, from basic packages for small needs to more advanced packages serving large applications or websites. This helps users make choices that suit their needs without wasting resources.
- Stable performance: With powerful infrastructure and quality assurance, Vinahost’s VPS services ensure stable performance and high reliability. This makes Vinahost a reliable choice for business applications and high-traffic websites.
- High security: VinaHost focuses on data security and network protection, providing firewall solutions and professional network security measures. This helps protect users’ important information from external threats.
- Professional customer support: VinaHost has an enthusiastic and professional customer support team, ready to answer questions and provide technical support during the process of using VPS services. This helps users feel secure and receive support when needed.
- Reasonable price: VinaHost provides VPS service packages at competitive prices in the market, ensuring cost efficiency for users in using and operating applications and services on the VPS platform.
With these outstanding advantages, VinaHost’s VPS service is a suitable choice for individuals and businesses in Vietnam who are looking for an effective and efficient platform to host and develop websites and applications.
Also Read: What is Minecraft VPS Hosting? | Top 6 Minecraft VPS Hosting Providers
5. Conclusion
VinaHost believes that through the article “What Is The Difference Between VPS And VPN”, you can now distinguish the differences between VPN and VPS and have the basis to choose the solution that best suits your needs. Along with the development of modern technology, businesses are gradually applying virtualization solutions (such as VPN and VPS) to solve the problem of internal information and data security. Find out more articles at our Blog and don’t hesitate to contact us for support:
- Email: support@vinahost.vn
- Hotline: 1900 6046
- Livechat: https://livechat.vinahost.vn/chat.php
What is VPS Security? | 13 Best Practices for VPS Security
What is Cambodia VPS Hosting? | Everything you need to know
What is Thailand VPS Hosting? Top 8 benefits of Thailand VPS Hosting
What is gaming VPS? | Choosing the Right gaming VPS Provider