Cloud computing has transformed the way businesses and individuals operate. Once a complex technology reserved for large corporations, it’s now an integral part of our digital lives. But what is cloud computing? Essentially, it’s the delivery of computing services – servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence – over the internet. Instead of owning your own hardware and software, you access these resources as a service, paying only for what you use. This VinaHost‘s article will demystify cloud computing, explaining its core concepts, benefits, and how it’s used in various sectors.
1. What is Cloud Computing?
What is Cloud Computing? Cloud computing is a technology that allows users to access and manage computing resources – such as servers, storage, databases, and applications – over the internet.
Instead of relying on local servers or personal computers, cloud computing enables individuals and organizations to use virtual resources hosted by third-party providers. These resources are available on-demand and can be scaled up or down based on needs, offering flexibility and cost efficiency.
So, what is cloud in cloud computing? In cloud computing, the term “cloud” refers to a metaphorical concept of a network of remote servers that store and manage data, applications, and computing resources over the internet. Instead of relying on local physical servers or personal devices, users access these resources via the internet, essentially “in the cloud“. In essence, the “cloud” represents a shift from traditional computing, where resources are confined to physical locations, to a more dynamic and accessible model that leverages internet-based resources for greater efficiency and flexibility.
Cloud computing operates on a pay-as-you-go model, which means users only pay for the resources they use, eliminating the need for significant upfront investments in physical infrastructure. This model supports a wide range of services, including data storage, software applications, and advanced computing capabilities, and is integral to modern business operations and digital transformation.
According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), cloud computing is defined as follows: “What is the cloud computing? Cloud computing is a model for enabling convenient, ubiquitous, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (servers, applications, storage, networks and services) that allow the users to rapidly release and provision with minimal service provider interaction or management effort.”
General features of cloud computing:
- Broad network access: Users can access cloud services from any network enabled devices like desktops, laptops, mobile devices…
- On-demand self-service: User can unilaterally provision computing capabilities as needed automatically without requiring human interaction with each service’s provider.
- Resource pooling: Resources of cloud services are flexibly coordinated and shared.
- Rapid elasticity: Resources of cloud services can be quickly, flexibly provided and has the ability to change on demand.
- Measured service: Resources on cloud services are enabled to monitor and measure.
Also read: What is a Server? Understanding the Backbone of Modern Technology
2. Types of Cloud Computing Services
Now that you understand what is Cloud Computing, let’s delve into an important aspect: Types of Cloud Computing Services.
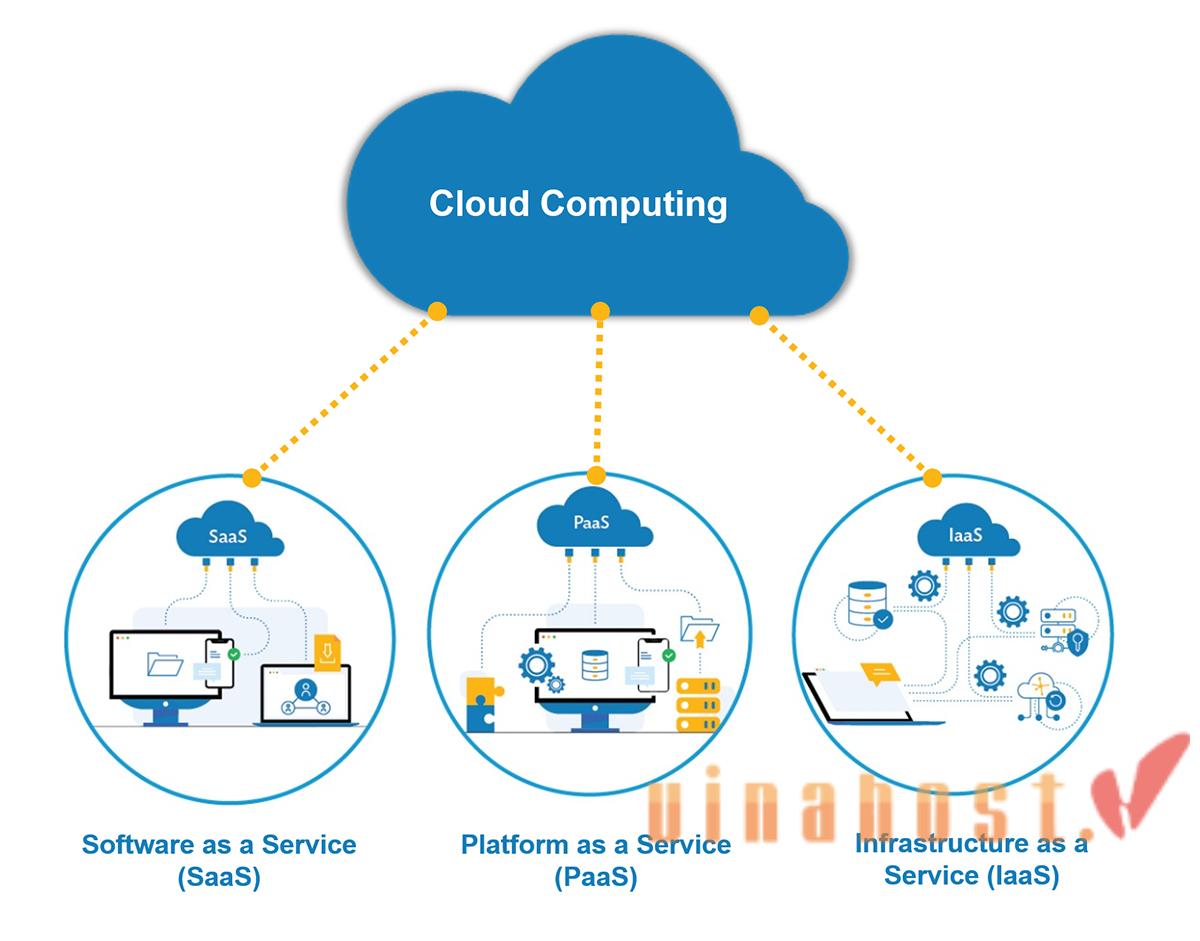
2.1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
What is cloud computing IaaS? Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides essential computing resources such as servers, storage, and networking over the internet. This model offers a high level of control over the infrastructure, allowing businesses to rent and scale resources as needed, without the hefty upfront investments in physical hardware.
IaaS is ideal for applications that require significant flexibility and customization, such as hosting websites, running complex applications, or creating development and testing environments. With its pay-as-you-go model, IaaS can be cost-effective, as businesses only pay for what they use, making it a versatile choice for a wide range of computing needs.
Prominent examples include Amazon Web Services (AWS) EC2, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
2.2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
What is cloud computing PaaS? Platform as a Service (PaaS) offers a comprehensive environment for developing, running, and managing applications without the complexities of infrastructure management. PaaS includes tools and services for application development, such as databases, middleware, and development frameworks, enabling developers to focus on coding and deploying applications.
This model supports collaboration among development teams and streamlines DevOps processes, reducing the costs associated with hardware, software, and personnel. PaaS is particularly suitable for building web and mobile applications, APIs, and collaborative software development projects.
Examples of PaaS offerings are Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure App Services, and Heroku.
2.3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
What is cloud computing SaaS? Software as a Service (SaaS) delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis, allowing users to access the software through web browsers without needing to install or maintain it. SaaS solutions are highly accessible, maintenance-free, and typically offered on a subscription model, making them cost-effective for businesses.
This model is ideal for applications like email, collaboration tools, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, and content management. By offloading the technical management to the service provider, businesses can focus on their core activities while benefiting from the latest software updates and security measures.
Well-known SaaS providers include Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, Salesforce, and Dropbox.
3. How Cloud Computing Works?
Having grasped the fundamentals of types of cloud, we can now explore a crucial factor: operation.
Cloud computing operates on the principle of delivering on-demand computing resources, software, and information over the internet. Both individuals and companies can access a virtual pool of shared resources, such as compute, storage, and networking services, hosted on remote servers owned and managed by cloud service providers. This model allows users to tap into powerful computing capabilities without the need to invest in and maintain their own physical infrastructure.
One significant advantage of cloud computing is its pay-as-you-go pricing model. Organizations only pay for the resources they use, enabling them to scale up or down quickly and efficiently. This flexibility eliminates the need for large upfront investments in data centers and servers, allowing businesses to allocate resources more effectively.
In essence, cloud computing leverages a network, typically the internet, to connect users to a cloud platform where they can request and access rented computing services. A central server manages all communications between client devices and the cloud infrastructure, ensuring seamless data exchange. Security and privacy are integral to cloud computing, with robust features in place to protect sensitive information and maintain data integrity.
When implementing cloud computing, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. Different businesses have unique needs, and the flexibility of cloud services allows organizations to tailor their approach to suit specific requirements. This adaptability is a key strength of cloud computing, enabling enterprises to respond swiftly to changing market conditions and evolving business metrics.
4. Benefits of Cloud Computing

4.1. Cost Efficiency & Scalability
Cloud computing significantly reduces the financial burden associated with traditional IT infrastructure. With a pay-as-you-go pricing model, individuals, organaztions and business only pay for the resources they use, so that eliminating the need for large upfront investments in hardware as well as software.
This model also allows for easy scalability, enabling organizations to quickly scale up or down based on demand. This flexibility helps businesses manage costs more effectively and allocate resources efficiently, ensuring they only use what they need when they need it.
4.2. Increased Agility & Innovation
Cloud computing accelerates the pace of innovation by providing businesses with rapid access to a wide range of technologies and tools. Organizations can quickly develop, test, and deploy applications without the delays associated with procuring and setting up physical infrastructure.
This agility allows individuals, organaztions and business to respond faster to market changes, experiment with new trends, new plans and bring products to market more quickly. The cloud’s extensive ecosystem of services and platforms fosters innovation by enabling seamless integration and collaboration across various development environments.
4.3. Enhanced Security & Reliability
Cloud service providers invest heavily in security measures and infrastructure to protect data and ensure reliability. These measures include advanced encryption, access controls, regular security audits, and compliance with industry standards.
Cloud providers also offer high levels of redundancy and disaster recovery capabilities, ensuring data is backed up and recoverable in case of failures or cyberattacks. This robust security and reliability framework allows businesses to trust that their data and applications are secure and always available.
4.4. Improved Collaboration & Accessibility
Cloud computing enhances collaboration by providing teams with easy access to shared resources and tools from any location with an internet connection. Cloud-based applications and services enable real-time collaboration, allowing multiple users to work on the same documents, projects, or applications simultaneously.
This improved accessibility ensures that employees can access the information and tools they need from anywhere, promoting productivity and enabling remote work. Cloud computing also supports seamless integration with other cloud services, further enhancing collaborative efforts across different platforms and devices.
Also read: What is VPS Security? | 13 Best Practices for VPS Security
5. Who Uses Cloud Computing?
Having covered the basics of cloud computing what is it and how it works, let’s now address a significant factor: it’s customer.
5.1. Individuals & Small Businesses
Cloud computing has democratized technology, making it accessible to individuals and small businesses.
Individuals:
- Online storage and backup (Dropbox, Google Drive)
- Email (Gmail, Outlook)
- Productivity suites (Google Workspace, Microsoft 365)
- Streaming services (Netflix, Spotify)
- Cloud gaming (Xbox Cloud Gaming, GeForce Now)
Small Businesses:
- Email and collaboration tools
- Customer relationship management (CRM)
- Accounting and finance software
- Marketing and sales platforms
- Website hosting and e-commerce
5.2. Enterprises & Large Organizations
Large organizations heavily rely on cloud computing to support their complex operations and scale.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): Managing core business processes (Oracle Cloud, SAP Cloud)
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Managing customer interactions (Salesforce, Microsoft Dynamics)
- Data Storage and Management: Storing and analyzing vast amounts of data (Amazon S3, Azure Blob Storage)
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Building and managing IT infrastructure (AWS, Azure, GCP)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Developing and deploying applications (Heroku, Google App Engine)
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Using cloud-based applications (Adobe Creative Cloud, Autodesk)
Also read: What is VPS? | Unveiling the Power Behind Virtual Private Servers
6. Deployment Models in Cloud Computing
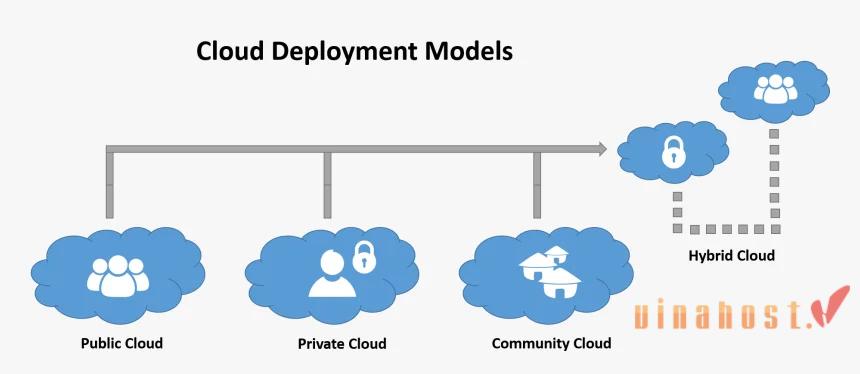
6.1. Public Cloud
Public cloud is a cloud computing model where services are delivered over the public internet and shared among multiple organizations. These services are owned and operated by third-party cloud service providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Public cloud services are typically available on a pay-as-you-go basis, allowing users to access and scale resources as needed without significant upfront costs.
Examples: Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Key features of Public cloud:
- Cost-Effective: No need for heavy capital expenditure as resources are rented.
- Scalability: Easily scalable to accommodate varying workloads.
- Maintenance-Free: Providers handle all infrastructure maintenance and upgrades.
- Accessibility: You can access to services from anywhere with an internet connection.
Use cases of Public cloud:
- Hosting websites and applications.
- Development and testing environments.
- Big data analytics and machine learning.
- Disaster recovery and backup solutions.
6.2. Private Cloud
Private cloud is a cloud computing model where services are dedicated to a single organization. These clouds can be hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider. Private clouds offer greater control over the infrastructure, enhanced security, and compliance capabilities, making them suitable for organizations with strict regulatory or security requirements.
Examples: OpenStack, VMware vCloud Suite.
Key features of Public cloud:
- Enhanced Security: Resources are isolated and only accessible by the specific organization.
- Customization: Greater ability to customize infrastructure to meet specific business needs.
- Control: Complete control over data, applications, and security policies.
- Compliance: Easier to comply with regulatory and industry standards.
Use cases of Public cloud:
- Sensitive data storage and management.
- Highly regulated industries (e.g., finance, healthcare).
- Custom business applications requiring specific configurations.
- Internal enterprise applications.
6.3. Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud is a cloud computing model that combines public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. This model provides greater flexibility and optimization, enabling organizations to leverage the benefits of both public and private clouds while meeting specific business requirements.
Key features of Public cloud:
- Flexibility: Ability to run workloads in the most appropriate environment.
- Cost Optimization: Utilize public cloud for less sensitive workloads and private cloud for critical operations.
- Scalability: Scale public cloud resources on demand while maintaining control over sensitive data in private cloud.
- Interoperability: Seamless integration and data transfer between public and private clouds.
Use cases Public cloud:
- Dynamic workloads (e.g., web applications with fluctuating traffic).
- Backup and disaster recovery solutions.
- Development and testing environments with production deployments in private cloud.
- Regulatory compliance while leveraging public cloud capabilities.
Also read: What is a Cloud Server? | How does a Cloud Server work?
7. Applications of Cloud Computing
As you have learned about what is cloud computing, it’s important to discuss another key aspect: Applications of Cloud Computing.
7.1. Data Storage & Backup
What is cloud computing storage & backup? Cloud computing provides robust solutions for data storage and backup, allowing individuals and businesses to store vast amounts of data securely and accessibly. Cloud storage services, such as Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, and Microsoft Azure Blob Storage, offer scalable storage options where users can upload, manage, and retrieve data as needed.
These services provide high durability, redundancy, and availability, ensuring data is safe from hardware failures. Additionally, cloud backup solutions enable automatic backups of critical data, reducing the risk of data loss due to accidental deletion, corruption, or disasters.
7.2. Streaming Services & Entertainment
What is cloud computing streaming services & entertainment?
The cloud plays a crucial role in the delivery of streaming services and entertainment. Platforms like Netflix, Spotify, and YouTube utilize cloud computing to stream video and audio content to millions of users worldwide. Cloud infrastructure enables these services to handle high traffic volumes, deliver content with low latency, and scale dynamically based on user demand.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) are often employed to cache content closer to users, further improving performance and user experience. The cloud also supports the storage and processing of vast media libraries, facilitating seamless access to a diverse range of entertainment options.
Also Read: What Is a Streaming Server?| Everything you need to know
7.3. Business Applications & Software
What is cloud computing business applications & software? Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses deploy and manage applications and software. Cloud-based business applications, such as Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software, and office productivity suites, provide accessible, scalable, and cost-effective solutions.
Applications like Salesforce, Microsoft 365, and Google Workspace allow organizations to streamline operations, enhance collaboration, and improve productivity without the need for extensive on-premises infrastructure. The cloud also supports Software as a Service (SaaS) models, where users can access and use software applications over the internet on a subscription basis, eliminating the need for local installations and maintenance.
Also Read: What is an Application Server? | How Application Server work?
7.4. Big Data Analytics & Artificial Intelligence
What is cloud computing big data analytics & artificial intelligence? Cloud computing is integral to big data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) initiatives. Cloud platforms offer powerful tools and services for processing and analyzing large datasets, enabling organizations to extract valuable insights and make data-driven decisions.
Services like Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, and Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics provide scalable data warehousing and analytics capabilities.
In the realm of AI, cloud computing supports machine learning (ML) and deep learning workloads with services like AWS SageMaker, Google AI Platform, and Azure Machine Learning.
These services provide the computational power and resources needed to train and deploy complex models, facilitating advancements in areas such as natural language processing, image recognition, and predictive analytics.
8. Security Considerations in Cloud Computing

8.1. Choosing a Reputable Cloud Provider
Selecting a reputable cloud provider is a critical security consideration in cloud computing. A reputable provider typically offers robust security measures, compliance certifications, and a track record of reliability and trustworthiness.
When evaluating cloud providers, it is important to consider factors such as data center security, physical security measures, and the provider’s ability to comply with industry standards and regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA). Reputable providers often have comprehensive security policies and practices, including regular security audits, vulnerability assessments, and incident response plans.
Additionally, they should offer transparency regarding their security protocols and be willing to provide documentation or attestations that demonstrate their commitment to protecting customer data.
8.2. Data Encryption & Access Controls
Data encryption and access controls are fundamental components of cloud security. Encryption ensures that data is protected both in transit and at rest, making it unreadable to unauthorized parties. Strong encryption protocols, such as AES-256, should be used to safeguard sensitive information. Cloud providers typically offer built-in encryption features, but customers must ensure that these are enabled and configured correctly.
Access controls are equally important, as they regulate who can access data and resources within the cloud environment. Implementing strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), helps prevent unauthorized access.
Role-based access control (RBAC) allows organizations to assign permissions based on the principle of least privilege, ensuring that users only have access to the data and resources necessary for their roles. Regular reviews of access permissions and monitoring for suspicious activity are essential practices for maintaining secure access controls.
8.3. Importance of Backups & Disaster Recovery
Backups and disaster recovery (DR) are vital components of a comprehensive cloud security strategy. Regular backups ensure that data can be restored in the event of accidental deletion, corruption, or cyberattacks such as ransomware. Cloud providers often offer automated backup services, allowing businesses to schedule and manage backups easily. It is important to verify that backups are stored securely and that they can be restored quickly when needed.
Disaster recovery involves planning and preparing for unexpected events that could disrupt business operations, such as natural disasters, hardware failures, or large-scale cyberattacks. A robust DR plan includes strategies for data recovery, system restoration, and maintaining business continuity.
Cloud providers typically offer DR solutions that leverage their global infrastructure to provide geographic redundancy and failover capabilities. Regular testing and updating of DR plans ensure that they remain effective and aligned with the organization’s evolving needs.
Also read: [HOT] Top 15 Best VPS Hosting Providers [Updated]
9. The Future of Cloud Computing
Given your knowledge of what is cloud computing, let’s shift our attention to an essential detail: its future!
In the future, key trends of cloud computing include the integration of AI and machine learning, the rise of edge computing and IoT, the adoption of hybrid and multi-cloud strategies, enhanced security and compliance measures, the proliferation of serverless computing and containers, and a focus on sustainability.
9.1. Continued growth and adoption
Cloud computing is expected to see continued and widespread adoption across various sectors, including healthcare, finance, retail, and manufacturing. As more businesses recognize the benefits of cloud computing, such as cost efficiency, scalability, and flexibility, the demand for cloud services will continue to rise. This growth will be fueled by both small businesses seeking to leverage enterprise-level technology and large organizations aiming to optimize their IT infrastructure.
9.2. Advancements in AI and Machine Learning
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) with cloud computing will become more prevalent. Cloud platforms will increasingly offer advanced AI and ML services that allow businesses to build, train, and deploy intelligent applications at scale. These capabilities will drive innovations in areas such as predictive analytics, natural language processing, and automated decision-making, enabling organizations to gain deeper insights and improve operational efficiency.
9.3. Edge computing and IoT Integration
Edge computing, which involves processing data closer to the source (e.g., IoT devices), will gain prominence in conjunction with cloud computing. This approach reduces latency and bandwidth usage, making it ideal for real-time applications and services that require immediate data processing. The convergence of edge computing and cloud computing will support the growing Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem, enabling faster, more reliable data analysis and decision-making at the edge.
9.3. Hybrid and Multi-Cloud strategies
Hybrid and multi-cloud strategies will become the norm for many organizations. Businesses will increasingly adopt a combination of public, private, and hybrid cloud environments to meet their specific needs and optimize performance, security, and cost. Multi-cloud approaches, where organizations use services from multiple cloud providers, will also become more common, allowing them to avoid vendor lock-in, enhance resilience, and leverage the best capabilities of each provider.
9.4. Enhanced cecurity and compliance
As cyber threats continue to evolve, the emphasis on cloud security and compliance will intensify. Cloud providers will invest heavily in advanced security technologies, such as zero-trust architectures, enhanced encryption methods, and AI-driven threat detection. Additionally, regulatory compliance will remain a critical focus, with cloud providers offering tools and services to help organizations meet stringent data protection and privacy standards.
9.5. Serverless computing and containers
Serverless computing and containerization will play a significant role in the future of cloud computing. Serverless computing allows developers to build and run applications without managing the underlying infrastructure, leading to greater efficiency and cost savings. Containers, which package applications and their dependencies into portable units, will enable consistent and scalable application deployment across different environments. These technologies will streamline development processes and enhance application scalability and portability.
9.6. Sustainable and green cloud computing
Environmental sustainability will become a key consideration in cloud computing. Cloud providers will focus on reducing their carbon footprint by using renewable energy sources, optimizing data center efficiency, and implementing sustainable practices. Businesses will also prioritize green cloud computing solutions to align with their corporate social responsibility goals and reduce their environmental impact.
Also read: What is Virtualization? | How Does Virtualization Work?
10. FAQs
10.1. Is cloud computing secure?
Yes, cloud computing can be secure, but it depends significantly on the measures taken by both the cloud service providers and the users.
Reputable cloud providers invest heavily in robust security frameworks, including data encryption, access controls, regular security audits, and compliance with industry standards and regulations. They also implement advanced security technologies such as intrusion detection systems, firewalls, and AI-driven threat detection.
However, users must also take responsibility for their own security by configuring their cloud environments correctly, using strong authentication methods, managing access controls effectively, and regularly updating their security practices. While no system can be completely immune to threats, with proper precautions and shared responsibility, cloud computing can offer a high level of security.
10.2. Is cloud computing right for my small business?

10.3. How Much Does Cloud Computing Cost?
Cloud computing costs vary widely based on several factors:
- Type of cloud service: IaaS, PaaS, or SaaS have different pricing models.
- Cloud provider: Different providers offer varying pricing structures and discounts.
- Resource usage: The amount of compute power, storage, and bandwidth you consume directly impacts cost.
- Service level agreements (SLAs): Higher levels of service and support often come with additional costs.
Generally, cloud computing costs are categorized into three main types:
- Pay-As-You-Go: Many cloud providers charge based on actual usage, meaning you pay only for the resources you consume. This can include computing power, storage, data transfer, and additional services. This model is flexible and cost-effective for businesses with fluctuating or unpredictable workloads.
- Subscription-Based: Some services offer fixed monthly or annual subscription plans, which may provide a set amount of resources or features. This can be beneficial for businesses with stable and predictable needs, as it allows for easier budgeting and cost management.
- Reserved Instances: Providers often offer discounts for committing to use their services for a longer period, such as one or three years. Reserved instances can significantly reduce costs compared to pay-as-you-go pricing, making them ideal for businesses with consistent usage patterns.
Costs can also be influenced by additional factors such as data storage and retrieval fees, network usage, and support services.
11. Conclusion
In this article, we have aimed to explain what is cloud computing with example and how it work. As we have explored, cloud computing encompasses various service models—such as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS)—each catering to different needs and use cases. Additionally, the deployment models—public, private, and hybrid clouds—allow for tailored solutions that meet specific requirements for performance, security, and compliance.
The essence of cloud computing lies in its ability to provide flexible, scalable, and cost-effective solutions tailored to diverse needs. Whether you’re a small business looking to streamline operations or a large enterprise aiming for digital transformation, cloud computing offers a wide array of services that can be tailored to your specific requirements. Find out more articles at our Blog and don’t hesitate to contact us for support, you can refer to the Server Vietnam service:
- Email: support@vinahost.vn
- Hotline: 1900 6046
- Livechat: https://livechat.vinahost.vn/chat.php
What Is Server Management? | Everything you need to know
What is a Thailand Server? Top 5 choosing the right Thailand Server Provider
What is a Cambodia Server? | Everything You Need to Know
What is Server Indonesia? Choosing the right server for your needs