What is a gTLD? gTLD stands for generic Top-Level Domain. It is part of the Internet’s domain name hierarchy, used to categorize and organize domain names. The gTLD is the last part of a domain name and is often used to denote the general purpose or nature of the websites that use that domain name. Find out the content below the article from VinaHost right away!
1. What is a gTLD (Generic Top-Level Domain)?
A Top Level Domain (TLD) is a part of the Internet domain name system that is located at the highest level of a domain name. A TLD is the last part of a website address after the dot.
TLDs are divided into two main categories: Generic TLDs (gTLDs) and Country Code TLDs (ccTLDs). Top Level TLDs are TLDs that are not country-specific.
For example, “.COM”, “.ORG”, “.NET”, “.INFO”, and many others. Country Code TLDs, such as “.US” for the United States, “.UK” for the United Kingdom, “.FR” for France, are TLDs that are country-specific.
Choosing the right TLD for a website can affect how easily that website can be found on the Internet.

Also Read: What is Domain & How It Impacts Your Online Presence
2. Example of Generic Top Level Domain
2.1. .COM
The .COM domain name is the most popular and widely known. It was originally intended for commercial businesses, but has since become a popular choice for all types of websites, from personal blogs to corporate websites. Because of its global familiarity and prestige, .COM is a top choice for businesses looking to build trust and attract a wide audience.
2.2. .ORG
The .ORG domain name was originally intended for non-profit organizations, and is still commonly used by charities, advocacy groups, and educational institutions. Websites using .ORG are generally considered trustworthy and have a clear purpose.
2.3. .NET
The .NET domain name was originally designed for network-related services, such as internet service providers and technology companies. Today, it is still popular in the technology industry, but is also used in many other fields. .NET is a good alternative when the .COM domain name you want is already taken, and it still provides credibility.
2.4. .CO
The .CO domain name is often considered a shortened version of .COM. Although it was originally the country code for Colombia, .CO has become widely used as an international domain name, especially among startups and entrepreneurs. It is popular because it is short and memorable.
2.5. .INFO
The .INFO domain name is for informational websites. It is often used by resource sites, databases, and websites that provide information about a specific topic. .INFO is flexible and suitable for a variety of purposes, although it is often related to non-commercial content.
2.6. Exploring other gTLD options
Here’s a more digestible version of the new gTLDs, with more specific domain name options that fit different purposes or industries:
- .TECH: Typically for technology-based websites.
- .ONLINE: Flexible, suitable for any type of online presence.
- .SHOP: Ideal for e-commerce sites and online stores.
- .BLOG: Perfect for personal or professional blogs.
- .APP: Typically used for websites about mobile or web apps.
- .SITE: A versatile domain, suitable for many different types of websites.
- .DESIGN: Suitable for designers or design-focused businesses.
- .NEWS: For news sites or blogs about current events.
- .GURU: Suitable for sites that offer expertise or advice in a particular field.
- .PHOTOGRAPHY: For photographers or photography related businesses.
Each of these domain has its own advantages, and you can choose one based on your website’s purpose and branding strategy.
Also Read: What is a Domain Extension? | How to Choose a Domain Extension
3. History of gTLDs
1980s: The Beginning
In 1984, the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) introduced the concept of gTLDs. By 1985, the first gTLDs were created, including .COM, .ORG, .NET, .EDU, .GOV, and .MIL.
1990s: The Internet Rises
As the Internet became more popular, .COM domain names became increasingly popular. By the late 1990s, demand for domain names increased, raising concerns about the shortage of gTLDs.
2000s: Expansion
In 2000, ICANN (the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers) introduced new gTLDs such as .INFO, .BIZ, and .PRO to meet growing demand.
2020s: Continued Growth
New gTLDs are increasingly accepted and used, providing more domain name options for users. Internet users are increasingly familiar with and recognizing these new gTLDs.
4. Why Do gTLDs Matter?
Using a top-level domain is important to identify the type of website, establish trust and credibility, increase discoverability, and convey the direction of the website.
- Identify the type of website: TLDs often tell visitors what type of website they are visiting. For example, “.COM” indicates that the website is an e-commerce site, “.ORG” indicates that the website is a non-profit organization, and “.EDU” indicates that the website is an educational institution.
- Establish trust and credibility: Using the right TLD can help establish trust and credibility with visitors. For example, an e-commerce website using a “.COM” domain name is often considered more professional and trustworthy than an e-commerce website using a different domain name.
- Increase findability: The right TLD can help increase the searchability of a website on the Internet. For example, if someone wants to find an e-commerce website, they can type in a keyword and add “.COM” to the end to narrow their search.
- Showing the direction of the website: The TLD can also help show the direction of the website. For example, a website about art using the domain name “.ART” can help visitors understand the main direction of the website.
Also Read: The Value of Domain Names: Choosing the Right Domain for Your Website
5. Advantages and Disadvantages of gTLDs
5.1. Pros of using gTLDs
- Flexibility in branding: New gTLDs like .TECH, .BLOG, and .SHOP allow businesses to choose a domain name that fits their industry or brand, helping customers immediately understand the purpose of the website.
- Easy to find unregistered domains: With hundreds of gTLDs available, it’s easy to find the domain name you want that hasn’t been registered yet, especially when popular extensions like .COM are taken.
- Geo-Targeting and Niche: gTLDs like .NYC or .LONDON help you target customers in a specific area, while gTLDs like .GURU or .PHOTOGRAPHY cater to niche markets, attracting a specific audience.
- SEO Potential: Although .COM is the most popular gTLD, search engines do not differentiate between different gTLDs. With a good SEO strategy, a website using any gTLD can rank well.
5.2. Cons of using gTLDs
- Recognition and Trust: Traditional gTLDs like .COM and .ORG are more well-known and trusted. Newer or less popular gTLDs may be viewed with suspicion by users, reducing trust.
- Memorability: People are more familiar with .COM, so websites using new domain may have a harder time remembering them, resulting in lost traffic.
- Risk of abuse: Some new domain may be used for spam or phishing activities, which can lead to search engines or browsers blacklisting them, affecting legitimate websites.
- Higher costs: Some premium or specialty gTLDs may be more expensive to register and renew than traditional gTLDs, increasing costs for website owners.

Also Read: What is Domain Privacy? | Do you need Domain Privacy?
6. How to Choose the Right gTLD
6.1. Target Market
Consider who you’re trying to reach. If you need to target a specific region, choose a local gTLD like .NYC or .LONDON. If you serve a niche market, choose a domain that reflects that area, like .TECH for technology or .BLOG for personal blogs.
6.2. Brand Image
Choose a gTLD that helps highlight your brand identity. For example, a technology company might choose .TECH to emphasize its expertise, while a fashion brand might choose .STYLE. The right gTLD will help customers easily recognize and understand your business.
6.3. Availability
Popular gTLDs like .COM may already be heavily registered. Explore other gTLDs to find an unused domain name that suits your needs. Newer gTLDs often offer more options.
6.4. Cost
Check the registration and renewal costs for different gTLDs. Traditional gTLDs are generally cheaper, while some specialty or premium gTLDs may be more expensive. Make sure the cost fits your budget and long-term plans. By considering your target market, brand image, availability, and cost, you can choose the best gTLD to support your website goals and enhance your online presence.
Also Read: What is Domain Backorder? | Everything you need to know
7. How gTLDs Impact SEO
- Domain Authority: Search engines like Google do not favor one gTLD over another. Whether your domain is .COM, .ORG, or any other domains, your website can still rank well if you implement good SEO strategies and provide quality content.
- Keywords in the Domain Name: Having relevant keywords in your domain name can help increase your website’s discoverability in search. However, content quality and other SEO factors are much more important.
- User Trust and Click-Through Rates: Users generally trust traditional gTLDs like .COM and .ORG more. If you use a less popular gTLD, this can affect user trust and your site’s click-through rate from search results.
- Geotargeting: Some domains are designed for geographic purposes, like .NYC or .LONDON. Using these gTLDs can help you improve your visibility in local search results if your site is targeted to a specific location.
- Brand recognition: Choosing a gTLD that fits your brand can improve brand recognition and consistency. This can indirectly help SEO by increasing engagement and searches related to your brand.
- Reputation and Spam: Some new gTLDs may be associated with spam or low-quality sites. This can affect user trust and search engine caution, reducing your site’s rankings.
While domain choice has little direct impact on SEO, it can still impact user trust, click-through rates, and geographic targeting. Ensuring high-quality content and good SEO practices are still the most important factors for ranking highly on search engines.
8. What is the difference between a gTLD and a ccTLD?
Here is a simple comparison between gTLDs and ccTLDs
| gTLD (Generic Top Level Domain) | ccTLD (Country Code Top Level Domain) | |
| Definition | Domain name extensions not related to a specific country | Domain name extensions specific to a country or territory |
| Examples | .COM, .ORG, .NET, .TECH, .INFO | .US, .UK, .JP, .AU |
| Purpose and uses | Widely used for many different industries and purposes | Shows a connection to a specific country or territory |
| Registration requirements | Usually easy to register with few restrictions | Often has a country-specific requirement, such as residing or operating in that country |
| Geographically relevant | Not related to a specific geographic location; can be used globally | Has a clear connection to a specific country or region |
Also Read: What is VN domain? | Overview of domain names .VN
9. How to Register a gTLD
To start registering a domain through VinaHost’s online platform, follow these easy steps:
9.1. Choose a Domain Name
Think about a domain name that represents your brand, business, or personal website. Choose a domain name that is memorable, easy to spell, and relevant to the content you provide. If possible, include keywords related to your industry or niche in your domain name to help with branding and SEO.
9.2. Check Availability
Visit the VinaHost website and enter your desired domain name in the search field. Click “Search” to check if it is available. If the domain is open, click “Register” to add it to your shopping cart. Additionally, VinaHost allows you to register multiple domains at once, streamlining the process.
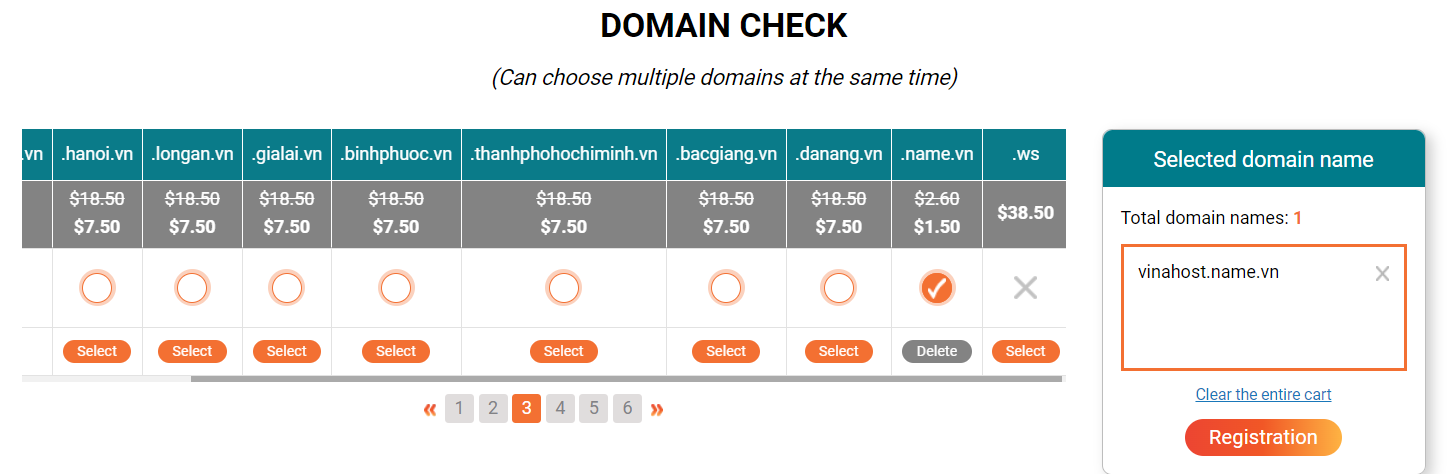
9.3. Select a Registrar
VinaHost stands out as one of the leading domain name registration service providers in Vietnam with the following key benefits:
- Diversified Choices: VinaHost offers a wide range of international and Vietnamese domain names, including unique and special options.
- Easy Registration Process: VinaHost’s platform simplifies domain name registration, helping you complete it quickly and efficiently through an online interface.
- Reasonable Pricing: VinaHost’s domain name registration service is competitively priced, suitable for many different budgets and needs.
- Dedicated Support: Their customer support team is always ready to help you with both domain name registration and ongoing management.
- Comprehensive Services: In addition to domain name registration, VinaHost also offers additional services such as web hosting, business email, and SSL certificates to support you in developing and managing your website.
These features have helped VinaHost build a solid reputation as a trusted domain name registration service provider in Vietnam for over 15 years.
Also Read: What is a Domain Registrar? | Function of a Domain Registrar
9.4. Complete Registration
Enter personal information
For individuals:
Select “Individual” to register.
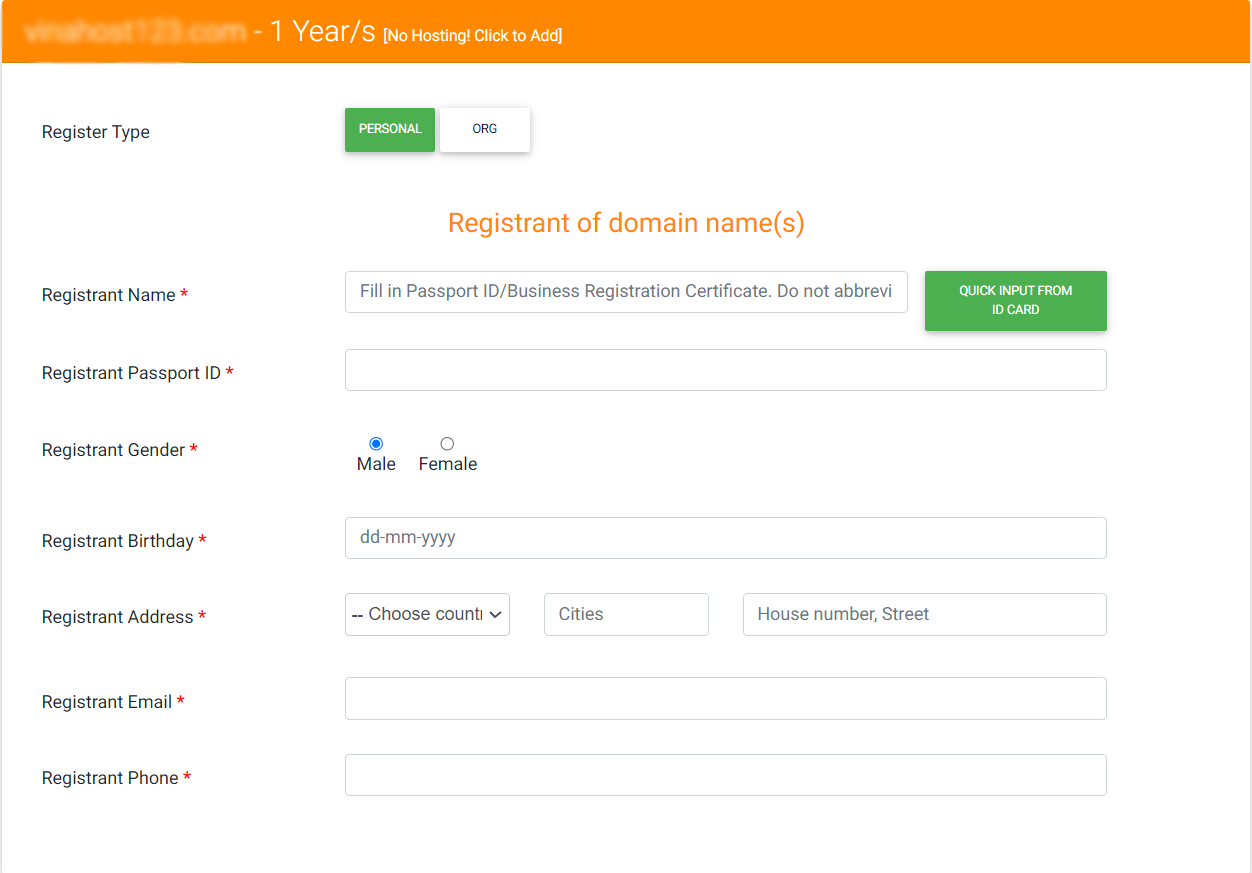
Provide the following information:
- Full name
- Identification number (such as ID card, ID card or passport)
- Gender
- Date of birth
- Full address (including country, province/city, district/county, ward/commune and specific address)
- Email address
- Phone number
If you are registering multiple domains, only enter the information for the first domain. Then, use the “Same as before” option to automatically apply to the remaining domains, saving time.
For organizations:
Select “Organization” to register.
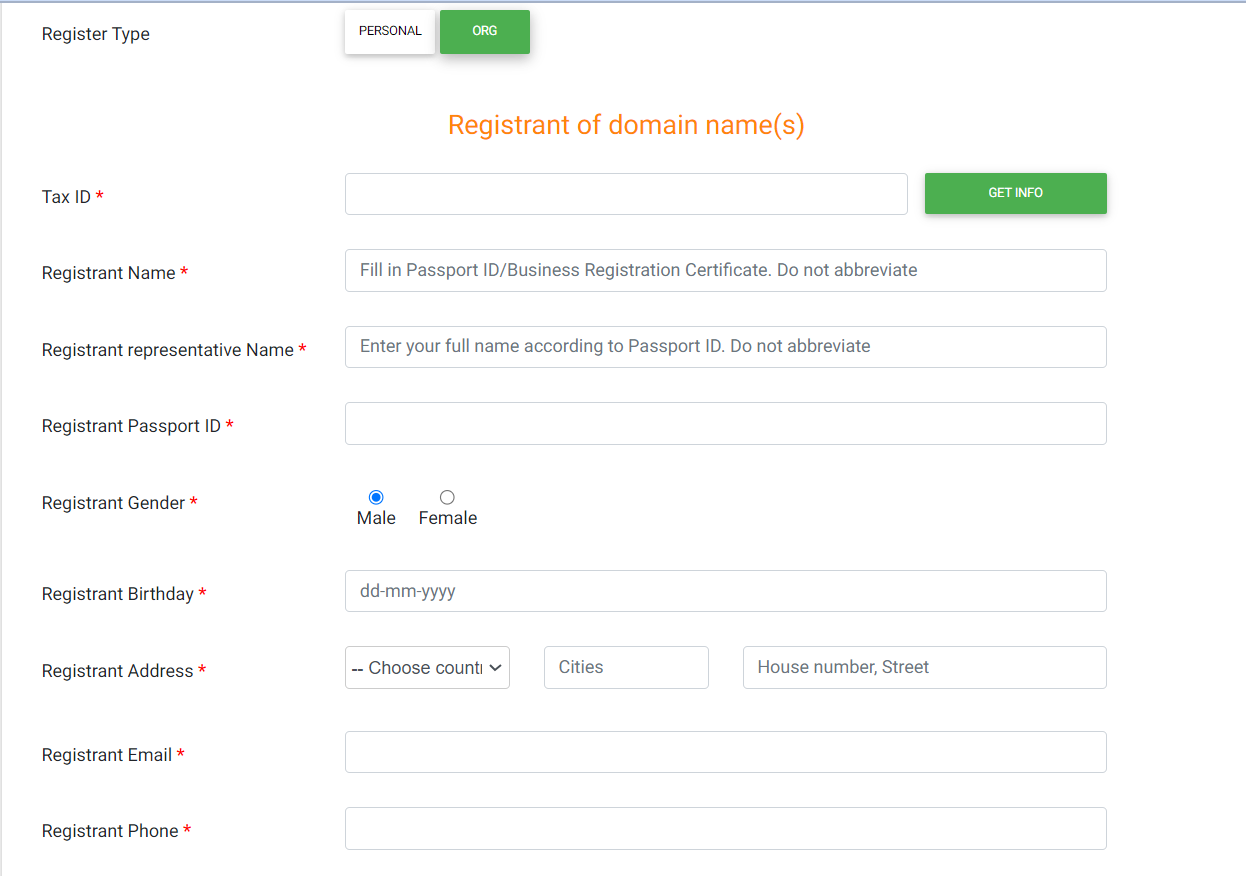
Provide required information about the organization and representative, including:
- Representative’s ID number or equivalent document (such as ID card or passport)
- Gender
- Date of birth
- Contact phone number
- Email address
After entering information about the organization and representative, the system will automatically fill in information for the domain manager and representative of the organization. You can edit this information if needed.
Finalize Your Purchase
Carefully review your order details and apply any applicable discount codes you may have.
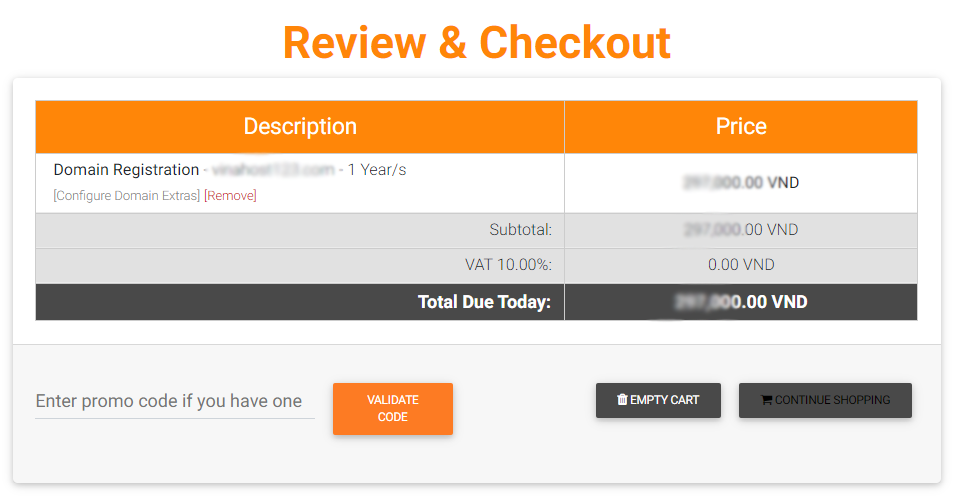
If you’re a new VinaHost user, you’ll need to create an account. Provide essential information, including your Name, Email Address, Phone Number, Physical Address, Password, and a security question for account protection. Ensure you also enter any required billing information.
Choose your preferred payment method. You can pay online or visit the VinaHost office for in-person transactions at: Cuu Long Apartment, 351/31 No Trang Long, Ward 13, Binh Thanh District, Ho Chi Minh City (Enter via Gate B on Pham Van Dong street).
Verify Your Domain
To activate your domain, go to VinaHost’s service management page at: https://secure.vinahost.vn/ac/clientarea.php?language=english. Select “Verify Domain Owner” from the main menu. In the Entity Verification section, you’ll find a list of domain profiles awaiting updates.
For assistance during this process, contact VinaHost’s customer support team:
- Email: support@vinahost.vn
- Hotline: 1900 6046
- Livechat: https://livechat.vinahost.vn/chat.php
VinaHost will complete the necessary verification procedures for your domain profile during regular business hours.
9.5. Domain Management
- Update your contact information: Make sure your contact information is correct so you don’t lose control of your domain name.
- Renew your domain name: Set reminders to renew your domain name before it expires or choose automatic renewal if available from your registrar.
- Manage your domain name settings: Use your registrar’s control panel to adjust DNS settings, set up email forwarding, and configure other options for your domain name.
Also Read: What is Whois? | Everything You Need To Know Whois
10. FAQs
10.1. Can I transfer my website to a different gTLD?
Steps to Migrate Your Website to a New gTLD
- Choose a New gTLD: Choose a new domain name extension (gTLD) for your website. Consider branding, availability, and relevance to your content.
- Register a New Domain Name: Register a new domain name with your chosen gTLD through a domain name provider. Make sure the domain name is available and complete the registration.
- Update DNS Settings: Update the new domain name’s DNS settings to point to your current web host. This helps ensure that visitors will land on the correct website.
- Move Website Content: Move all website content from the old domain to the new domain, including files, databases, and other components. Your web host or content management system may provide tools to help with this.
- Update Links and Configuration: Update all internal links and configurations on your site to match the new domain, to avoid broken links.
- Set up redirects: Set up a 301 redirect from the old domain to the new domain. This helps users and search engines automatically redirect to the new domain and maintain search rankings.
- Notify Search Engines: Update your site information in search engines (like Google Search Console) to reflect the new domain. Submit a change of address request if necessary to notify search engines of the domain switch.
- Monitor and Test: Monitor your site’s performance and check for any issues after the switch. Make sure everything is running smoothly on the new domain.
By following these steps, you can move your website to a new gTLD without major disruption and maintain your online presence.
Also Read: What is Transfer Domain? & How to Transfer a Domain?
10.2. Do I need to register a gTLD for every country I want to target?
You don’t need a separate gTLD for each country. A single gTLD can serve a global audience. If you want to target a specific country market, you can use a ccTLD or create regionally relevant content on your main domain.
Additionally, you can create subdomains or subfolders for regional content and use SEO techniques, like hreflang tags, to manage different languages and regions.
10.3. Can I use multiple gTLDs for the same website?
Yes, you can use multiple gTLDs for the same website. Here are some of the benefits of doing so:
- Brand protection: Registering multiple gTLDs like .COM, .NET, and .ORG helps protect your brand by preventing others from using similar domain names.
- Expand your audience: Using different domain can help you reach different audiences. For example, you can use .SHOP for your online store and .BLOG for your content site.
- SEO and redirects: You can redirect different gTLDs to a single main domain. This helps concentrate traffic and maintain SEO benefits.
- Domain Name Variations: Different gTLDs can serve different purposes, such as advertising campaigns or special services, all leading to your main website.
Using multiple gTLDs gives you more flexibility and can enhance your brand’s online presence.
10.4. How much does it cost to register a gTLD?
gTLD registration costs can vary depending on a number of factors:
Type of gTLD
- Popular gTLDs: gTLDs like .COM, .NET, and .ORG typically cost between $10 and $20 per year.
- New or specialty gTLDs: Newer or specialty gTLDs can cost between $20 and $100 or more per year, depending on the gTLD and provider.
Registrar
Domain registrars may have different prices for the same domain. Compare prices and check for additional fees or promotions.
Premium Domains
If you choose a premium or high-demand domain, the price can go into the hundreds or thousands of dollars.
Additional Services
Services like privacy protection, email hosting, and SSL certificates can increase the total cost.
gTLD registration costs typically range from $10 to $100 per year, with additional costs for premium domains and additional services.
10.5. Do I need to renew my gTLD every year?
Yes, you need to renew your gTLD every year to maintain ownership. Here’s why:
- Maintaining ownership: Domain names are typically only registered for one year. To keep your domain name, you need to renew it before it expires.
- Renewal period: Many registrars allow renewals for a period of time after your domain name expires, but you may have to pay an additional fee. This period varies between registrars.
- Automatic renewal: Most registrars offer an automatic renewal option, which allows you to automatically renew your domain name every year and avoid accidental expiration.
- Losing a Domain Name: If you do not renew your domain name, you may lose control and someone else may register it.
To avoid losing your ownership and losing your domain name, keep track of your renewal dates and consider enabling automatic renewal with your registrar.
Also Read: What is Registry Lock? | Protect Domain with Registry Lock
11. Conclusion
In short, generic top-level domains (gTLDs) are important domain extensions on the internet, as opposed to traditional country-code domains. Popular gTLDs such as .COM, .ORG, and .NET are widely used for a variety of purposes, from personal websites to global business platforms.
Understanding what is a gTLD, their benefits, and their impact on branding and SEO will help you make informed domain name registration decisions. Whether you are starting a new website or managing an existing one, choosing the right domain is an important step in building an effective online identity. Find out more articles at our Blog and don’t hesitate to contact us for support:
- Email: support@vinahost.vn
- Hotline: 1900 6046
- Livechat: https://livechat.vinahost.vn/chat.php
What is a root domain? | Why does a root domain matter?
What are expired Domains? | How to check domain expiration?